Discover the 5 cervical adenopathy levels, understanding lymph node swelling, neck masses, and cancer staging, to diagnose and treat cervical lymphadenopathy effectively.
Cervical adenopathy, also known as cervical lymphadenopathy, refers to the enlargement of lymph nodes in the neck. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancers. Understanding the different levels of cervical adenopathy is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. In this article, we will delve into the 5 cervical adenopathy levels, their characteristics, and the implications for patient care.
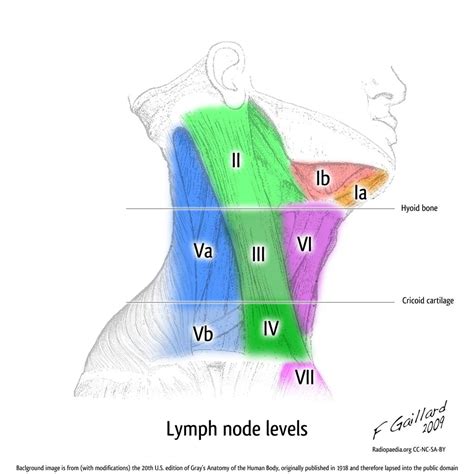
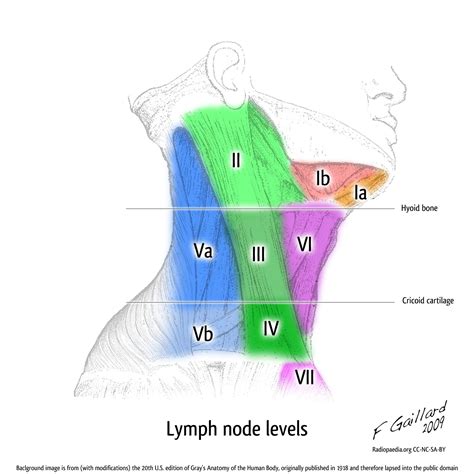
The neck is divided into several levels, each containing a group of lymph nodes that drain specific areas of the head and neck. These levels are used to describe the location and extent of lymph node enlargement. The 5 cervical adenopathy levels are defined by their anatomical location and the structures they drain. Each level has distinct boundaries and contains specific lymph node groups.
Introduction to Cervical Adenopathy Levels
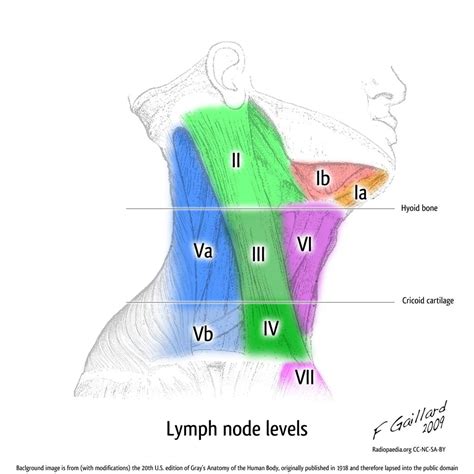
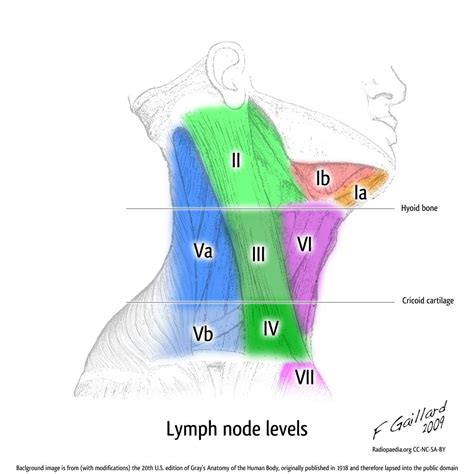
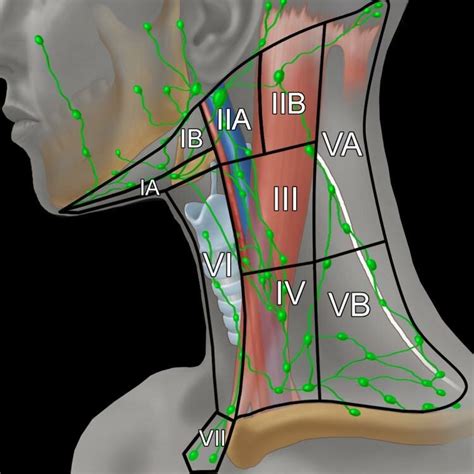
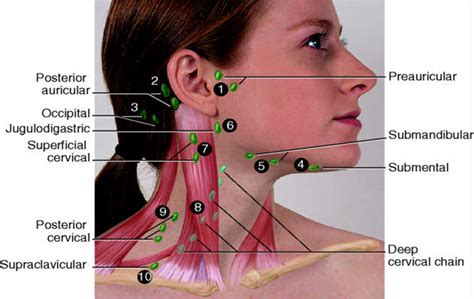
Level I: Submental and Submandibular Lymph Nodes
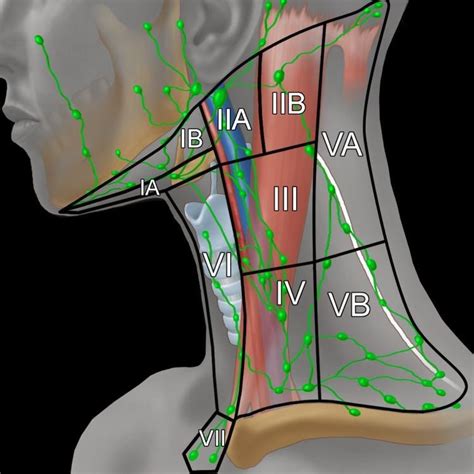
Submental Lymph Nodes
The submental lymph nodes are situated under the chin and receive lymphatic drainage from the anterior tongue, the floor of the mouth, and the lower lip. These nodes are often involved in cases of oral infections or malignancies.Submandibular Lymph Nodes
The submandibular lymph nodes are located below the jawline and drain the posterior tongue, the posterior mouth, and the retromolar trigone. Enlargement of these nodes can be caused by a variety of conditions, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancers.Level II: Upper Internal Jugular Lymph Nodes
Upper Internal Jugular Lymph Nodes
The upper internal jugular lymph nodes are located around the upper part of the internal jugular vein and drain the posterior tongue, the posterior mouth, and the nasopharynx. These nodes are often involved in cases of head and neck infections or malignancies.Level III: Middle Internal Jugular Lymph Nodes
Middle Internal Jugular Lymph Nodes
The middle internal jugular lymph nodes are located around the middle part of the internal jugular vein and drain the larynx, the hypopharynx, and the thyroid gland. These nodes are often involved in cases of head and neck infections or malignancies.Level IV: Lower Internal Jugular Lymph Nodes
Lower Internal Jugular Lymph Nodes
The lower internal jugular lymph nodes are located around the lower part of the internal jugular vein and drain the thyroid gland, the larynx, and the hypopharynx. These nodes are often involved in cases of head and neck infections or malignancies.Level V: Posterior Triangle Lymph Nodes
Posterior Triangle Lymph Nodes
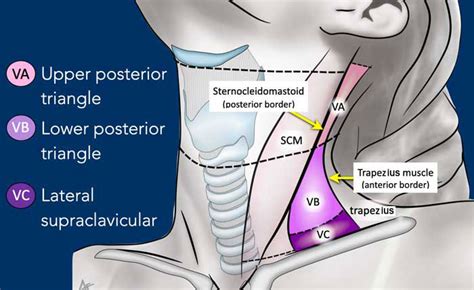
The posterior triangle lymph nodes are located in the posterior triangle of the neck and drain the scalp, the posterior neck, and the shoulder region. These nodes are often involved in cases of head and neck infections or malignancies.Cervical Adenopathy Image Gallery

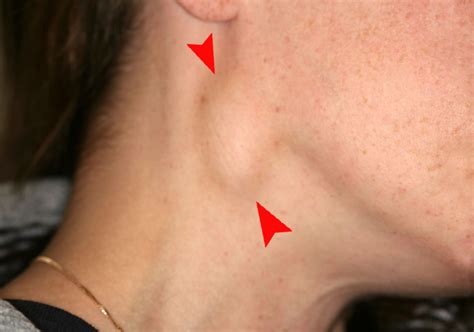
In conclusion, understanding the 5 cervical adenopathy levels is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of various head and neck conditions. Each level has distinct characteristics and drains specific areas of the head and neck. By recognizing the different levels of cervical adenopathy, clinicians can provide better patient care and improve treatment outcomes. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with cervical adenopathy and its treatment in the comments section below. Additionally, we encourage readers to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
