Intro
Discover 5 key facts about CH3CH2OH, also known as ethanol, including its chemical properties, uses, and effects, exploring its role in chemistry, biochemistry, and everyday applications.
Ethanol, also known as ethyl alcohol, is a commonly used chemical compound with the molecular formula CH3CH2OH. It is a colorless, volatile, and flammable liquid with a characteristic odor. Ethanol is widely used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food production. Here are five interesting facts about CH3CH2OH:
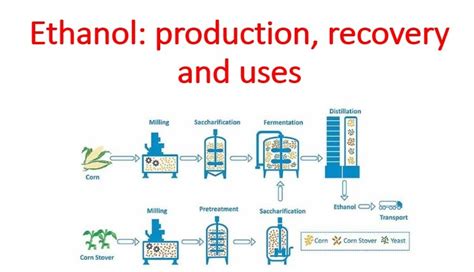
Ethanol is a highly versatile compound that can be produced through various methods, including fermentation and synthetic processes. The most common method of production is through the fermentation of biomass, such as sugarcane, corn, and wheat. This process involves the conversion of sugars into ethanol by microorganisms like yeast. On the other hand, synthetic ethanol is produced through the hydration of ethylene, a petrochemical derivative.
The unique properties of ethanol make it an essential component in various applications. For instance, its high solubility in water and organic solvents makes it an excellent solvent for a wide range of substances. Additionally, ethanol's low toxicity and non-corrosive nature make it a popular choice for use in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food products. Its antimicrobial properties also make it an effective disinfectant and antiseptic agent.
Chemical Properties of Ethanol
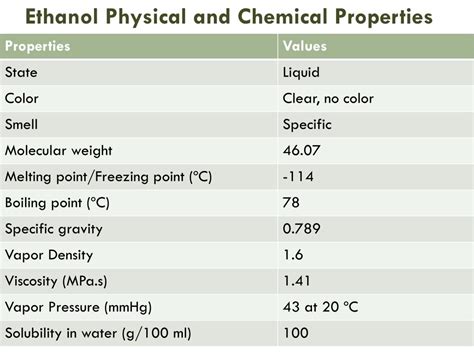
Physical Properties of Ethanol
The physical properties of ethanol are also noteworthy. Its density is 0.789 g/cm³, making it less dense than water. Ethanol's viscosity is 1.2 mPa·s, which is relatively low compared to other liquids. Its refractive index is 1.361, and its surface tension is 22.3 mN/m. These physical properties make ethanol an excellent solvent and a popular choice for various industrial applications.Industrial Applications of Ethanol

Pharmaceutical Applications of Ethanol
In the pharmaceutical industry, ethanol is used as a solvent, an antiseptic, and a disinfectant. Its high solubility in water and organic solvents makes it an excellent solvent for a wide range of substances. Ethanol is also used in the production of various pharmaceutical products, including cough syrups, tonics, and elixirs. Its antimicrobial properties make it an effective agent against bacterial and fungal infections.Environmental Impact of Ethanol
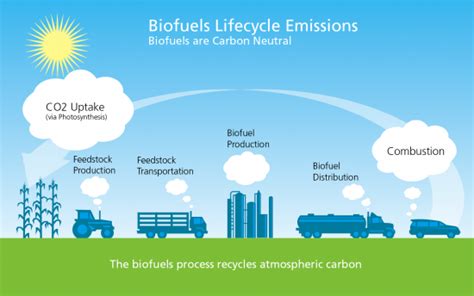
Renewable Energy Source
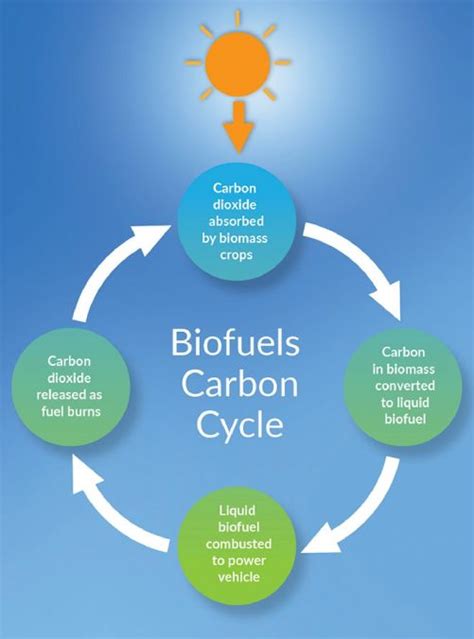
Ethanol is considered a renewable energy source because it can be produced from biomass, such as sugarcane, corn, and wheat. The production of ethanol from biomass can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. Additionally, ethanol can be used as a fuel additive in the production of gasoline, helping to reduce emissions and improve engine performance.Health Effects of Ethanol
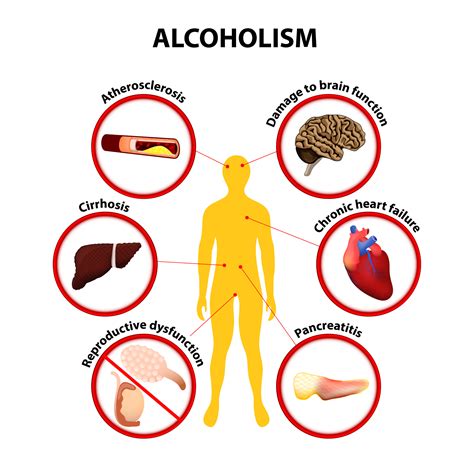
Risks and Benefits
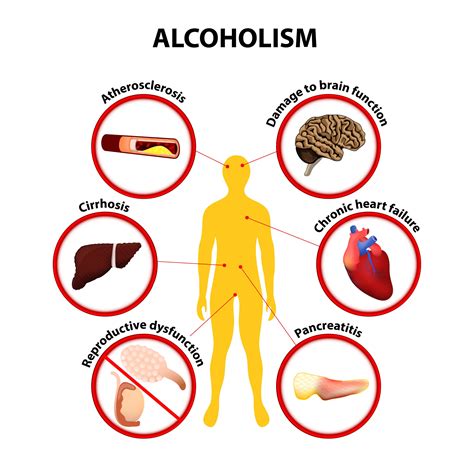
The risks and benefits of ethanol consumption are complex and multifaceted. On the one hand, ethanol can have negative health effects, including liver damage and addiction. On the other hand, moderate consumption of ethanol can have potential health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease and certain types of cancer. It is essential to consume ethanol in moderation and be aware of the potential risks and benefits.Conclusion and Future Directions

Gallery of Ethanol-Related Images






We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of ethanol, its properties, applications, and environmental impact. Whether you are a student, researcher, or industry professional, we encourage you to share your thoughts and insights on the topic. Please feel free to comment, share this article, or take specific actions to learn more about ethanol and its role in our world.
