Intro
Explore the 11 body systems, including nervous, circulatory, and digestive systems, and discover how they function and interact to maintain overall health and wellness, covering anatomy, physiology, and interconnectedness.
The human body is a complex and fascinating entity, comprising numerous systems that work together in harmony to maintain overall health and well-being. Understanding these systems is essential for appreciating the intricacies of human physiology and the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. In this article, we will delve into the 11 major body systems, exploring their functions, mechanisms, and significance in maintaining our overall health.
The study of human body systems is crucial for various fields, including medicine, healthcare, and fitness. By grasping the concepts of anatomy and physiology, individuals can better comprehend the consequences of their lifestyle choices and make informed decisions to promote their well-being. Furthermore, knowledge of the body systems can help people appreciate the importance of preventive care, early detection, and treatment of diseases, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
As we navigate the complexities of human physiology, it becomes evident that each body system plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis, or a state of balance and equilibrium. From the circulatory system, which transports oxygen and nutrients to cells, to the nervous system, which enables communication and coordination, every system contributes to the overall functioning of the body. In the following sections, we will explore each of the 11 major body systems in detail, highlighting their unique features, functions, and significance.
Introduction to Body Systems
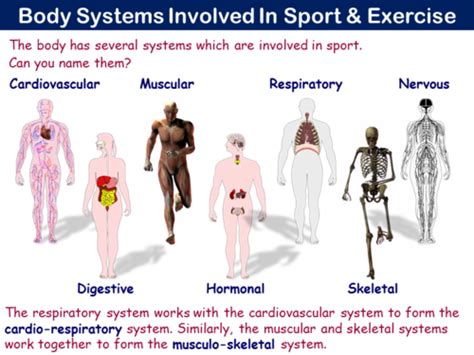
The human body is composed of 11 major systems, each with distinct functions and mechanisms. These systems include the circulatory, respiratory, digestive, nervous, endocrine, integumentary, muscular, skeletal, urinary, reproductive, and immune systems. While each system operates independently, they are interconnected and interdependent, working together to maintain overall health and well-being.
Overview of Body Systems
The 11 body systems can be categorized into two main groups: systems that maintain internal balance and systems that facilitate interaction with the external environment. The circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and urinary systems are primarily responsible for maintaining internal balance, while the nervous, endocrine, and immune systems regulate and coordinate the body's responses to internal and external stimuli. The integumentary, muscular, and skeletal systems provide structure and support, enabling the body to interact with its surroundings.Circulatory System
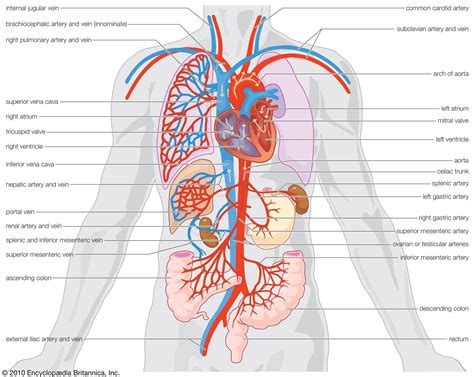
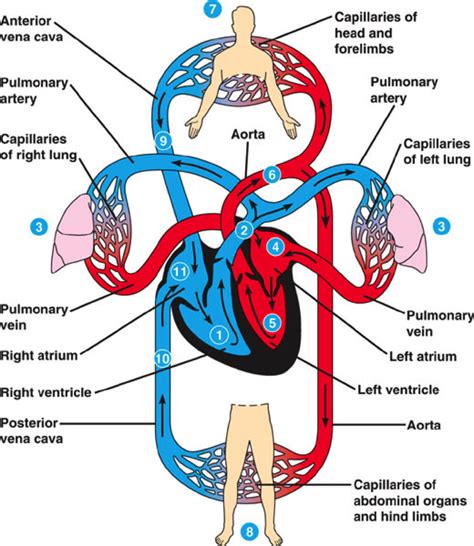
The circulatory system, also known as the cardiovascular system, is responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. This system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, which work together to maintain blood flow and pressure. The circulatory system plays a critical role in delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells, removing waste products, and regulating body temperature.
Functions of the Circulatory System
The circulatory system performs several essential functions, including: * Transporting oxygen and nutrients to cells * Removing waste products, such as carbon dioxide and lactic acid * Regulating body temperature * Maintaining blood pressure and flow * Supporting immune function by transporting white blood cellsRespiratory System
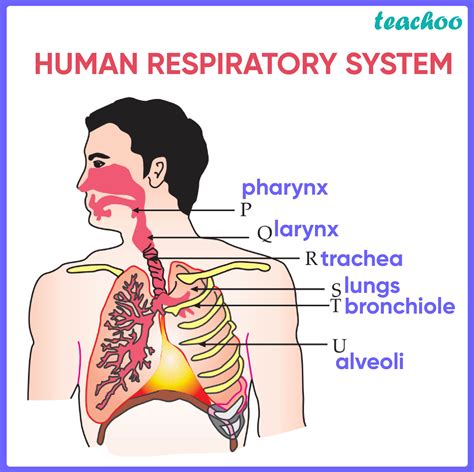
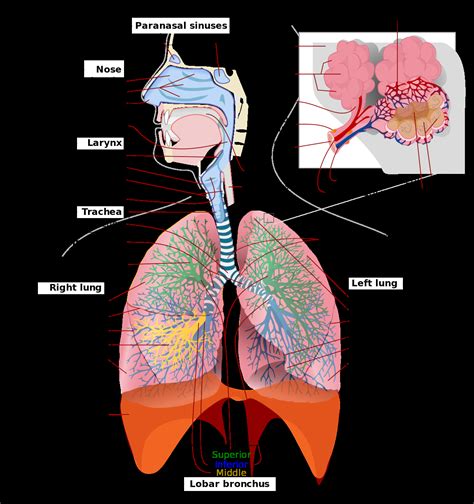
The respiratory system is responsible for bringing oxygen into the body and removing carbon dioxide through the process of breathing. This system consists of the lungs, airways, and breathing muscles, which work together to facilitate gas exchange. The respiratory system plays a critical role in maintaining oxygenation of the body and removing waste gases.
Functions of the Respiratory System
The respiratory system performs several essential functions, including: * Bringing oxygen into the body through inhalation * Removing carbon dioxide through exhalation * Regulating pH levels by removing excess hydrogen ions * Supporting immune function by filtering out pathogens and irritantsDigestive System
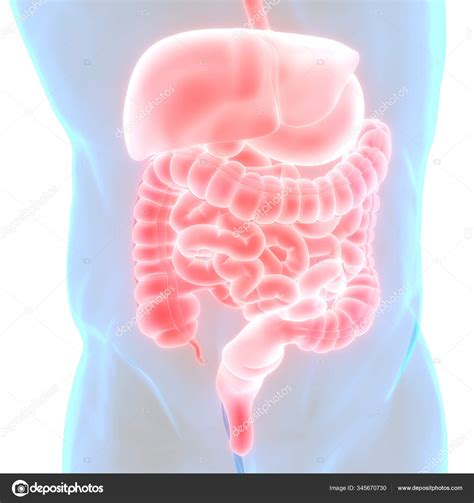
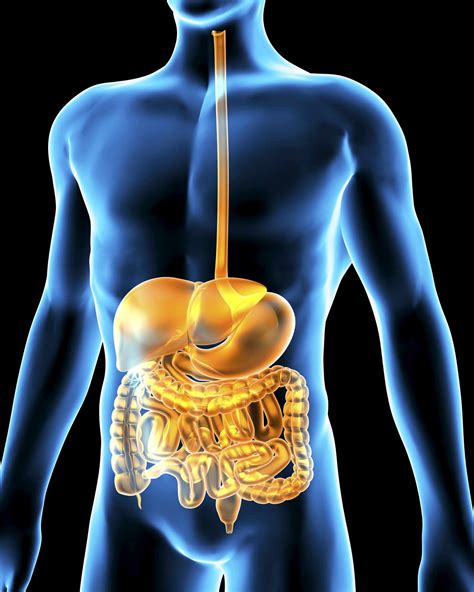
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into nutrients, which can be absorbed and utilized by the body. This system consists of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, which work together to facilitate digestion and absorption. The digestive system plays a critical role in maintaining nutrition and energy balance.
Functions of the Digestive System
The digestive system performs several essential functions, including: * Breaking down food into nutrients through mechanical and chemical digestion * Absorbing nutrients into the bloodstream * Eliminating waste products through defecation * Supporting immune function by filtering out pathogens and toxinsNervous System
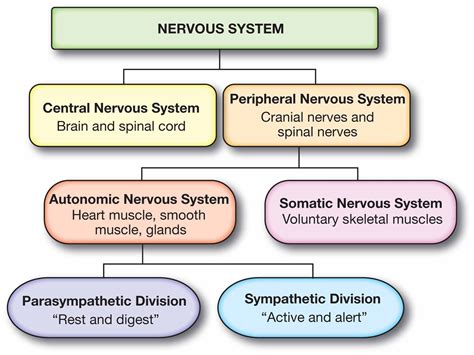
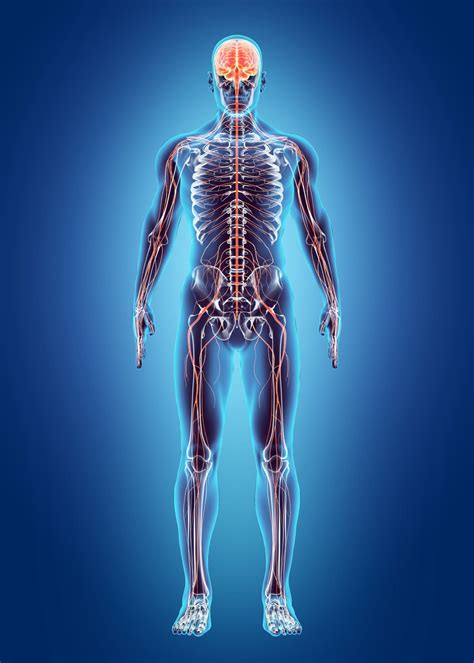
The nervous system is responsible for controlling and coordinating the body's functions, including movement, sensation, and cognition. This system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS), which work together to facilitate communication and coordination. The nervous system plays a critical role in maintaining homeostasis and enabling the body to respond to internal and external stimuli.
Functions of the Nervous System
The nervous system performs several essential functions, including: * Controlling and coordinating movement * Processing sensory information * Regulating body functions, such as heart rate and blood pressure * Enabling cognition and consciousnessEndocrine System

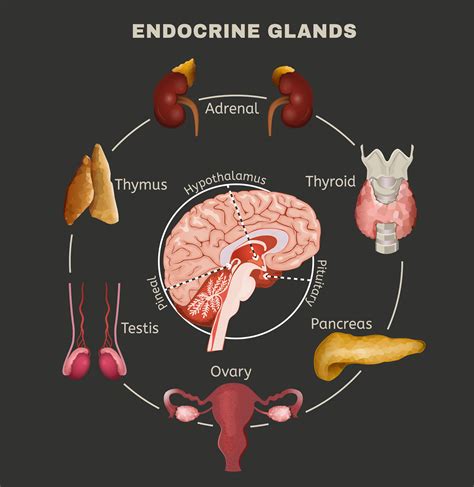
The endocrine system is responsible for producing and regulating hormones, which play a critical role in maintaining homeostasis and enabling the body to respond to internal and external stimuli. This system consists of glands and organs, such as the pancreas, thyroid, and adrenal glands, which work together to produce and regulate hormones. The endocrine system plays a critical role in maintaining growth and development, metabolism, and reproductive function.
Functions of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system performs several essential functions, including: * Regulating growth and development * Controlling metabolism and energy balance * Enabling reproductive function * Maintaining homeostasis and responding to stressIntegumentary System
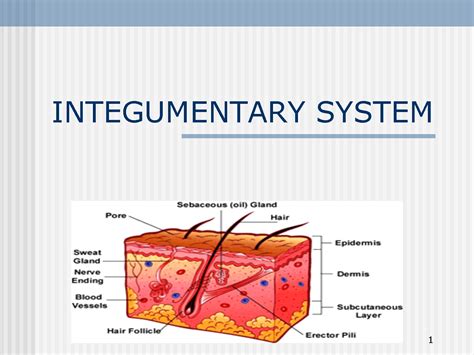
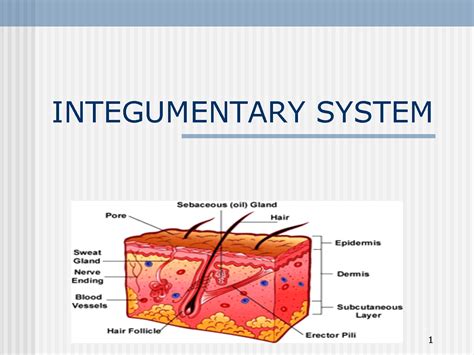
The integumentary system is responsible for protecting the body from external damage and maintaining body temperature. This system consists of the skin, hair, nails, and associated glands, which work together to provide a barrier against external pathogens and regulate body temperature. The integumentary system plays a critical role in maintaining skin health and preventing infection.
Functions of the Integumentary System
The integumentary system performs several essential functions, including: * Protecting the body from external damage * Regulating body temperature * Maintaining skin health and preventing infection * Supporting immune function by filtering out pathogensMuscular System
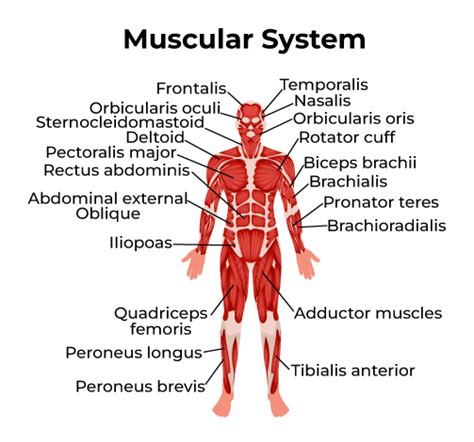
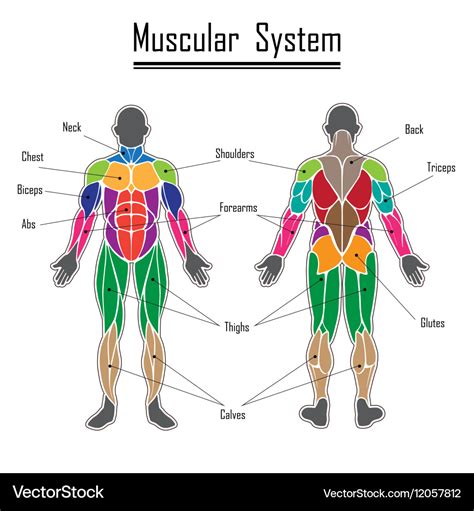
The muscular system is responsible for enabling movement and maintaining posture. This system consists of skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscle, which work together to facilitate movement and maintain muscle tone. The muscular system plays a critical role in maintaining mobility and supporting overall health.
Functions of the Muscular System
The muscular system performs several essential functions, including: * Enabling movement and maintaining posture * Regulating body temperature * Supporting immune function by filtering out pathogens * Maintaining muscle tone and preventing muscle atrophySkeletal System
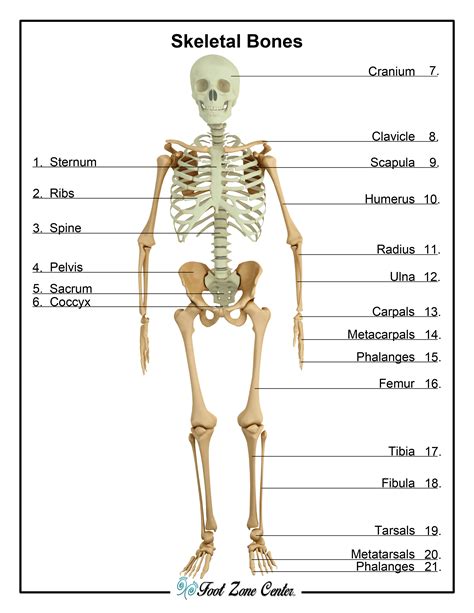
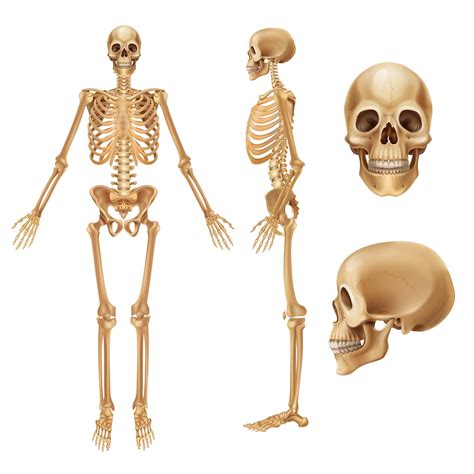
The skeletal system is responsible for providing structure and support to the body. This system consists of bones, cartilage, and ligaments, which work together to facilitate movement and maintain posture. The skeletal system plays a critical role in maintaining mobility and supporting overall health.
Functions of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system performs several essential functions, including: * Providing structure and support to the body * Facilitating movement and maintaining posture * Protecting internal organs * Supporting immune function by filtering out pathogensUrinary System
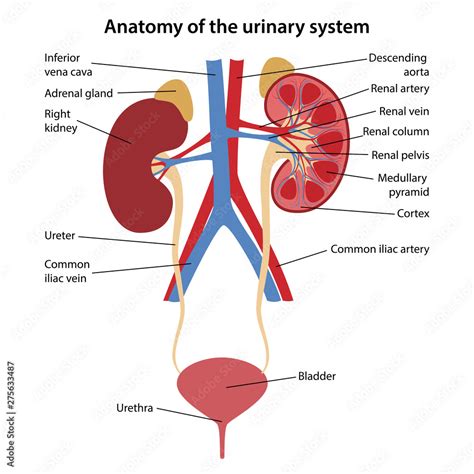
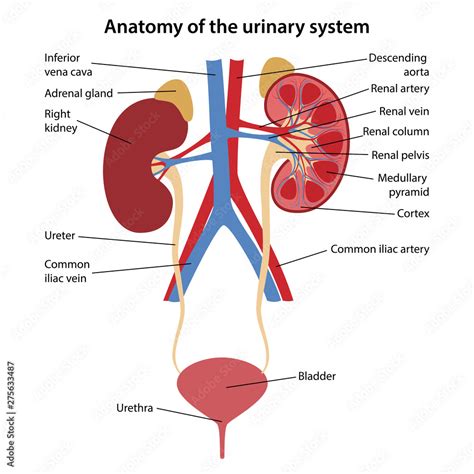
The urinary system is responsible for removing waste and excess fluids from the body. This system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, which work together to facilitate waste removal and maintain fluid balance. The urinary system plays a critical role in maintaining overall health and preventing disease.
Functions of the Urinary System
The urinary system performs several essential functions, including: * Removing waste and excess fluids from the body * Maintaining fluid balance and electrolyte levels * Regulating blood pressure * Supporting immune function by filtering out pathogensReproductive System
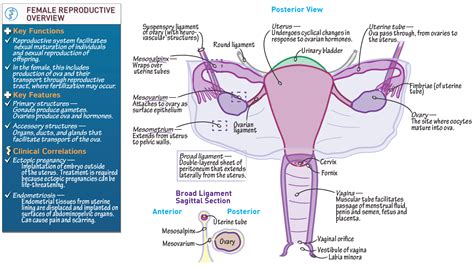
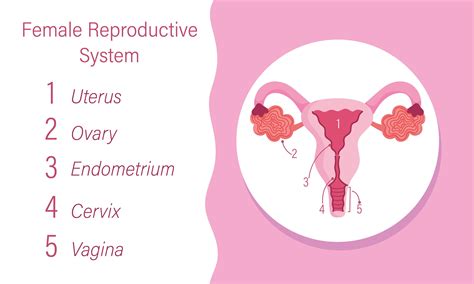
The reproductive system is responsible for enabling the creation of new life. This system consists of the male and female reproductive organs, which work together to facilitate fertilization and support the development of a fetus. The reproductive system plays a critical role in maintaining the continuation of the species.
Functions of the Reproductive System
The reproductive system performs several essential functions, including: * Enabling the creation of new life * Supporting the development of a fetus * Regulating reproductive hormones * Maintaining reproductive health and preventing diseaseImmune System
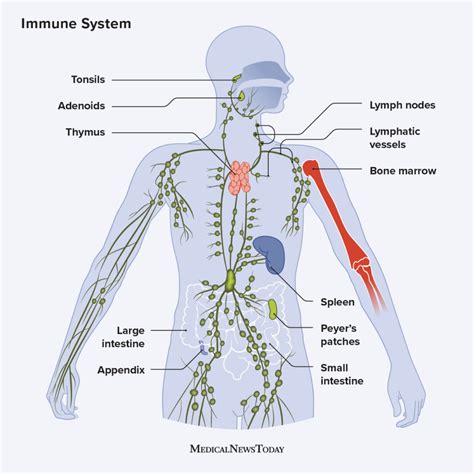
The immune system is responsible for protecting the body from external pathogens and maintaining overall health. This system consists of the lymphoid organs, immune cells, and proteins, which work together to facilitate immune function and prevent disease. The immune system plays a critical role in maintaining overall health and preventing infection.
Functions of the Immune System
The immune system performs several essential functions, including: * Protecting the body from external pathogens * Maintaining overall health and preventing disease * Regulating immune function and preventing autoimmune disorders * Supporting immune function by filtering out pathogensBody Systems Image Gallery
As we conclude our exploration of the 11 body systems, it becomes evident that each system plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being. By understanding the functions and mechanisms of each system, individuals can appreciate the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and make informed decisions to promote their well-being. We invite readers to share their thoughts and questions about the body systems and encourage them to explore further resources to deepen their understanding of human physiology. By working together to promote health and wellness, we can create a brighter future for ourselves and future generations.
