Intro
Master the art of chest tube nursing with our comprehensive guide. Learn the 7 essential steps for managing chest tubes, from insertion to removal, and understand the importance of proper care and maintenance. Discover tips for troubleshooting common complications and improve patient outcomes with our expert advice on chest tube management, pleural drainage, and thoracic care.
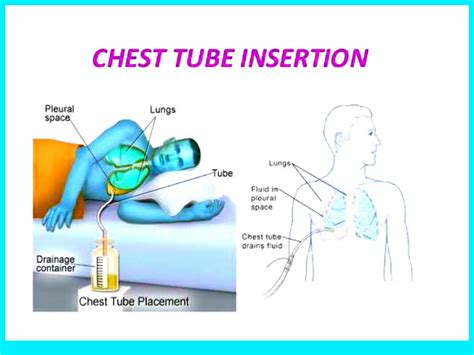
Chest tubes are a vital medical device used to drain fluid, blood, or air from the chest cavity, and their proper management is crucial for patient recovery. As a nurse, understanding the essential steps for chest tube care is vital to ensure the best possible outcomes for patients. In this article, we will delve into the seven essential steps for chest tube nursing, providing you with a comprehensive guide to help you master this critical skill.
The Importance of Chest Tube Care
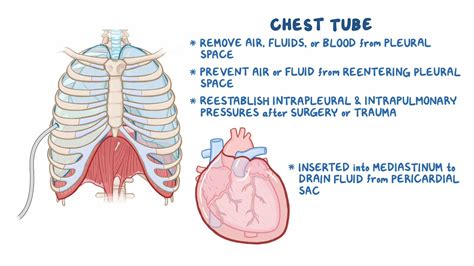
Chest tubes are used in a variety of medical conditions, including pneumothorax, pleural effusion, and hemoptysis. Improper care of chest tubes can lead to serious complications, such as infection, bleeding, and respiratory distress. As a nurse, it is your responsibility to ensure that chest tubes are managed correctly, and patients receive the best possible care.

Step 1: Assess the Patient
Before initiating chest tube care, it is essential to assess the patient's condition. Evaluate the patient's vital signs, oxygen saturation, and respiratory status. Assess the patient's pain level and administer analgesia as needed. Check the chest tube for any signs of bleeding, crepitus, or drainage.
Assessment Criteria
- Vital signs
- Oxygen saturation
- Respiratory status
- Pain level
- Chest tube condition
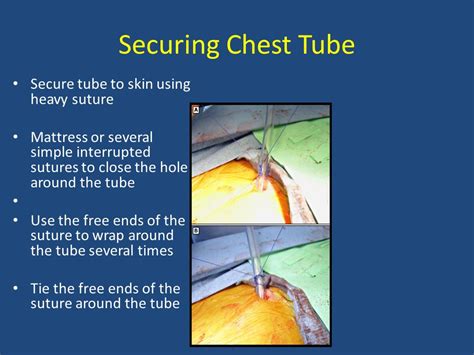
Step 2: Secure the Chest Tube
Securing the chest tube is crucial to prevent dislodgment and ensure proper drainage. Use a securement device, such as a chest tube strap or a dressing, to keep the tube in place. Ensure the tube is not kinked or twisted, and the drainage system is properly connected.
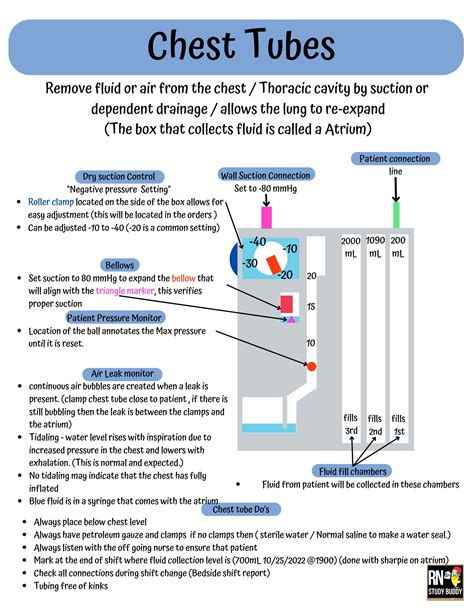
Step 3: Monitor Drainage
Monitoring drainage is a critical aspect of chest tube care. Check the drainage system regularly for signs of bleeding, crepitus, or blockage. Measure and record the drainage output, and notify the physician if there are any changes in the drainage pattern.
Drainage Monitoring Criteria
- Drainage output
- Drainage characteristics (e.g., bloody, serous, purulent)
- Signs of bleeding or crepitus
- Blockage or kinking of the tube
Step 4: Maintain the Drainage System
The drainage system should be maintained according to the manufacturer's instructions and hospital policy. Check the system for any signs of blockage or malfunction, and ensure the tubing is not kinked or twisted.
Step 5: Provide Patient Education
Patient education is essential to ensure the patient understands the importance of chest tube care. Educate the patient on the purpose of the chest tube, the risks and benefits of the procedure, and the signs and symptoms of complications.
Patient Education Criteria
- Purpose of the chest tube
- Risks and benefits of the procedure
- Signs and symptoms of complications
- Importance of following instructions
Step 6: Document Care
Accurate documentation of chest tube care is crucial to ensure continuity of care. Document the patient's condition, drainage output, and any complications or concerns. Notify the physician of any changes in the patient's condition or drainage pattern.

Step 7: Prepare for Removal
When the chest tube is no longer needed, prepare the patient for removal. Ensure the patient is stable, and the drainage output has decreased significantly. Follow hospital policy and physician orders for chest tube removal.
Removal Criteria
- Patient stability
- Decreased drainage output
- Physician orders
- Hospital policy
Chest Tube Nursing Image Gallery






By following these seven essential steps for chest tube nursing, you can ensure that your patients receive the best possible care and minimize the risk of complications. Remember to always follow hospital policy and physician orders, and to stay up-to-date with the latest evidence-based practices in chest tube care.
