Intro
Discover ocean decomposers, including bacteria, fungi, and worms, that break down organic matter, recycling nutrients and sustaining marine ecosystems through decomposition processes.
The ocean, often referred to as the heart of our planet, is home to a vast array of marine life. From the tiny plankton to the massive blue whale, each species plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of the ocean's ecosystem. One of the most fascinating and crucial groups of organisms in the ocean is the decomposers. These microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and other small creatures, are responsible for breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. Without decomposers, the ocean would be a very different place, with dead plants and animals accumulating and causing harm to the environment.
Decomposers are the unsung heroes of the ocean, working tirelessly behind the scenes to keep the ecosystem healthy and thriving. They are found in every corner of the ocean, from the surface waters to the deepest depths of the sea floor. These microorganisms are incredibly diverse, with different species specializing in breaking down different types of organic matter. For example, some bacteria are experts at decomposing cellulose, a tough component of plant cell walls, while others are skilled at breaking down proteins and fats. This diversity of decomposers allows the ocean to efficiently recycle nutrients and maintain its incredible productivity.
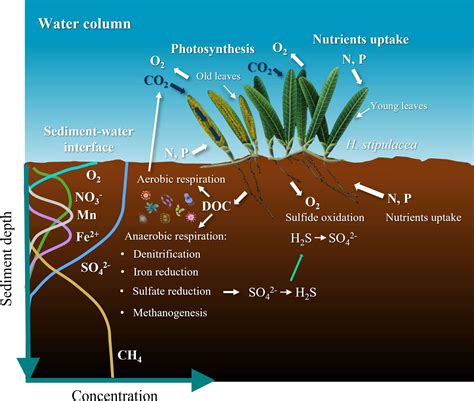
The importance of ocean decomposers cannot be overstated. They play a critical role in the ocean's carbon cycle, helping to regulate the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. By breaking down organic matter, decomposers release nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and iron back into the water, where they can be used by other organisms to grow and thrive. This process also helps to prevent the buildup of dead organic matter, which can lead to the formation of "dead zones" in the ocean, where oxygen levels are too low to support life. In addition, decomposers help to maintain the ocean's water quality, by breaking down pollutants and toxins that can harm marine life.
Types of Ocean Decomposers

There are many different types of ocean decomposers, each with their own unique characteristics and roles in the ecosystem. Bacteria are one of the most common types of decomposers, and are found in almost every environment in the ocean. They are incredibly diverse, with different species specializing in breaking down different types of organic matter. Fungi are another important group of decomposers, and are often found in association with bacteria. They play a critical role in breaking down tough, organic materials such as wood and other plant matter. Other types of decomposers, such as protozoa and nematodes, are also important in the ocean ecosystem, and help to break down smaller organisms such as algae and bacteria.
Benefits of Ocean Decomposers
The benefits of ocean decomposers are numerous and far-reaching. By breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients, they help to maintain the ocean's productivity and support the growth of marine life. They also play a critical role in regulating the ocean's carbon cycle, and help to prevent the buildup of dead organic matter that can lead to the formation of "dead zones". In addition, decomposers help to maintain the ocean's water quality, by breaking down pollutants and toxins that can harm marine life. They also provide a source of food for other organisms, such as fish and invertebrates, which feed on them and help to transfer nutrients up the food chain.Working Mechanisms of Ocean Decomposers

The working mechanisms of ocean decomposers are complex and involve a variety of different processes. One of the key mechanisms is the breakdown of organic matter into smaller components, such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. This process is carried out by enzymes, which are produced by the decomposers and help to break down the chemical bonds in the organic matter. The decomposers then absorb the broken-down nutrients, using them to fuel their own growth and metabolism. In addition to breaking down organic matter, decomposers also play a role in the ocean's nutrient cycles, helping to regulate the availability of nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus.
Steps Involved in the Decomposition Process
The decomposition process in the ocean involves several key steps. The first step is the breakdown of organic matter into smaller components, such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. This process is carried out by enzymes, which are produced by the decomposers and help to break down the chemical bonds in the organic matter. The second step is the absorption of the broken-down nutrients by the decomposers, which use them to fuel their own growth and metabolism. The third step is the release of excess nutrients back into the water, where they can be used by other organisms to grow and thrive. This process helps to maintain the ocean's productivity and support the growth of marine life.Practical Examples of Ocean Decomposers
There are many practical examples of ocean decomposers in action. One example is the decomposition of phytoplankton, which are tiny plants that drift in the ocean's surface waters. When phytoplankton die, they sink to the ocean floor, where they are broken down by decomposers such as bacteria and fungi. This process helps to recycle nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus, which are then used by other organisms to grow and thrive. Another example is the decomposition of fish and other marine animals, which are broken down by decomposers such as bacteria and protozoa. This process helps to maintain the ocean's water quality, by preventing the buildup of dead organic matter that can lead to the formation of "dead zones".
Statistical Data on Ocean Decomposers
According to recent studies, ocean decomposers play a critical role in the ocean's ecosystem, with some estimates suggesting that they are responsible for breaking down up to 90% of the organic matter that enters the ocean. This process helps to maintain the ocean's productivity and support the growth of marine life, with some studies suggesting that decomposers help to support the growth of up to 50% of the ocean's phytoplankton. In addition, decomposers help to regulate the ocean's carbon cycle, with some estimates suggesting that they help to remove up to 10% of the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.Importance of Ocean Decomposers in the Ecosystem

The importance of ocean decomposers in the ecosystem cannot be overstated. They play a critical role in maintaining the ocean's productivity and supporting the growth of marine life. They also help to regulate the ocean's carbon cycle, and prevent the buildup of dead organic matter that can lead to the formation of "dead zones". In addition, decomposers help to maintain the ocean's water quality, by breaking down pollutants and toxins that can harm marine life. They also provide a source of food for other organisms, such as fish and invertebrates, which feed on them and help to transfer nutrients up the food chain.
Challenges Facing Ocean Decomposers
Despite their importance, ocean decomposers are facing several challenges in the ecosystem. One of the main challenges is climate change, which is altering the ocean's temperature and chemistry, and making it more difficult for decomposers to survive. Another challenge is pollution, which is releasing large amounts of nutrients and pollutants into the ocean, and disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem. In addition, overfishing and habitat destruction are also major challenges, as they are reducing the amount of organic matter available for decomposers to break down, and altering the ocean's nutrient cycles.Future of Ocean Decomposers

The future of ocean decomposers is uncertain, as they face several challenges in the ecosystem. However, there are several steps that can be taken to help protect and conserve these important organisms. One step is to reduce pollution, by implementing policies and practices that reduce the amount of nutrients and pollutants released into the ocean. Another step is to protect and restore habitats, such as coral reefs and mangroves, which provide important habitat for decomposers. In addition, reducing overfishing and promoting sustainable fishing practices can help to maintain the ocean's nutrient cycles, and ensure that there is enough organic matter available for decomposers to break down.
Gallery of Ocean Decomposers
Ocean Decomposers Image Gallery









In conclusion, ocean decomposers play a critical role in maintaining the health and productivity of the ocean ecosystem. They help to break down organic matter, recycle nutrients, and regulate the ocean's carbon cycle. Despite facing several challenges, including climate change, pollution, and overfishing, there are several steps that can be taken to help protect and conserve these important organisms. By reducing pollution, protecting and restoring habitats, and promoting sustainable fishing practices, we can help to ensure the long-term health and productivity of the ocean ecosystem. We invite you to share your thoughts and ideas on the importance of ocean decomposers, and to join us in our efforts to protect and conserve these vital organisms. Together, we can make a difference and help to ensure the long-term health and productivity of our ocean planet.
