Intro
Discover the vital role of decomposers in temperate grasslands, including fungi, bacteria, and insects, breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients, supporting ecosystem balance and biodiversity.
Decomposers play a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems, and temperate grasslands are no exception. These ecosystems, characterized by their temperate climate and dominance of grasses, rely heavily on decomposers to break down organic matter and recycle nutrients. In this article, we will delve into the world of decomposers in temperate grasslands, exploring their importance, types, and the processes they facilitate.
Temperate grasslands, also known as prairies, are found on every continent except Antarctica. They are home to a diverse array of plant and animal species, and their unique characteristics make them an fascinating subject of study. Decomposers, including microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi, as well as invertebrates like insects and earthworms, are the unsung heroes of these ecosystems. They work tirelessly to break down dead plant and animal matter, releasing essential nutrients that support the growth of new plants and, in turn, the entire food chain.
The importance of decomposers in temperate grasslands cannot be overstated. Without these organisms, the ecosystem would quickly become overwhelmed with dead plant and animal matter, leading to a decline in soil quality and a reduction in biodiversity. Decomposers help to maintain soil fertility, structure, and overall health, making it possible for plants to thrive and support the complex web of life that exists in these ecosystems. In addition, decomposers play a crucial role in the carbon cycle, helping to regulate the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Types of Decomposers in Temperate Grasslands

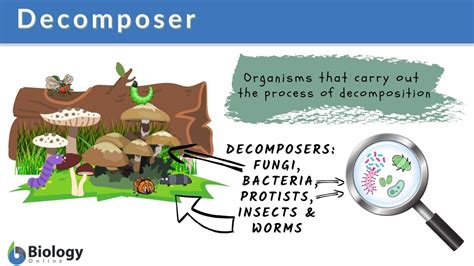
There are several types of decomposers that can be found in temperate grasslands, each playing a unique role in the ecosystem. Microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, are the primary decomposers in these ecosystems. They are responsible for breaking down complex organic matter into simpler compounds that can be used by other organisms. Invertebrates, like insects and earthworms, also play a crucial role in decomposition, helping to break down plant and animal matter and recycle nutrients.
Microorganisms
Microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi, are the most abundant decomposers in temperate grasslands. They are found in the soil, on plant surfaces, and in the guts of animals, where they work to break down complex organic matter. These microorganisms are responsible for a range of processes, including decomposition, fermentation, and nitrogen fixation. They are also involved in the production of antibiotics, vitamins, and other compounds that are essential for the health of plants and animals.Invertebrates
Invertebrates, such as insects and earthworms, are also important decomposers in temperate grasslands. They help to break down plant and animal matter, recycling nutrients and improving soil fertility. Insects, like beetles and flies, are attracted to dead plant and animal matter, where they lay their eggs and feed on the decaying material. Earthworms, on the other hand, are ecosystem engineers, burrowing into the soil and creating tunnels that aerate the soil and improve drainage.Process of Decomposition in Temperate Grasslands
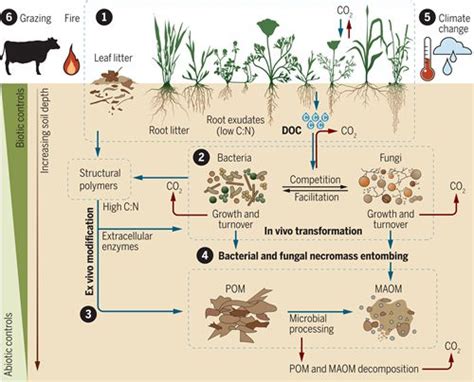
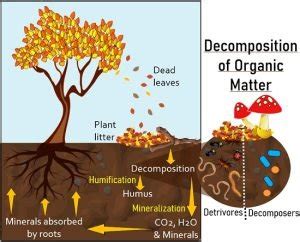
The process of decomposition in temperate grasslands is complex and involves a range of organisms and processes. It begins with the death of plants and animals, which provides a source of energy and nutrients for decomposers. Microorganisms, like bacteria and fungi, are the first to colonize the dead material, breaking it down into simpler compounds. Invertebrates, like insects and earthworms, then feed on the decaying material, further breaking it down and recycling nutrients.
The decomposition process can be divided into several stages, including:
- Necrosis: The death of plants and animals, which provides a source of energy and nutrients for decomposers.
- Decomposition: The breakdown of complex organic matter into simpler compounds by microorganisms and invertebrates.
- Humification: The formation of humus, a stable form of organic matter that is resistant to decomposition.
- Mineralization: The release of nutrients, like nitrogen and phosphorus, into the soil, where they can be used by plants.
Factors Affecting Decomposition in Temperate Grasslands
Several factors can affect the decomposition process in temperate grasslands, including:- Temperature: Decomposition rates are higher in warmer temperatures, as microorganisms and invertebrates are more active.
- Moisture: Decomposition rates are higher in moist soils, as microorganisms and invertebrates require water to function.
- pH: Decomposition rates are higher in soils with a neutral pH, as microorganisms and invertebrates are more active in these conditions.
- Nutrient availability: Decomposition rates are higher in soils with adequate nutrient availability, as microorganisms and invertebrates require nutrients to function.
Importance of Decomposers in Temperate Grasslands

Decomposers play a vital role in maintaining the balance of temperate grassland ecosystems. They help to:
- Recycle nutrients: Decomposers release essential nutrients, like nitrogen and phosphorus, into the soil, where they can be used by plants.
- Maintain soil fertility: Decomposers help to maintain soil fertility by breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients.
- Support biodiversity: Decomposers support biodiversity by providing a source of food and habitat for a range of organisms.
- Regulate the carbon cycle: Decomposers help to regulate the carbon cycle by breaking down organic matter and releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Benefits of Decomposers in Temperate Grasslands
The benefits of decomposers in temperate grasslands are numerous, including:- Improved soil fertility: Decomposers help to maintain soil fertility by breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients.
- Increased crop yields: Decomposers help to increase crop yields by providing essential nutrients to plants.
- Enhanced biodiversity: Decomposers support biodiversity by providing a source of food and habitat for a range of organisms.
- Regulation of the carbon cycle: Decomposers help to regulate the carbon cycle by breaking down organic matter and releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Conservation of Decomposers in Temperate Grasslands

The conservation of decomposers in temperate grasslands is essential for maintaining the balance of these ecosystems. Several strategies can be used to conserve decomposers, including:
- Reduced tillage: Reduced tillage can help to conserve decomposers by reducing soil disturbance and preserving soil structure.
- Organic amendments: Organic amendments, like compost and manure, can help to conserve decomposers by providing a source of nutrients and habitat.
- Conservation of habitat: Conservation of habitat can help to conserve decomposers by providing a source of food and habitat for a range of organisms.
- Regulation of pollutants: Regulation of pollutants can help to conserve decomposers by reducing the impact of pollutants on these organisms.
Challenges Facing Decomposers in Temperate Grasslands
Several challenges face decomposers in temperate grasslands, including:- Climate change: Climate change can alter the composition and activity of decomposer communities, leading to changes in ecosystem function.
- Land use change: Land use change can lead to the destruction of habitat and the loss of decomposer diversity.
- Pollution: Pollution can harm decomposers and alter ecosystem function.
- Invasive species: Invasive species can outcompete native decomposers and alter ecosystem function.
Decomposers in Temperate Grasslands Image Gallery







In conclusion, decomposers play a vital role in maintaining the balance of temperate grassland ecosystems. They help to recycle nutrients, maintain soil fertility, support biodiversity, and regulate the carbon cycle. However, decomposers face several challenges, including climate change, land use change, pollution, and invasive species. Conservation strategies, such as reduced tillage, organic amendments, conservation of habitat, and regulation of pollutants, can help to protect decomposers and maintain ecosystem function. We hope that this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of the importance of decomposers in temperate grasslands and the challenges they face. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this topic and to explore further the fascinating world of decomposers in temperate grasslands.
