Explore NATOs pivotal role in the Cold War, a decades-long ideological conflict between the US and Soviet Union. Learn how the North Atlantic Treaty Organizations military strategy, diplomatic efforts, and collective defense commitments shaped the wars trajectory, deterring Soviet aggression and promoting democratic values amidst the backdrop of communism, nuclear deterrence, and proxy wars.
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, commonly known as NATO, played a crucial role in the Cold War, which lasted from the end of World War II until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. The Cold War was a state of tension and competition between the United States and the Soviet Union, with their respective allies, that did not involve direct military action.
The creation of NATO in 1949 marked a significant shift in the international relations landscape. The alliance was formed in response to the threat posed by the Soviet Union's expansionist policies in Europe, and its primary goal was to provide collective defense against potential Soviet aggression. NATO's role in the Cold War was multifaceted, and it played a crucial part in maintaining stability and security in Europe during this period.

NATO's Formation and Structure
NATO was established on April 4, 1949, when 12 Western countries signed the North Atlantic Treaty in Washington, D.C. The founding members were Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The treaty committed its signatories to mutual defense in the event of an attack on any member state.
NATO's structure consisted of a council, a secretary-general, and a military committee. The council, composed of representatives from each member state, was responsible for making key decisions and setting the alliance's overall direction. The secretary-general served as the chief administrative officer, while the military committee provided advice on military matters.
NATO's Military Strategy
NATO's military strategy during the Cold War was centered on the concept of collective defense. The alliance's military forces were designed to deter Soviet aggression, and in the event of an attack, to defend member states. NATO's military strategy was based on the principle of "flexible response," which allowed for a range of responses to Soviet aggression, from conventional to nuclear.
NATO's military forces were organized into several commands, including the Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR) and the Supreme Allied Commander Atlantic (SACLANT). SACEUR was responsible for NATO's land and air forces, while SACLANT commanded the alliance's naval forces.

NATO's Role in the Cold War
NATO played a crucial role in the Cold War, serving as a bulwark against Soviet expansion in Europe. The alliance's military presence helped to deter Soviet aggression, and its collective defense commitment provided a sense of security and stability to its member states.
NATO also played a key role in several Cold War crises, including the Berlin Blockade and Airlift (1948-1949), the Hungarian Revolution (1956), and the Cuban Missile Crisis (1962). In each of these crises, NATO's military presence and collective defense commitment helped to prevent Soviet aggression and maintain stability in the region.
NATO's Relations with the Soviet Union
NATO's relations with the Soviet Union were tense throughout the Cold War. The alliance's creation was seen as a direct challenge to Soviet interests in Europe, and the Soviet Union responded by forming the Warsaw Pact, a military alliance of Eastern European communist states.
Despite the tensions, NATO and the Soviet Union engaged in several diplomatic efforts to reduce tensions and improve relations. These efforts included the Helsinki Accords (1975) and the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty (1987). However, these efforts were ultimately unsuccessful in resolving the underlying differences between the two sides.
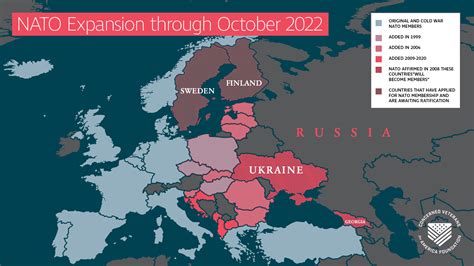
NATO's Impact on the Cold War
NATO's impact on the Cold War was significant. The alliance's military presence and collective defense commitment helped to deter Soviet aggression and maintain stability in Europe. NATO's existence also helped to prevent the spread of communism in Western Europe, as it provided a sense of security and stability to its member states.
NATO's impact on the Cold War can be seen in several key areas:
- Deterrence: NATO's military presence helped to deter Soviet aggression, as the Soviet Union was aware that an attack on any member state would trigger a collective response from the alliance.
- Stability: NATO's collective defense commitment provided a sense of security and stability to its member states, which helped to prevent the spread of communism in Western Europe.
- Containment: NATO's military presence helped to contain Soviet expansion in Europe, as the alliance's military forces were deployed along the Iron Curtain, the border between Western and Eastern Europe.

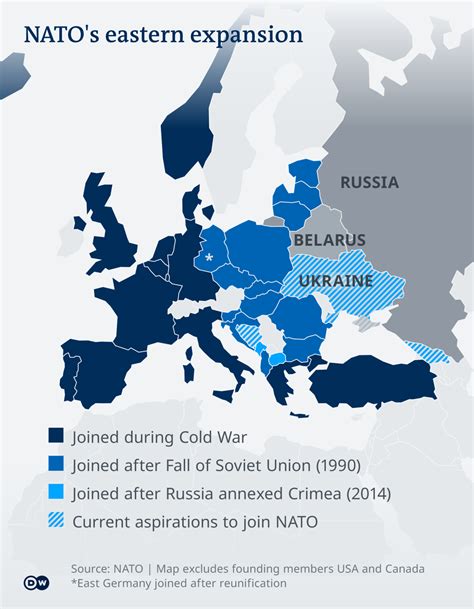
NATO After the Cold War
The end of the Cold War marked a significant turning point for NATO. With the collapse of the Soviet Union, the alliance's primary purpose – collective defense against Soviet aggression – was no longer relevant. However, NATO adapted to the new security environment, and its role evolved to address new challenges.
Today, NATO remains a key player in international security, with a membership of 30 countries. The alliance continues to play a crucial role in maintaining stability and security in Europe, and its military presence is still deployed in several regions, including the Balkans and Afghanistan.
NATO's Future Challenges
NATO faces several challenges in the future, including:
- Terrorism: The alliance must continue to adapt to the threat of terrorism, which remains a significant challenge to international security.
- Cybersecurity: NATO must also address the growing threat of cyber attacks, which can have significant consequences for national security.
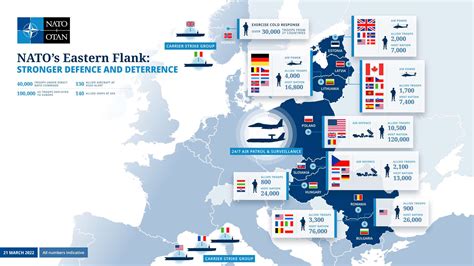
- Russia's resurgence: The alliance must continue to monitor Russia's military activities, particularly in Eastern Europe, and be prepared to respond to any potential aggression.
NATO Image Gallery







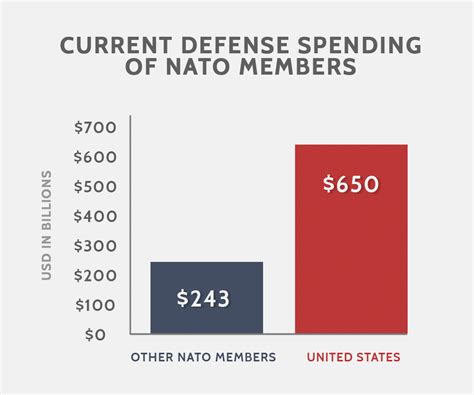
In conclusion, NATO played a crucial role in the Cold War, serving as a bulwark against Soviet expansion in Europe. The alliance's military presence and collective defense commitment helped to deter Soviet aggression and maintain stability in the region. Today, NATO continues to play a key role in international security, and its future challenges include addressing the threats of terrorism, cybersecurity, and Russia's resurgence.
