Intro
Discover how zebrafish develop axis through 5 key stages, involving embryonic patterning, morphogenesis, and tissue formation, driven by genetic and molecular mechanisms.
The development of the axis in zebrafish is a complex and highly regulated process that has been extensively studied in the field of developmental biology. Zebrafish are a popular model organism for studying embryonic development due to their rapid growth rate, transparent embryos, and genetic similarity to humans. Understanding how zebrafish develop their axis is crucial for gaining insights into the underlying mechanisms of embryonic development and for developing new treatments for developmental disorders. In this article, we will explore five ways zebrafish develop their axis, highlighting the key players and processes involved.
The development of the axis in zebrafish is a critical process that lays the foundation for the formation of the entire embryo. The axis refers to the longitudinal axis of the embryo, which runs from the head to the tail. The formation of the axis is a highly coordinated process that involves the interaction of multiple cell types, signaling pathways, and genetic regulators. Zebrafish are an ideal model organism for studying axis development due to their ease of manipulation and the availability of powerful genetic tools.
The study of axis development in zebrafish has far-reaching implications for our understanding of human development and disease. Many of the genes and signaling pathways involved in axis development in zebrafish are conserved in humans, and mutations in these genes have been linked to developmental disorders such as spina bifida and caudal regression syndrome. By studying axis development in zebrafish, researchers can gain valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of these disorders and develop new treatments.
Introduction to Axis Development

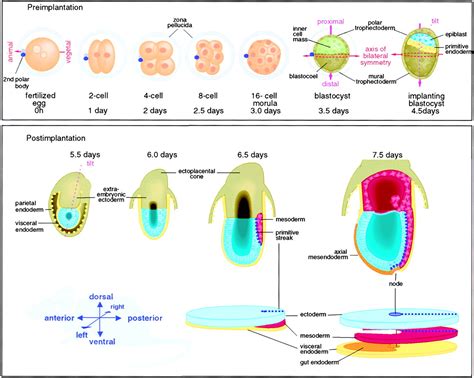
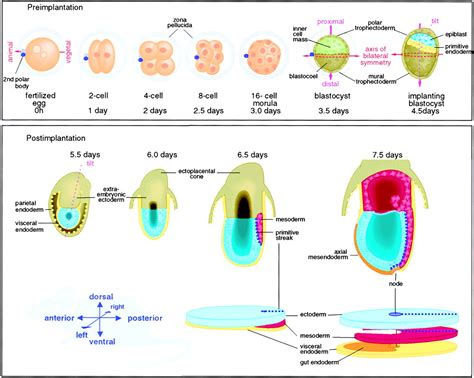
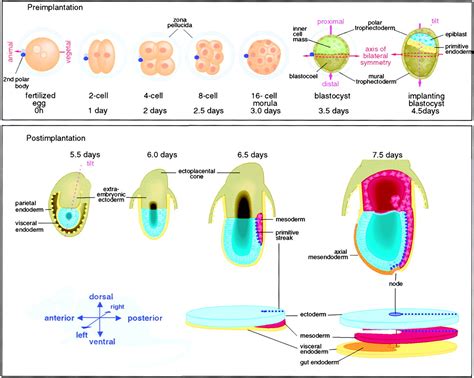
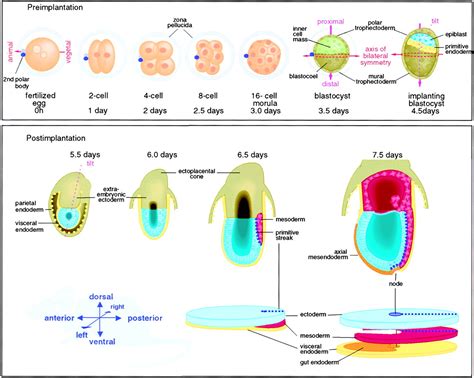
Axis development in zebrafish is a complex process that involves the coordinated action of multiple cell types and signaling pathways. The process begins with the formation of the blastula, a hollow ball of cells that forms during the earliest stages of embryonic development. As the blastula develops, it undergoes a series of complex cellular movements and signaling events that ultimately give rise to the formation of the axis. The axis is composed of three primary axes: the anterior-posterior axis, the dorsal-ventral axis, and the left-right axis. Each of these axes is established through the interaction of specific cell types and signaling pathways.
Establishment of the Anterior-Posterior Axis
The anterior-posterior axis is the first axis to be established during zebrafish development. This axis is formed through the interaction of two primary cell types: the germ ring and the blastoderm. The germ ring is a ring of cells that forms at the margin of the blastula, while the blastoderm is a layer of cells that forms on top of the germ ring. The interaction between these two cell types gives rise to the formation of the anterior-posterior axis, with the germ ring giving rise to the posterior portion of the embryo and the blastoderm giving rise to the anterior portion.Formation of the Dorsal-Ventral Axis
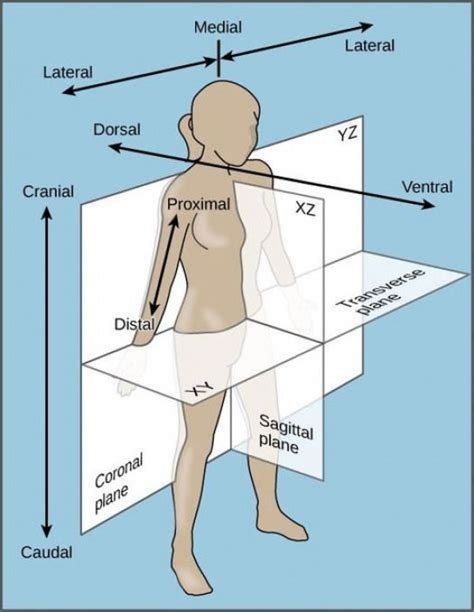
The dorsal-ventral axis is established through the interaction of two primary signaling pathways: the BMP and Wnt pathways. The BMP pathway is involved in the formation of the ventral portion of the embryo, while the Wnt pathway is involved in the formation of the dorsal portion. The interaction between these two pathways gives rise to the formation of the dorsal-ventral axis, with the BMP pathway promoting ventral fates and the Wnt pathway promoting dorsal fates.
Establishment of the Left-Right Axis
The left-right axis is established through the interaction of two primary cell types: the lateral plate mesoderm and the endoderm. The lateral plate mesoderm is a layer of cells that forms on either side of the embryo, while the endoderm is a layer of cells that forms the lining of the gut. The interaction between these two cell types gives rise to the formation of the left-right axis, with the lateral plate mesoderm giving rise to the left and right sides of the embryo.Genetic Regulators of Axis Development
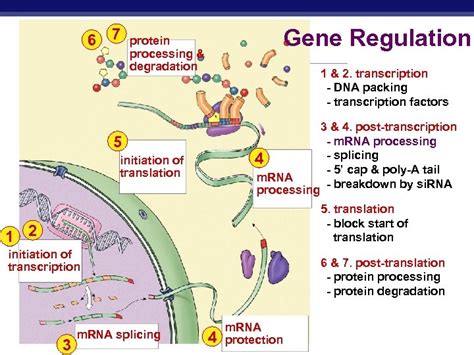
Axis development in zebrafish is regulated by a complex array of genetic regulators, including transcription factors, signaling molecules, and microRNAs. Some of the key genetic regulators of axis development include the T-box transcription factors, the Hox genes, and the Wnt signaling pathway. These genetic regulators work together to coordinate the formation of the axis, ensuring that the embryo develops properly and that the various cell types and tissues are established in the correct locations.
Role of Signaling Pathways in Axis Development
Signaling pathways play a critical role in axis development, regulating the formation of the various axes and the establishment of the different cell types and tissues. Some of the key signaling pathways involved in axis development include the Wnt, BMP, and Notch pathways. These pathways work together to coordinate the formation of the axis, regulating the expression of specific genes and the behavior of different cell types.5 Ways Zebrafish Develop Axis

Here are five ways zebrafish develop their axis:
- Formation of the blastula: The blastula is a critical stage in zebrafish development, marked by the formation of a hollow ball of cells. The blastula is the precursor to the formation of the axis, and its development is regulated by a complex array of genetic regulators and signaling pathways.
- Establishment of the anterior-posterior axis: The anterior-posterior axis is the first axis to be established during zebrafish development, and is formed through the interaction of the germ ring and the blastoderm. This axis is critical for the formation of the head and tail of the embryo.
- Formation of the dorsal-ventral axis: The dorsal-ventral axis is established through the interaction of the BMP and Wnt signaling pathways, which regulate the formation of the ventral and dorsal portions of the embryo.
- Establishment of the left-right axis: The left-right axis is established through the interaction of the lateral plate mesoderm and the endoderm, which regulate the formation of the left and right sides of the embryo.
- Coordination of axis development: Axis development in zebrafish is a highly coordinated process, regulated by a complex array of genetic regulators and signaling pathways. The coordination of axis development ensures that the embryo develops properly and that the various cell types and tissues are established in the correct locations.
Practical Applications of Axis Development Research
Research on axis development in zebrafish has a number of practical applications, including the development of new treatments for developmental disorders and the improvement of our understanding of human development and disease. By studying axis development in zebrafish, researchers can gain valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of developmental disorders and develop new treatments.Future Directions for Axis Development Research

Future research on axis development in zebrafish is likely to focus on the development of new genetic tools and technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing and single-cell RNA sequencing. These tools will enable researchers to study axis development in greater detail, and to develop new treatments for developmental disorders.
Gallery of Axis Development Images
Axis Development Image Gallery
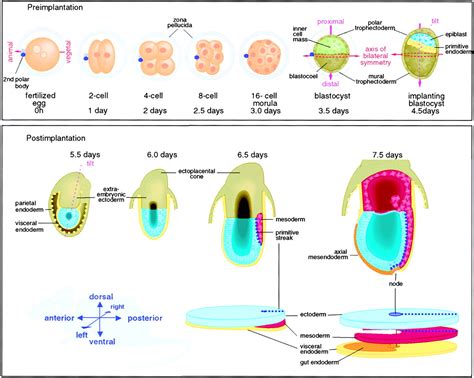
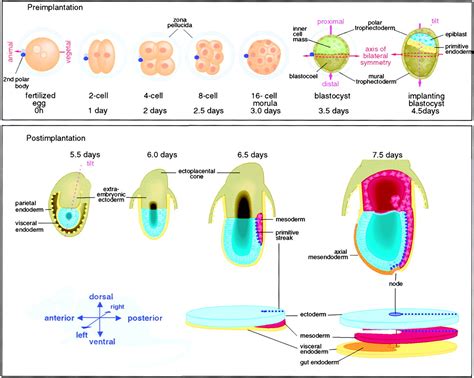
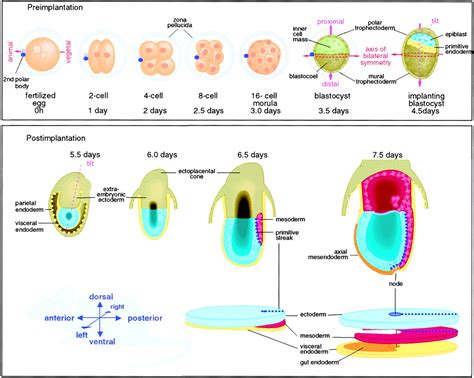
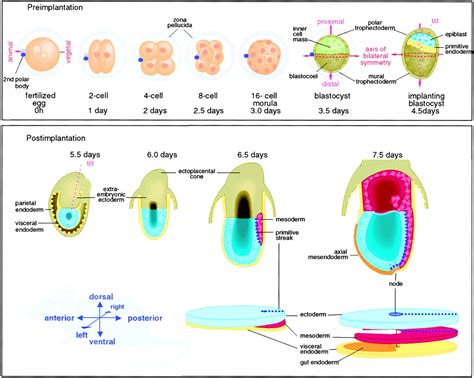
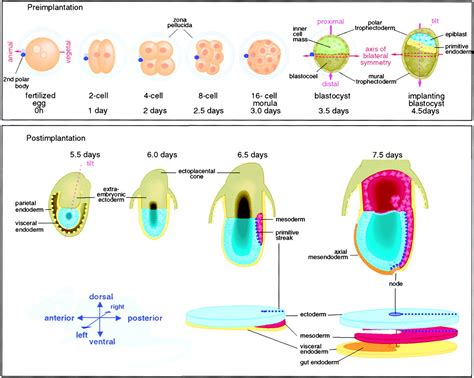

In conclusion, the development of the axis in zebrafish is a complex and highly regulated process that involves the interaction of multiple cell types, signaling pathways, and genetic regulators. By studying axis development in zebrafish, researchers can gain valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of developmental disorders and develop new treatments. We hope that this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the ways in which zebrafish develop their axis, and has highlighted the importance of continued research in this field. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about axis development in zebrafish.
