Intro
Learn how to manage diabetic ketoacidosis with these 6 effective strategies. Discover the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for DKA, and find out how to prevent future episodes. Master blood glucose monitoring, insulin dosing, and nutrition planning to regain control over your diabetes and reduce ketoacidosis risk.
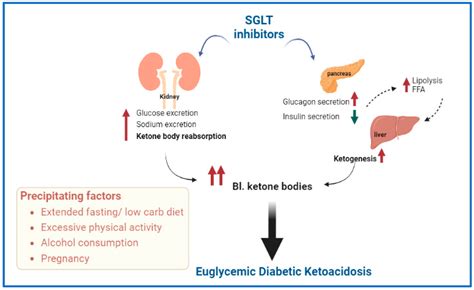
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones, which are acidic substances that can poison the body. DKA is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment. Managing DKA requires a comprehensive approach that involves lifestyle changes, medication, and close monitoring of blood sugar levels.
Understanding Diabetic Ketoacidosis
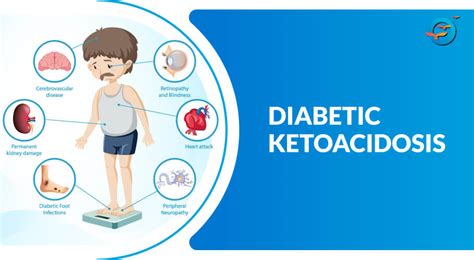
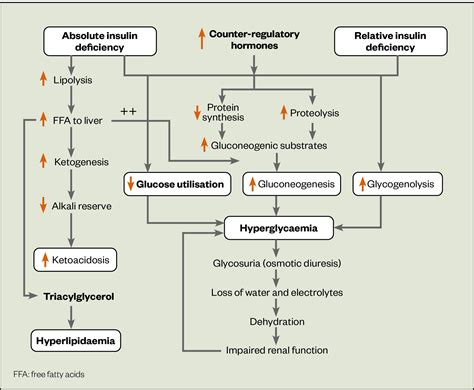
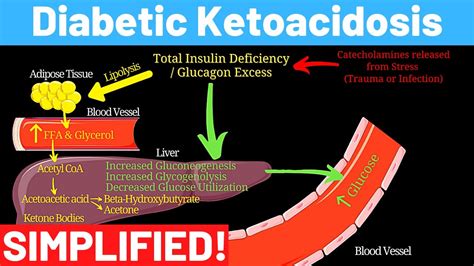
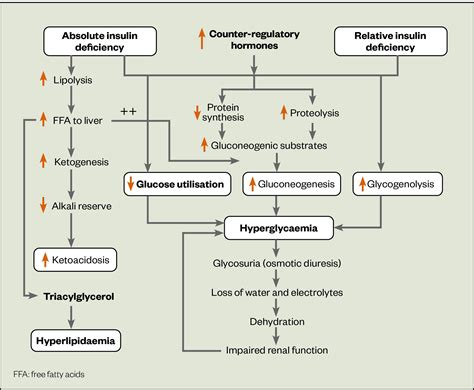
DKA is a condition that occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. As a result, the body begins to break down fat for energy, producing ketones in the process. Ketones can build up in the blood and cause a range of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and difficulty breathing.
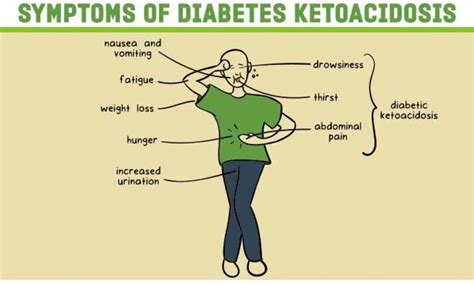
Recognizing the Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
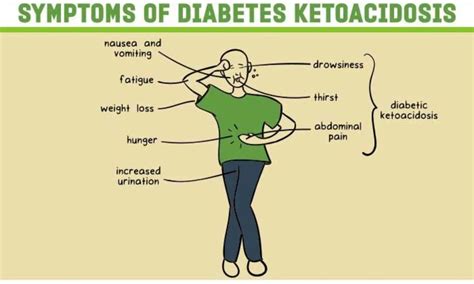
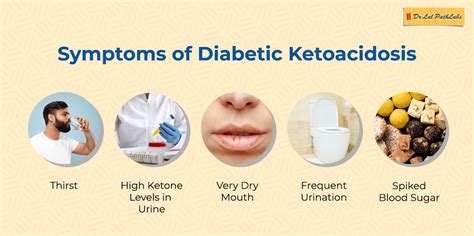
The symptoms of DKA can develop rapidly, often over a period of 24 hours. Common symptoms include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue
- Confusion
- Difficulty breathing
- Flu-like symptoms
Risk Factors for Diabetic Ketoacidosis
DKA can occur in anyone with diabetes, but certain individuals are at higher risk. These include:
- People with type 1 diabetes
- People with a history of DKA
- People who do not take their diabetes medication as prescribed
- People who have a fever or infection
- People who are dehydrated
6 Ways to Manage Diabetic Ketoacidosis
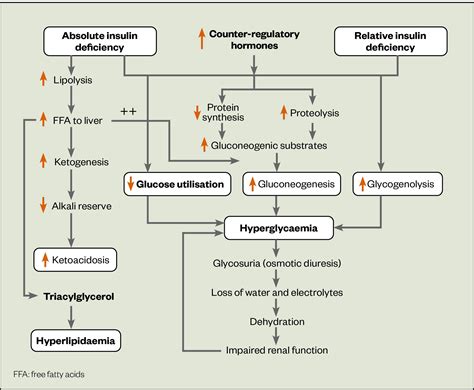
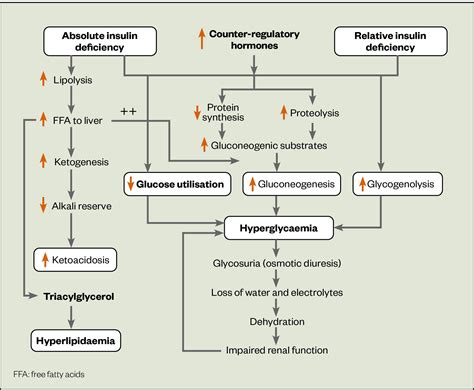
While DKA is a serious condition, it can be managed with the right treatment and lifestyle changes. Here are six ways to manage DKA:
1. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
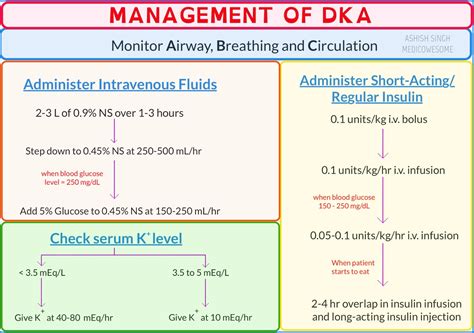
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for managing DKA. This involves checking blood sugar levels regularly, especially when symptoms occur. A healthcare provider can recommend the best times to check blood sugar levels and what levels are considered normal.
2. Take Medication as Prescribed
Taking diabetes medication as prescribed is essential for managing DKA. This includes insulin, which helps regulate blood sugar levels. A healthcare provider can recommend the best medication and dosage for each individual.
3. Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated is crucial for managing DKA. Drinking plenty of fluids, such as water and electrolyte-rich beverages, can help replace lost fluids and electrolytes.
4. Eat a Balanced Diet
Eating a balanced diet is essential for managing DKA. A healthcare provider can recommend a meal plan that is tailored to each individual's needs. This may include eating foods that are high in fiber, low in sugar, and rich in nutrients.
5. Get Enough Rest
Getting enough rest is crucial for managing DKA. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night and take regular breaks throughout the day.
6. Seek Medical Attention Promptly
Seeking medical attention promptly is essential for managing DKA. If symptoms occur, seek medical attention immediately. A healthcare provider can provide prompt treatment and prevent complications.
Gallery of Diabetic Ketoacidosis Management
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Management Image Gallery

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is diabetic ketoacidosis? A: Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones.
Q: What are the symptoms of DKA? A: The symptoms of DKA include increased thirst and urination, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, confusion, and difficulty breathing.
Q: How is DKA treated? A: DKA is treated with insulin, fluids, and electrolytes. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
Q: Can DKA be prevented? A: Yes, DKA can be prevented by monitoring blood sugar levels, taking medication as prescribed, staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and getting enough rest.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable information on managing diabetic ketoacidosis. If you have any questions or concerns, please leave a comment below. Don't forget to share this article with your friends and family who may be affected by diabetes.
