Intro
Learn about Diazepam medication with our comprehensive template and administration guide. Understand its uses, dosage, side effects, and contraindications. Discover how to safely administer Diazepam for anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Get expert advice on managing potential interactions and overdose risks, and download a free template for easy reference.
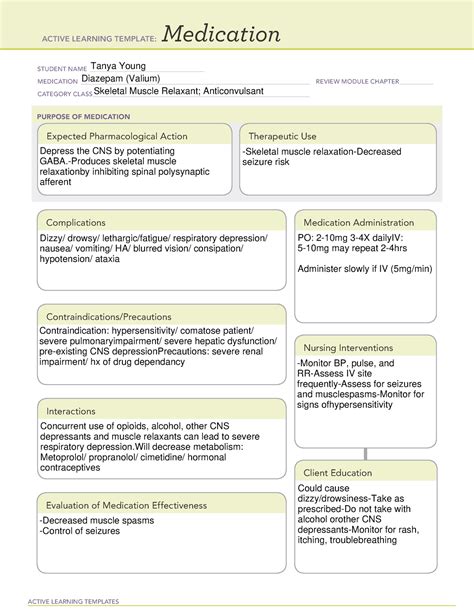
Diazepam, commonly known by its brand name Valium, is a medication that belongs to the class of benzodiazepines. It is widely used to treat various conditions, including anxiety disorders, alcohol withdrawal symptoms, muscle spasms, and seizures. As a medication, diazepam has a specific template and administration guide that healthcare professionals and patients should follow to ensure safe and effective use.
Understanding Diazepam
Diazepam works by enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that helps calm nerve activity in the brain. This results in a sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant effect. Diazepam is available in various forms, including tablets, oral solutions, and injectable solutions.

Indications for Use
Diazepam is indicated for the treatment of:
- Anxiety disorders
- Alcohol withdrawal symptoms
- Muscle spasms
- Seizures
- Status epilepticus (a life-threatening condition characterized by prolonged seizures)
Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of diazepam vary depending on the specific condition being treated, the patient's age, weight, and medical history.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Diazepam is available in the following dosage forms and strengths:
- Tablets: 2 mg, 5 mg, and 10 mg
- Oral solution: 1 mg/mL and 5 mg/mL
- Injectable solution: 5 mg/mL
Adult Dosage
The recommended adult dosage for diazepam is:
- Anxiety disorders: 2-10 mg, 2-4 times a day
- Alcohol withdrawal symptoms: 10-20 mg, 3-4 times a day
- Muscle spasms: 2-10 mg, 3-4 times a day
- Seizures: 10-30 mg, 2-3 times a day
Pediatric Dosage
The recommended pediatric dosage for diazepam is:
- Children under 6 months: 1-2 mg, 2-3 times a day
- Children 6 months to 2 years: 2-5 mg, 2-3 times a day
- Children 2-12 years: 5-10 mg, 2-3 times a day
Administration Guide
Diazepam can be administered orally or intravenously.
Oral Administration
- Tablets: Swallow whole with water
- Oral solution: Measure the correct dose using a syringe or spoon
Intravenous Administration
- Inject slowly over a period of 3-5 minutes
- Monitor vital signs and electrocardiogram (ECG) during administration
Contraindications and Warnings
Diazepam is contraindicated in patients with:
- Known hypersensitivity to diazepam or other benzodiazepines
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma
- Severe respiratory depression
- Sleep apnea
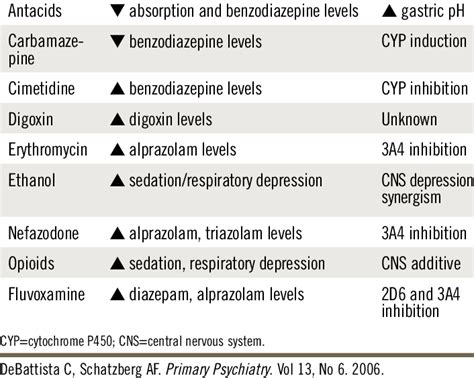
Interactions with Other Medications
Diazepam may interact with other medications, including:
- Central nervous system (CNS) depressants
- Anticonvulsants
- Antihistamines
- Opioids
Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Common side effects of diazepam include:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Headache
Serious adverse reactions include:
- Respiratory depression
- Cardiac arrest
- Seizures
- Psychiatric disturbances

Monitoring and Laboratory Tests
Patients receiving diazepam should be monitored for:
- Vital signs
- ECG
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Liver function tests (LFTs)
Gallery of Diazepam Medication
Diazepam Medication Image Gallery





Conclusion
Diazepam is a widely used medication for the treatment of various conditions, including anxiety disorders, alcohol withdrawal symptoms, muscle spasms, and seizures. By following the recommended dosage and administration guide, patients can safely and effectively use diazepam to manage their symptoms. It is essential to monitor patients for potential side effects and adverse reactions and to adjust the dosage as needed.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of diazepam medication and its administration guide. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below.
