Intro
Learn the key differences between Syncope and Seizure, including fainting, convulsions, and loss of consciousness, to understand their distinct symptoms and causes.
Syncope and seizures are two distinct medical conditions that can present with similar symptoms, often leading to confusion and misdiagnosis. Understanding the differences between these conditions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Syncope, also known as fainting, is a temporary loss of consciousness caused by a sudden decrease in blood flow to the brain. On the other hand, a seizure is a sudden surge of electrical activity in the brain that can cause changes in a person's behavior, movements, or sensations.
Both syncope and seizures can cause a person to lose consciousness, but the underlying causes and characteristics of these conditions are different. Syncope is often triggered by factors such as dehydration, stress, or certain medical conditions, whereas seizures are typically caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It is essential to recognize the warning signs and symptoms of each condition to provide appropriate care and treatment. In this article, we will delve into the differences between syncope and seizures, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Syncope Overview
Causes of Syncope
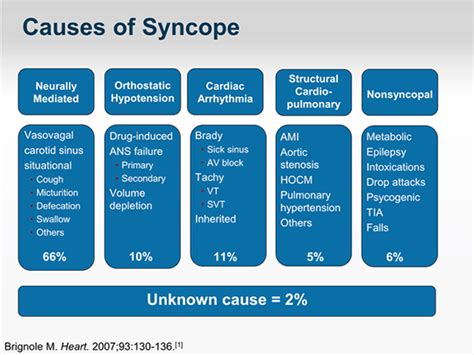
The causes of syncope can be divided into several categories, including: * Cardiac causes: Abnormal heart rhythms, heart valve problems, or heart failure can reduce blood flow to the brain, leading to syncope. * Neurological causes: Certain neurological conditions, such as migraines or multiple sclerosis, can affect blood flow to the brain and cause syncope. * Vasovagal causes: The vasovagal nerve can cause blood vessels to dilate, leading to a decrease in blood pressure and syncope. * Orthostatic causes: Standing up too quickly or changing positions can cause a sudden drop in blood pressure, leading to syncope.Seizure Overview
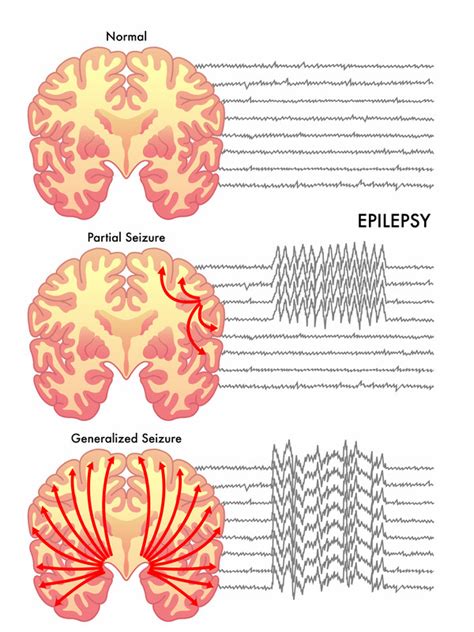
Causes of Seizures
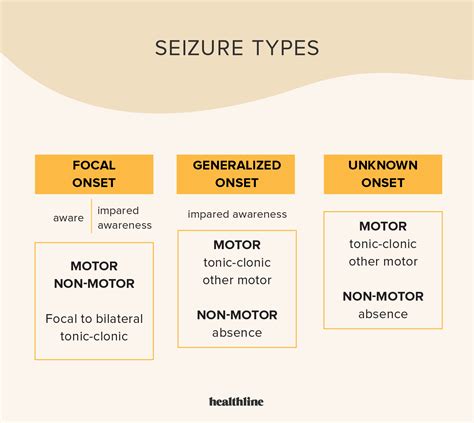
The causes of seizures can be divided into several categories, including: * Genetic causes: Certain genetic disorders, such as epilepsy, can increase the risk of seizures. * Traumatic causes: Head trauma or brain injury can cause seizures. * Infectious causes: Infections such as meningitis or encephalitis can cause seizures. * Metabolic causes: Certain metabolic disorders, such as low blood sugar or electrolyte imbalances, can cause seizures.Difference Between Syncope and Seizure
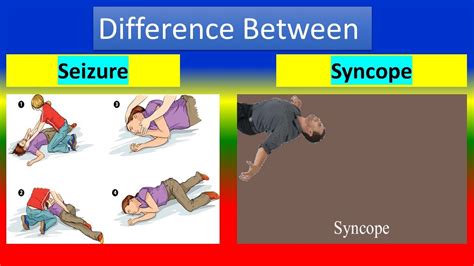
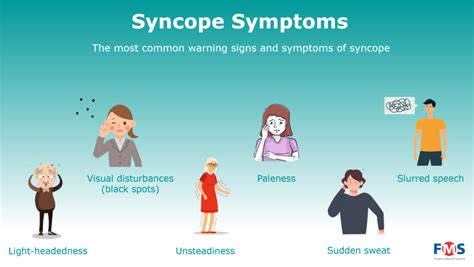
Diagnosis and Treatment
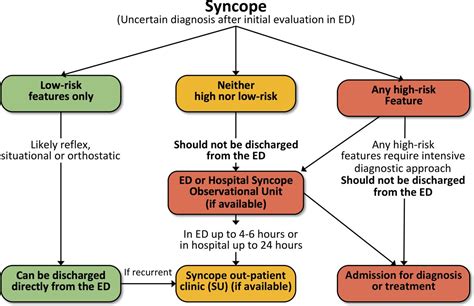
Diagnosing syncope and seizures requires a comprehensive medical evaluation, including a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as electroencephalograms (EEGs) or imaging studies. Treatment for syncope and seizures depends on the underlying cause of the condition. For syncope, treatment may involve addressing underlying medical conditions, such as heart disease or dehydration, and making lifestyle changes, such as increasing fluid intake or avoiding triggers. For seizures, treatment may involve medications, such as anticonvulsants, or surgery to remove the affected area of the brain.Prevention and Management

Emergency Response
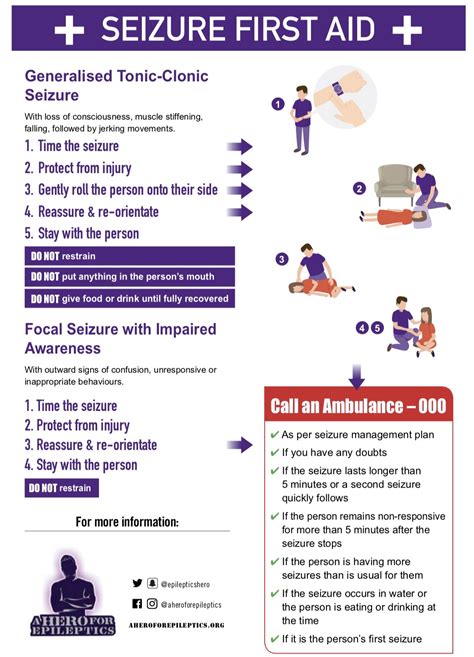
In the event of a syncopal or seizure episode, it is essential to respond quickly and effectively. For syncope, emergency response may involve calling for medical help, providing a safe environment, and administering first aid, such as CPR or the recovery position. For seizures, emergency response may involve calling for medical help, providing a safe environment, and administering first aid, such as turning the person onto their side or loosening tight clothing.Syncope and Seizure Image Gallery





In conclusion, syncope and seizures are two distinct medical conditions that require accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. By understanding the differences between these conditions, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage their symptoms, and emergency responders can provide effective care in the event of an episode. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with syncope and seizures in the comments below, and to share this article with others who may be affected by these conditions.
