Intro
Master the use of digoxin medication with our comprehensive ATi nursing guide. Learn about digoxin dosage, indications, contraindications, side effects, and nursing considerations. Understand how to safely administer digoxin, monitor for toxicity, and manage potential complications. Elevate your nursing skills with this essential resource for cardiac care.
Digoxin is a widely used medication for treating heart conditions, particularly atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure. As a crucial part of the nursing guide, understanding the mechanisms, benefits, and potential risks of digoxin is essential for providing high-quality patient care.
Digoxin: Mechanisms and Benefits
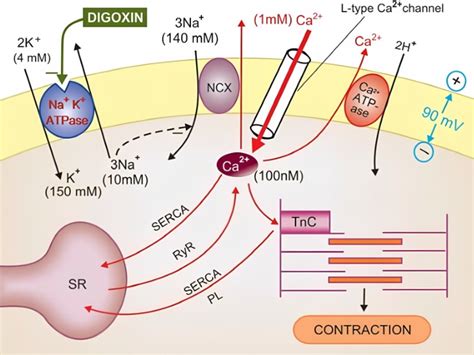
Digoxin belongs to the digitalis glycoside class of medications, which work by increasing the strength of cardiac contractions and slowing the heart rate. This is achieved by inhibiting the sodium-potassium ATPase pump, leading to increased intracellular calcium levels. The resulting effects include:
- Increased contractility of the heart muscle
- Slowed heart rate
- Increased cardiac output
- Reduced symptoms of heart failure
These benefits make digoxin an effective treatment for various cardiac conditions, including atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and congestive heart failure.
Digoxin Administration and Dosage
Digoxin is available in oral and intravenous forms, with the oral form being the most common. The typical dosage range is 0.125-0.25 mg per day, taken orally. However, the exact dosage and administration schedule may vary depending on the patient's specific needs and medical history.
It is essential to monitor the patient's kidney function and electrolyte levels, as digoxin is primarily excreted by the kidneys and can be affected by electrolyte imbalances. Additionally, digoxin can interact with other medications, such as diuretics and beta-blockers, which may impact its efficacy and safety.
Potential Risks and Side Effects

While digoxin can be an effective treatment for heart conditions, it can also cause a range of side effects, including:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Cardiac arrhythmias
In severe cases, digoxin toxicity can occur, characterized by symptoms such as:
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Visual disturbances
It is crucial to closely monitor patients receiving digoxin for signs of toxicity and adjust the dosage or discontinue treatment as needed.
Digoxin Toxicity and Overdose
Digoxin toxicity can occur due to various factors, including:
- Excessive dosage
- Renal impairment
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Interactions with other medications
In the event of digoxin overdose, prompt medical attention is necessary. Treatment may involve:
- Discontinuation of digoxin
- Administration of digoxin-specific antibody fragments (Fab)
- Supportive care, such as cardiac monitoring and fluid management
Nursing Considerations and Interventions

To ensure safe and effective use of digoxin, nurses should:
- Monitor patients closely for signs of toxicity and side effects
- Assess kidney function and electrolyte levels regularly
- Adjust the dosage or discontinue treatment as needed
- Educate patients on the importance of adherence to the prescribed dosage schedule
- Provide guidance on recognizing and reporting signs of toxicity or side effects
By following these nursing considerations and interventions, healthcare professionals can optimize patient outcomes and minimize the risks associated with digoxin therapy.
Patient Education and Adherence
Patient education plays a crucial role in ensuring adherence to digoxin therapy and minimizing the risk of toxicity. Nurses should:
- Explain the importance of taking digoxin as prescribed
- Discuss the potential risks and side effects
- Provide guidance on recognizing and reporting signs of toxicity or side effects
- Emphasize the need for regular follow-up appointments and monitoring
By empowering patients with knowledge and promoting adherence to treatment, nurses can contribute to improved patient outcomes and reduced morbidity.
Digoxin Medication Image Gallery
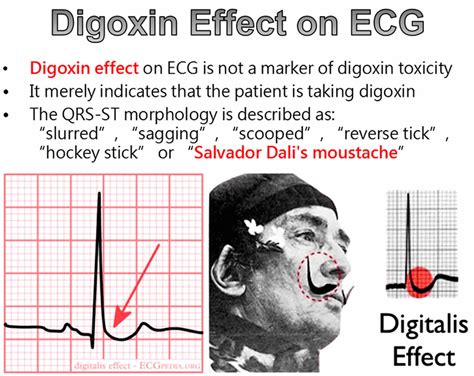




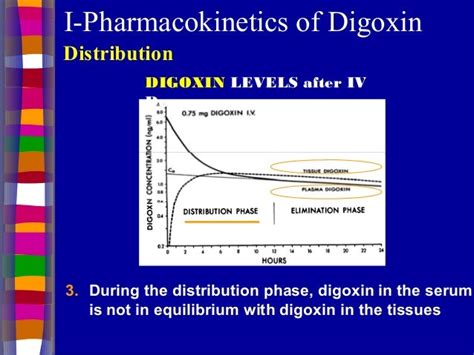
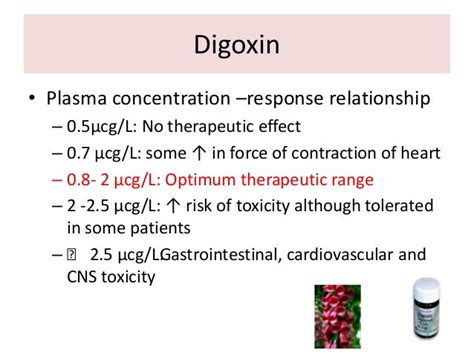
We hope this comprehensive guide to digoxin medication has provided valuable insights and information for healthcare professionals. By understanding the mechanisms, benefits, and potential risks of digoxin, nurses can optimize patient outcomes and provide high-quality care. Share your thoughts and experiences with digoxin therapy in the comments below.
