Intro
Discover the Disc Osteophyte Complex formation process, exploring spinal disc degeneration, osteophyte growth, and herniation, to understand this complex condition affecting intervertebral discs and spine health.
The human spine is a complex and intricate structure, comprised of numerous vertebrae, discs, and other components that work together to provide support, flexibility, and movement. One of the key elements of the spine is the intervertebral disc, which acts as a cushion between adjacent vertebrae, absorbing shock and facilitating smooth motion. However, over time, these discs can undergo changes that lead to the formation of disc osteophyte complexes, a condition that can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. In this article, we will delve into the world of disc osteophyte complex formation, exploring the underlying causes, mechanisms, and implications of this condition.
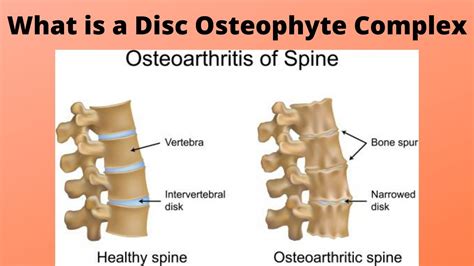
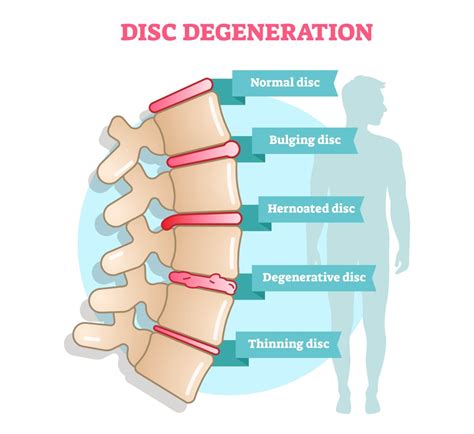
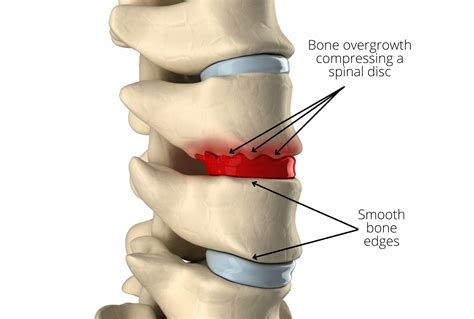
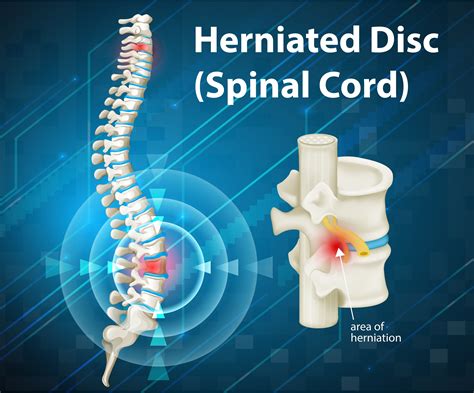
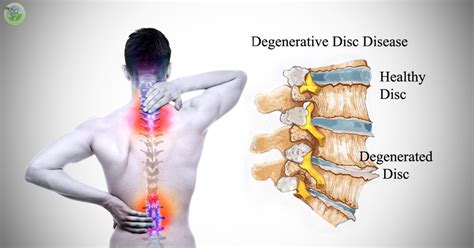
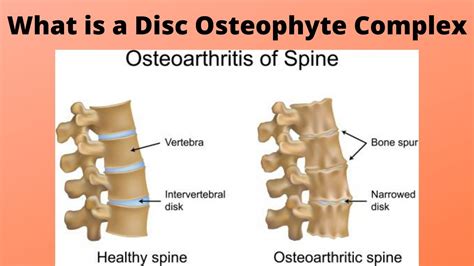
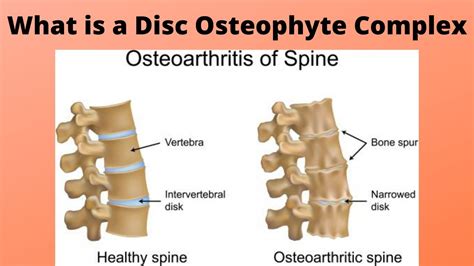
The intervertebral disc is a remarkable structure, consisting of a tough outer layer called the annulus fibrosus and a soft, gel-like inner layer called the nucleus pulposus. As we age, the discs can undergo degenerative changes, including dehydration, fibrosis, and the formation of osteophytes, which are bony outgrowths that can develop on the edges of the vertebrae. These changes can lead to the formation of disc osteophyte complexes, which are characterized by the presence of osteophytes, disc herniation, and other degenerative features. Understanding the causes and mechanisms of disc osteophyte complex formation is essential for developing effective treatments and prevention strategies.
Introduction to Disc Osteophyte Complex Formation
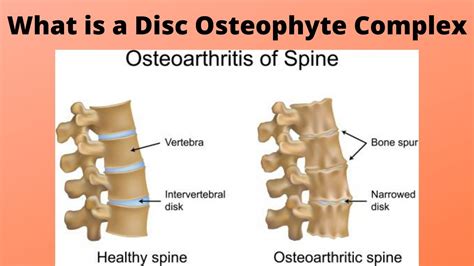
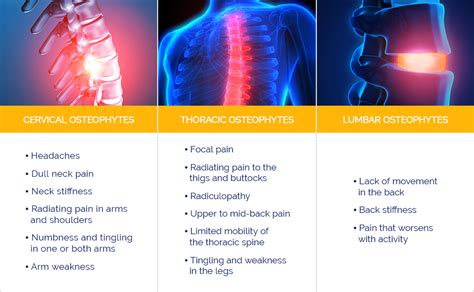
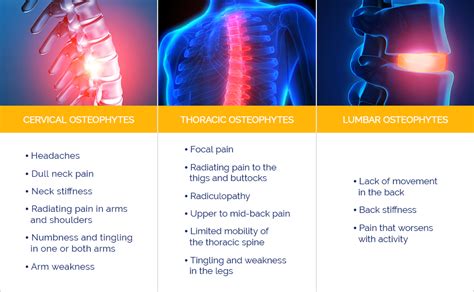
Causes and Risk Factors of Disc Osteophyte Complex Formation
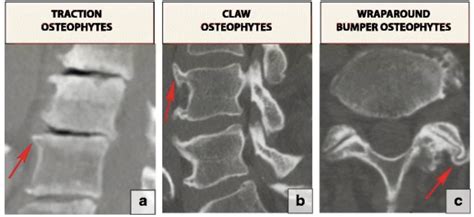
Mechanisms of Disc Osteophyte Complex Formation
The mechanisms of disc osteophyte complex formation are complex and involve the interplay of multiple factors, including the breakdown of the extracellular matrix, the formation of osteophytes, and the development of disc herniation. The process begins with the breakdown of the extracellular matrix, which is the network of proteins and other molecules that provide structure and support to the disc. As the extracellular matrix breaks down, the disc becomes more susceptible to degenerative changes, including the formation of osteophytes and disc herniation.Diagnosis and Treatment of Disc Osteophyte Complex Formation

Prevention and Management of Disc Osteophyte Complex Formation
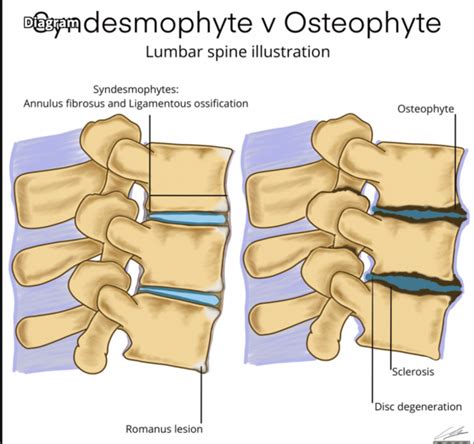
Future Directions in Disc Osteophyte Complex Formation Research
The future directions in disc osteophyte complex formation research are focused on developing a greater understanding of the underlying causes and mechanisms of this condition. Researchers are exploring a range of new treatments and interventions, including stem cell therapy, gene therapy, and tissue engineering. Additionally, there is a growing interest in the development of personalized medicine approaches, which involve tailoring treatment to the individual needs and characteristics of each patient.Conclusion and Final Thoughts
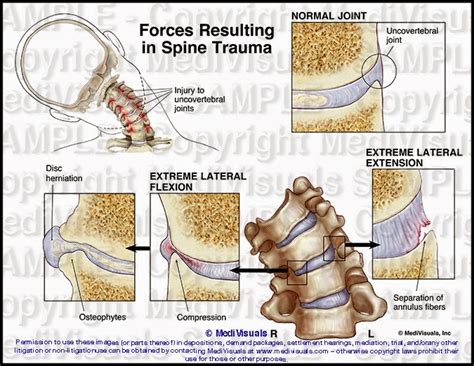
Disc Osteophyte Complex Formation Image Gallery
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of disc osteophyte complex formation, including the underlying causes, mechanisms, and implications of this condition. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about this topic. Additionally, we invite you to explore our other articles and resources on spinal health and wellness. By working together, we can promote greater awareness and understanding of spinal health issues and develop effective strategies for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
