Intro
Explore the truth behind Australias nuclear capabilities. Discover if Australia possesses nuclear weapons today, its history with nuclear programs, and the countrys current stance on nuclear arms. Uncover the facts about Australias nuclear policies, uranium reserves, and defense strategies. Get the inside scoop on Australias nuclear status and what it means for global security.
The question of whether Australia possesses nuclear weapons today is a topic of significant interest and debate. As a nation, Australia has a complex history with nuclear energy and nuclear weapons, with various policies and developments shaping its stance over the years. To address this question, it is essential to delve into Australia's past, present, and future in relation to nuclear capabilities.
Australia's Nuclear History
Australia's nuclear history dates back to the 1950s and 1960s, when the country collaborated with the United Kingdom on nuclear research and development. In the 1960s, Australia signed the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), committing itself to non-proliferation and disarmament. Despite this commitment, Australia has been involved in various nuclear-related activities, including the testing of British nuclear bombs on Australian soil in the 1950s and 1960s.
In the 1970s and 1980s, Australia's nuclear policy shifted towards a more cautious approach, with the government emphasizing the importance of nuclear disarmament and non-proliferation. In 1987, Australia established the Nuclear Non-Proliferation and Disarmament Initiative, a program aimed at promoting nuclear disarmament and strengthening the NPT.

Current Nuclear Capabilities
Today, Australia does not possess nuclear weapons. The country's nuclear policy is focused on nuclear energy, with a strong emphasis on safety, security, and non-proliferation. Australia's nuclear energy sector is regulated by the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA), which oversees the safe use of nuclear materials and facilities.
Australia's nuclear energy sector is relatively small, with only one nuclear reactor, the Lucas Heights reactor, which is used for research and the production of radioisotopes for medical and industrial applications. The reactor is owned and operated by the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO).

Nuclear Cooperation and Agreements
Australia has signed several nuclear cooperation agreements with other countries, including the United States, France, and China. These agreements facilitate cooperation on nuclear energy, research, and development, while also promoting non-proliferation and disarmament.
In 2015, Australia signed a nuclear cooperation agreement with India, which allows for the export of Australian uranium to India for civil nuclear purposes. This agreement has sparked controversy, with some critics arguing that it could facilitate the development of nuclear weapons in India.

Future Nuclear Developments
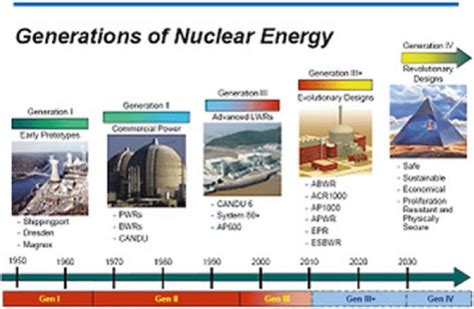
Australia's future nuclear developments are focused on nuclear energy and research, rather than nuclear weapons. The country is investing in new nuclear technologies, including small modular reactors and advanced reactor designs, which are designed to be safer and more efficient than traditional nuclear reactors.
Australia is also playing a key role in international efforts to promote nuclear disarmament and non-proliferation. In 2019, the country co-chaired the Nuclear Non-Proliferation and Disarmament Initiative, which aimed to promote disarmament and non-proliferation efforts among nuclear-armed states.
Australia's Nuclear Policy: Benefits and Challenges
Australia's nuclear policy is shaped by a range of benefits and challenges. Some of the key benefits of Australia's nuclear policy include:
- Promoting non-proliferation and disarmament: Australia's nuclear policy is focused on promoting non-proliferation and disarmament, which helps to reduce the risk of nuclear conflict and promote international security.
- Supporting nuclear energy: Australia's nuclear energy sector is small but growing, with the country investing in new nuclear technologies and research.
- Enhancing international cooperation: Australia's nuclear cooperation agreements with other countries facilitate cooperation on nuclear energy, research, and development, while also promoting non-proliferation and disarmament.
However, there are also challenges associated with Australia's nuclear policy, including:
- Controversy over nuclear cooperation agreements: Australia's nuclear cooperation agreements, such as the agreement with India, have sparked controversy and raised concerns about the potential for nuclear proliferation.
- Limited public awareness: There is limited public awareness about Australia's nuclear policy and the benefits and risks associated with nuclear energy and nuclear cooperation agreements.
- Need for greater transparency: There is a need for greater transparency and accountability in Australia's nuclear policy, particularly in relation to nuclear cooperation agreements and the development of new nuclear technologies.
Conclusion: Australia's Nuclear Future
In conclusion, Australia does not possess nuclear weapons today, and its nuclear policy is focused on nuclear energy, research, and non-proliferation. While there are benefits and challenges associated with Australia's nuclear policy, the country is committed to promoting non-proliferation and disarmament, and supporting the safe and secure use of nuclear energy.
We invite our readers to share their thoughts on Australia's nuclear policy and the benefits and challenges associated with it. What do you think about Australia's nuclear cooperation agreements? Do you think the country should invest more in nuclear energy and research? Share your comments below.
Australia's Nuclear Policy Image Gallery