Discover how lectins trigger inflammation, affecting gut health, immune response, and chronic disease risk, through 5 key mechanisms, including leaky gut and cytokine activation, to understand the lectin-inflammation connection.
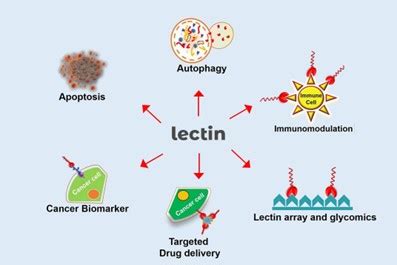
Lectins are a type of protein found in various foods, particularly in plant-based foods such as legumes, grains, and nightshades. While they play a crucial role in the defense mechanisms of plants, lectins can have detrimental effects on human health. One of the primary concerns associated with lectin consumption is its potential to cause inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system, but chronic inflammation can lead to various health problems, including arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. In this article, we will delve into the ways lectins cause inflammation and explore the potential consequences of lectin consumption.
The human body is equipped with a complex immune system that protects against harmful pathogens and foreign substances. However, when lectins enter the body, they can trigger an immune response, leading to inflammation. Lectins can bind to sugar molecules on the surface of cells, causing damage and activating the immune system. This can result in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are signaling molecules that promote inflammation. Chronic inflammation can have severe consequences, including tissue damage, oxidative stress, and an increased risk of chronic diseases.
The mechanisms by which lectins cause inflammation are complex and multifaceted. Lectins can alter the gut microbiome, leading to an imbalance of beneficial and harmful bacteria. This imbalance, also known as dysbiosis, can result in the production of pro-inflammatory compounds and the disruption of the gut barrier. Additionally, lectins can activate immune cells, such as macrophages and T-cells, leading to the production of inflammatory cytokines. The activation of these immune cells can also result in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can cause oxidative stress and damage to cellular components.
Introduction to Lectins and Inflammation

How Lectins Interact with the Immune System
The human body is equipped with a complex immune system that protects against harmful pathogens and foreign substances. However, when lectins enter the body, they can trigger an immune response, leading to inflammation. Lectins can bind to sugar molecules on the surface of cells, causing damage and activating the immune system. This can result in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are signaling molecules that promote inflammation. Chronic inflammation can have severe consequences, including tissue damage, oxidative stress, and an increased risk of chronic diseases.The Mechanisms of Lectin-Induced Inflammation
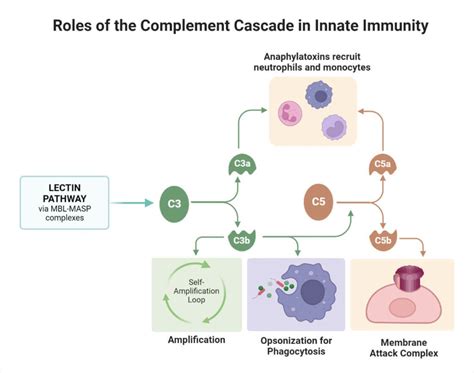
The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Lectin-Induced Inflammation
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in the development of lectin-induced inflammation. The gut microbiome is composed of trillions of microorganisms that live in the gastrointestinal tract and play a vital role in various physiological processes, including digestion, immune function, and the production of certain vitamins. However, when lectins enter the gut, they can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome, leading to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria and a decrease in beneficial bacteria. This imbalance can result in the production of pro-inflammatory compounds and the disruption of the gut barrier, leading to inflammation and oxidative stress.5 Ways Lectins Cause Inflammation

The Consequences of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation can have severe consequences, including an increased risk of chronic diseases such as arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Chronic inflammation can also lead to tissue damage, oxidative stress, and an imbalance of the gut microbiome. Additionally, chronic inflammation can disrupt the functioning of various physiological systems, including the immune system, the digestive system, and the nervous system.Reducing Lectin Consumption to Minimize Inflammation

The Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is essential for maintaining optimal health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. A balanced diet should include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources. It is also important to avoid processed and packaged foods that may contain high amounts of lectins and other pro-inflammatory compounds. Additionally, staying hydrated and getting regular exercise can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.Conclusion and Future Directions

Gallery of Lectin-Related Images
Lectin Image Gallery





We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the ways lectins can cause inflammation in the body. By reducing lectin consumption and maintaining a balanced diet, you can help minimize inflammation and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. We encourage you to share this article with others and to leave your comments and questions below. Additionally, we invite you to explore our website for more information on lectins, inflammation, and nutrition. Together, we can work towards promoting optimal health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
