Intro
Discover the various ways soldiers get compensated for their service, including base pay, allowances, and special pays. Learn how military personnel receive payment for hazardous duty, special skills, and combat zones. Get insights into the military pay scale, bonuses, and education benefits, making military service a rewarding career.
Serving in the military comes with its own set of rewards and benefits, one of which is the various ways soldiers get paid for their service. The military offers a competitive compensation package that includes a range of pay and allowances, making it an attractive career choice for many individuals. In this article, we will explore five ways soldiers get paid for their service, highlighting the different components of military pay and the benefits that come with serving in the armed forces.
1. Basic Pay
Basic pay is the fundamental component of a soldier's salary, and it is based on their rank and time in service. The military uses a pay grade system, which categorizes soldiers into different ranks, each with its own corresponding pay scale. The pay grade system ensures that soldiers are paid fairly and consistently, regardless of their branch of service or job specialty.
Basic pay is calculated based on a soldier's pay grade and time in service, with higher ranks and more experienced soldiers earning higher salaries. For example, a Private (E-1) in the Army with less than two years of service can expect to earn around $1,733 per month, while a Captain (O-3) with over 10 years of service can earn upwards of $7,000 per month.
Pay Grades and Their Corresponding Salaries
- Private (E-1): $1,733 - $2,043 per month
- Private First Class (E-2): $1,942 - $2,344 per month
- Specialist/Corporal (E-4): $2,343 - $3,085 per month
- Sergeant (E-5): $2,664 - $3,646 per month
- Staff Sergeant (E-6): $3,051 - $4,372 per month
- Sergeant First Class (E-7): $3,616 - $5,184 per month
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (E-8): $4,345 - $6,366 per month
- Sergeant Major (E-9): $5,429 - $7,484 per month
2. Allowances
Allowances are additional forms of compensation that soldiers receive to help cover the costs of living and serving in the military. There are several types of allowances, including:
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): This allowance helps soldiers cover the cost of food and is based on the local cost of living.
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): This allowance helps soldiers cover the cost of housing, whether they choose to live on or off base.
- Cost of Living Allowance (COLA): This allowance helps soldiers cover the cost of living in areas with a high cost of living.

Allowance Rates
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): $369.39 per month
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): varies depending on location and rank
- Cost of Living Allowance (COLA): varies depending on location and rank
3. Special Pay
Special pay is a type of compensation that soldiers receive for performing specific duties or serving in certain locations. Examples of special pay include:
- Hazardous Duty Pay: This pay is given to soldiers who perform duties that are considered hazardous, such as parachute jumping or explosive ordnance disposal.
- Subspecialty Pay: This pay is given to soldiers who possess specialized skills, such as language proficiency or medical expertise.
- Combat Pay: This pay is given to soldiers who serve in combat zones or areas of high risk.

Special Pay Rates
- Hazardous Duty Pay: $150 - $500 per month
- Subspecialty Pay: $100 - $500 per month
- Combat Pay: $225 - $1,000 per month
4. Bonuses
Bonuses are one-time payments that soldiers receive for performing specific tasks or achieving certain milestones. Examples of bonuses include:
- Enlistment Bonus: This bonus is given to new recruits who enlist in the military.
- Reenlistment Bonus: This bonus is given to soldiers who reenlist in the military.
- Student Loan Repayment Bonus: This bonus is given to soldiers who agree to serve in the military in exchange for student loan repayment.

Bonus Rates
- Enlistment Bonus: $5,000 - $20,000
- Reenlistment Bonus: $10,000 - $50,000
- Student Loan Repayment Bonus: $20,000 - $65,000
5. Education Benefits
Education benefits are a type of compensation that soldiers receive to help them pursue higher education. Examples of education benefits include:
- Montgomery GI Bill: This benefit provides soldiers with a monthly stipend to attend college or vocational school.
- Post-9/11 GI Bill: This benefit provides soldiers with a monthly stipend to attend college or vocational school, as well as a housing allowance and book stipend.
- Military Tuition Assistance: This benefit provides soldiers with a monthly stipend to attend college or vocational school.

Education Benefit Rates
- Montgomery GI Bill: $1,200 - $2,000 per month
- Post-9/11 GI Bill: $1,500 - $2,500 per month
- Military Tuition Assistance: $250 - $4,500 per year
Military Pay and Benefits Image Gallery


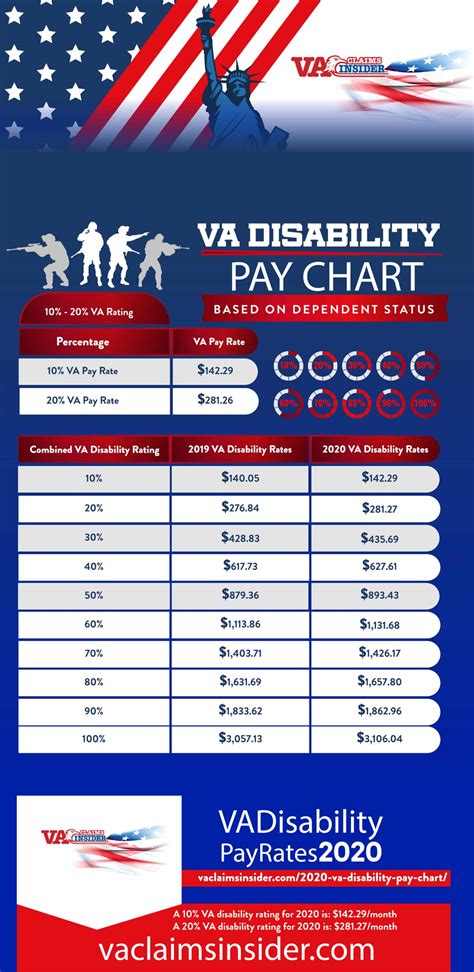



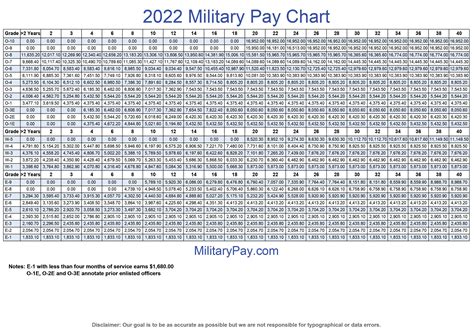



We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the various ways soldiers get paid for their service. From basic pay to education benefits, the military offers a range of compensation packages that make it an attractive career choice for many individuals. Whether you're considering a career in the military or are already serving, we encourage you to take advantage of the many benefits and allowances available to you.
