Unlock the truth behind air movement in nature. Does cold air really sink or rise? Explore the science behind temperature and density, and discover how wind patterns, atmospheric pressure, and climate interact. Learn about convection, inversion layers, and the surprising ways cold air behaves in different environments.
Have you ever wondered why some people claim that cold air sinks, while others argue that it rises? This debate has been ongoing for years, and it's essential to understand the concept to grasp the fundamental principles of atmospheric science. In this article, we'll delve into the world of thermodynamics and explore the behavior of cold air in nature.
What Determines the Movement of Air in the Atmosphere?
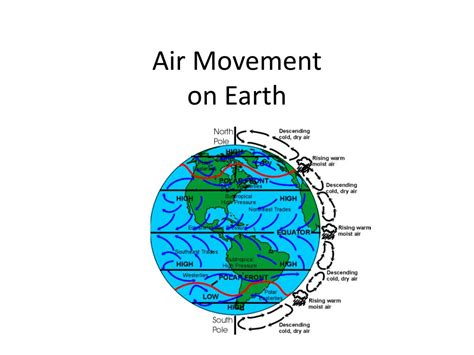
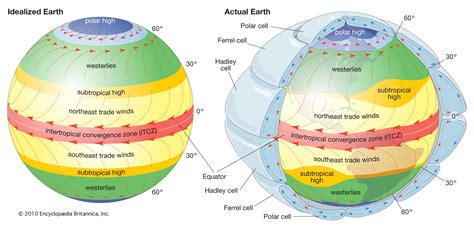
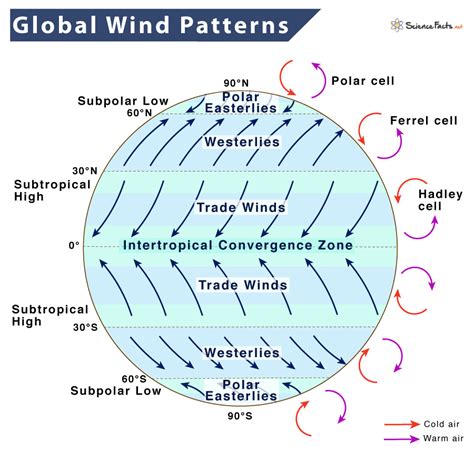
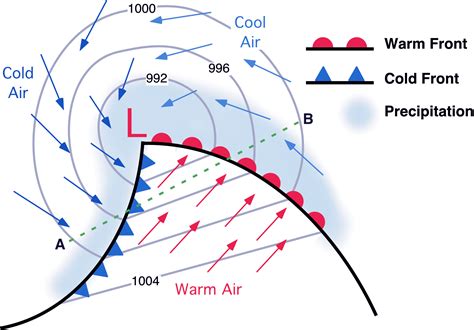
The movement of air in the atmosphere is primarily driven by temperature differences. When the sun heats the Earth's surface, it warms the air closest to the ground. As this warm air rises, it creates an area of low pressure near the ground. Nature abhors a vacuum, so air from surrounding areas moves in to fill the gap. This process is known as convection.
Convection and the Role of Density
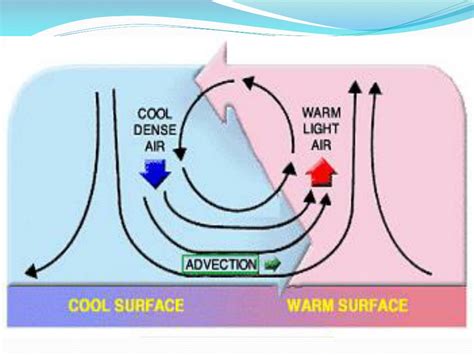
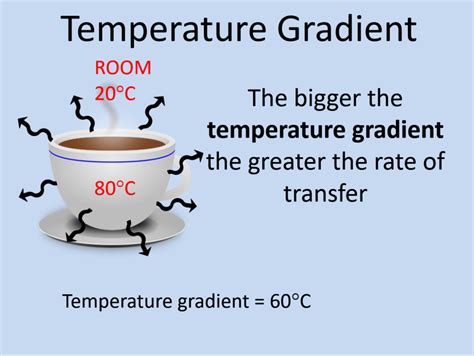
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids. In the atmosphere, convection occurs when there is a temperature difference between two areas. Warm air is less dense than cold air, so it rises, while cold air is denser and sinks. This concept is crucial in understanding the behavior of cold air in nature.
Does Cold Air Really Sink?

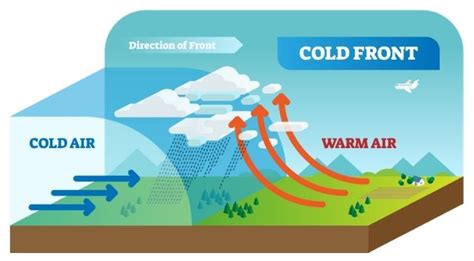
Yes, cold air does sink. When cold air is introduced into a warmer environment, it will sink to the ground due to its higher density. This is because cold air is denser than warm air, and it tends to move downwards under the influence of gravity. However, this concept only applies to certain situations.
Exceptions to the Rule: Cold Air Rising
There are instances where cold air can rise. For example, when cold air is trapped in a valley or a basin, it can be forced to rise as it flows over surrounding mountains or hills. This is known as orographic lift. Additionally, when cold air is cooled further, it can become even denser, causing it to sink. However, if this cold air is then heated from below, it can expand and rise.
Factors Influencing the Movement of Cold Air
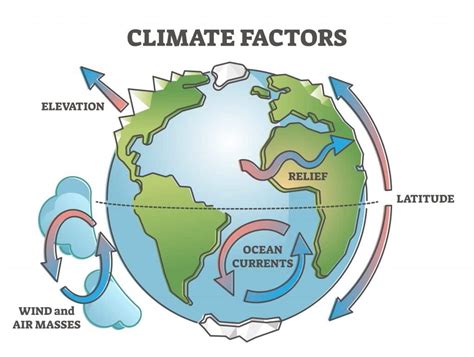
Several factors can influence the movement of cold air in nature, including:
- Topography: Mountains, hills, and valleys can force cold air to rise or sink, depending on the terrain.
- Humidity: High humidity can affect the density of air, causing cold air to behave differently.
- Wind: Wind can displace cold air, causing it to move in different directions.
- Temperature gradients: Temperature differences between two areas can drive the movement of cold air.
Understanding the Complexities of Atmospheric Science
The movement of cold air in nature is a complex phenomenon, influenced by various factors. While it's true that cold air sinks in certain situations, there are exceptions to the rule. By understanding the underlying principles of atmospheric science, we can appreciate the intricacies of the Earth's atmosphere.
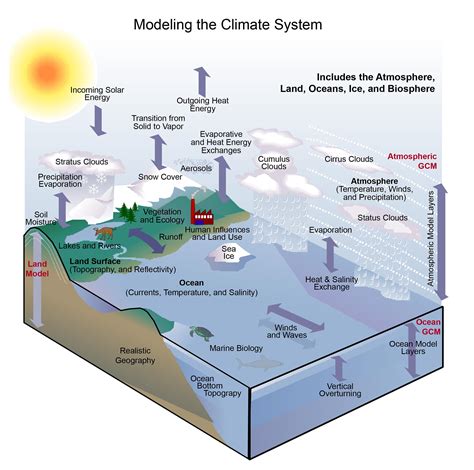
Real-World Applications: Weather Forecasting and Climate Modeling
Understanding the behavior of cold air in nature has significant implications for weather forecasting and climate modeling. Accurate predictions of temperature and precipitation patterns rely on a deep understanding of atmospheric science. By incorporating the complexities of cold air movement into weather models, meteorologists can improve the accuracy of their forecasts.
The Future of Atmospheric Science: Research and Development
Ongoing research in atmospheric science continues to advance our understanding of the Earth's atmosphere. New technologies, such as satellite imaging and computational modeling, enable scientists to study the atmosphere in greater detail. As our understanding of the atmosphere improves, so too will our ability to predict weather patterns and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Cold Air Movement Image Gallery



Conclusion: Understanding the Movement of Cold Air in Nature
In conclusion, the movement of cold air in nature is a complex phenomenon influenced by various factors. While it's true that cold air sinks in certain situations, there are exceptions to the rule. By understanding the underlying principles of atmospheric science, we can appreciate the intricacies of the Earth's atmosphere.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of the movement of cold air in nature. If you have any questions or would like to share your thoughts, please leave a comment below.
