Intro
Millions of Americans rely on government assistance programs to access essential healthcare and nutrition. Two of the most critical programs are Medicaid, which provides health coverage, and the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), commonly known as food stamps. While these programs are distinct, they are interconnected in ways that may affect eligibility. Understanding the relationship between food stamps and Medicaid eligibility is crucial for individuals and families who rely on these programs.
In the United States, Medicaid is a joint federal-state program that provides health insurance coverage to eligible low-income adults, children, pregnant women, and people with disabilities. SNAP, on the other hand, is a federal program that helps low-income individuals and families purchase food. While the two programs are separate, the application and eligibility processes are often linked, and changes in one program can impact the other.
How Food Stamps Impact Medicaid Eligibility
The relationship between food stamps and Medicaid eligibility is complex, and changes in one program can have unintended consequences on the other. Here are three ways food stamps can impact Medicaid eligibility:
1. Income and Resource Calculations
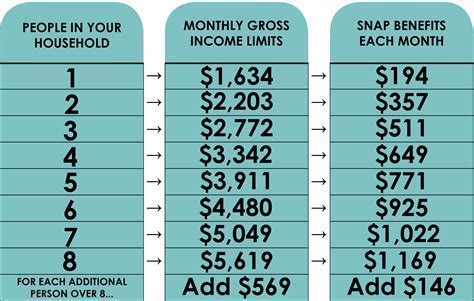
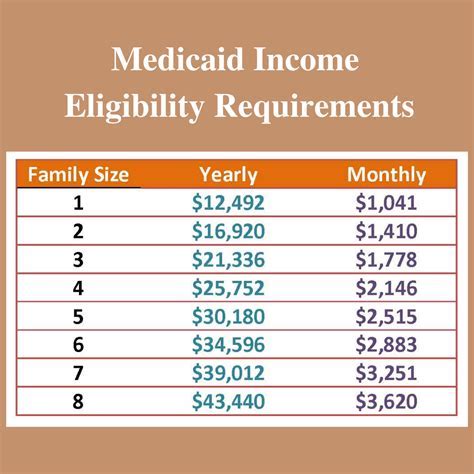
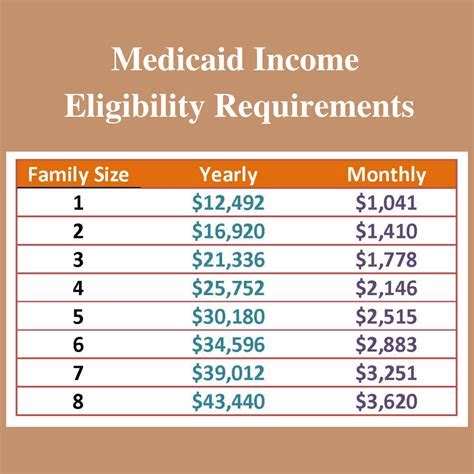
When applying for Medicaid, individuals must provide income and resource information to determine eligibility. In some states, food stamp benefits are counted as income when calculating Medicaid eligibility. This means that if an individual receives food stamps, the value of those benefits may be included in their overall income, potentially affecting their Medicaid eligibility.
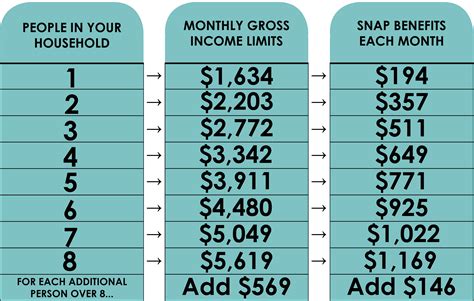
For example, if an individual receives $200 in food stamps per month, that amount may be added to their gross income when determining Medicaid eligibility. If the individual's total income exceeds the Medicaid eligibility threshold, they may be ineligible for Medicaid coverage.
Implications for Medicaid Eligibility
In states where food stamp benefits are counted as income, individuals who receive food stamps may be more likely to exceed the Medicaid eligibility threshold. This can lead to a reduction in Medicaid enrollment, particularly among low-income individuals who rely on food stamps to access nutrition.
2. Streamlined Applications and Renewals
To simplify the application and renewal process, many states have implemented streamlined processes that allow individuals to apply for multiple benefits, including Medicaid and food stamps, using a single application. While this can reduce administrative burdens and increase access to benefits, it can also create challenges for individuals who experience changes in their eligibility status.
For instance, if an individual's food stamp benefits are terminated due to changes in their income or family size, they may also be at risk of losing their Medicaid coverage. This is because the streamlined application process may automatically trigger a review of their Medicaid eligibility, potentially resulting in termination of benefits.
Implications for Medicaid Eligibility
The use of streamlined applications and renewals can lead to a higher risk of Medicaid disenrollment, particularly among individuals who experience changes in their food stamp benefits. To mitigate this risk, individuals should carefully review their eligibility status and take steps to ensure that they remain eligible for Medicaid coverage.

3. State-Specific Rules and Variations
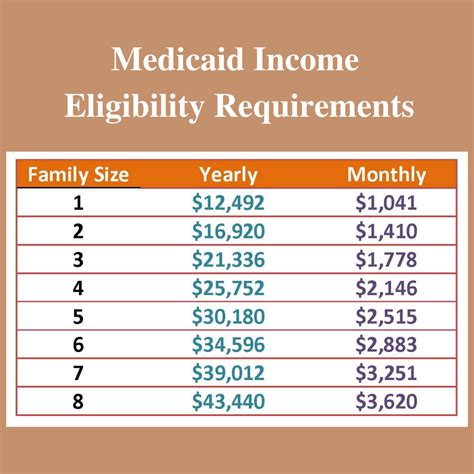
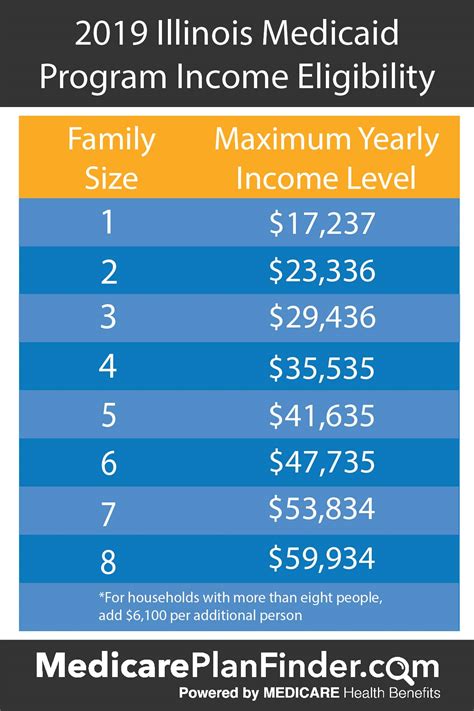
Medicaid eligibility rules vary significantly from state to state, and the impact of food stamps on Medicaid eligibility can differ depending on the state in which an individual resides. Some states, such as California and New York, have implemented rules that disregard food stamp benefits when calculating Medicaid eligibility. In these states, individuals who receive food stamps are not at risk of exceeding the Medicaid eligibility threshold due to their food stamp benefits.
However, other states, such as Texas and Florida, count food stamp benefits as income when determining Medicaid eligibility. In these states, individuals who receive food stamps may be at risk of losing their Medicaid coverage if their total income exceeds the eligibility threshold.
Implications for Medicaid Eligibility
The state-specific rules and variations in Medicaid eligibility can create confusion and uncertainty for individuals who rely on food stamps and Medicaid. To navigate these complexities, individuals should familiarize themselves with their state's Medicaid eligibility rules and seek guidance from a qualified benefits counselor if needed.
Gallery of Medicaid Eligibility and Food Stamps
Medicaid Eligibility and Food Stamps Image Gallery



Final Thoughts
The relationship between food stamps and Medicaid eligibility is complex, and changes in one program can have unintended consequences on the other. By understanding the three ways food stamps can impact Medicaid eligibility, individuals can take steps to ensure that they remain eligible for Medicaid coverage. If you have questions about your Medicaid eligibility or food stamp benefits, don't hesitate to reach out to a qualified benefits counselor for guidance. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below!
