Intro
Discover how food stamps verify income and eligibility. Learn about the income limits, required documents, and frequency of checks. Understand how income affects food stamp benefits and find out what types of income are counted. Get the facts on Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) income verification.
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), also known as food stamps, is a vital government program aimed at helping low-income individuals and families purchase the food they need to maintain good health. With over 37 million participants, SNAP is one of the largest food assistance programs in the United States. If you're considering applying for food stamps, you might wonder whether the program checks your income.
In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of the SNAP program, exploring how income affects eligibility and the application process. We'll also discuss other factors that influence eligibility, such as resources, expenses, and family size.
Why is Income Important for Food Stamps?
The primary goal of SNAP is to provide food assistance to individuals and families who struggle to make ends meet. To achieve this goal, the program uses a complex set of rules to determine who is eligible for benefits. Income is a crucial factor in this process, as it helps determine whether an applicant's household income is low enough to qualify for assistance.
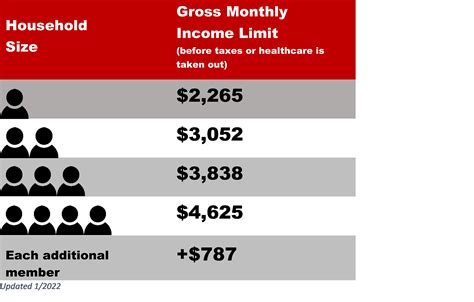
When you apply for food stamps, your income is compared to the federal poverty guidelines (FPG) to determine whether you're eligible for benefits. The FPG is a measure of the minimum amount of income required for an individual or family to meet their basic needs. If your household income is below a certain percentage of the FPG, you may be eligible for SNAP benefits.
How Does the SNAP Program Check Income?
To determine your eligibility for food stamps, the SNAP program checks your income in several ways:
- Gross Income: The program starts by calculating your gross income, which includes all income earned by household members, such as wages, salaries, tips, and self-employment income.
- Deductions: The program then allows certain deductions, such as taxes, child support payments, and housing costs, to reduce your gross income.
- Net Income: After deducting these expenses, your net income is calculated. This is the amount of income available for food and other living expenses.
What Types of Income are Considered?
The SNAP program considers various types of income when determining eligibility, including:
- Earned Income: Wages, salaries, tips, and self-employment income are all considered earned income.
- Unearned Income: Unearned income includes sources such as social security benefits, pensions, and unemployment compensation.
- Child Support: Child support payments received by a household member are considered income.
- Alimony: Alimony payments received by a household member are considered income.
What Expenses are Deducted from Income?
To calculate your net income, the SNAP program allows certain deductions, including:
- Taxes: Federal, state, and local taxes are deductible from gross income.
- Child Support Payments: If a household member makes child support payments, these expenses can be deducted from gross income.
- Housing Costs: Rent or mortgage payments, property taxes, and insurance premiums can be deducted from gross income.
- Medical Expenses: Out-of-pocket medical expenses, such as copays and prescription medication, can be deducted from gross income.
How Does Family Size Affect SNAP Eligibility?
In addition to income, family size plays a significant role in determining SNAP eligibility. The larger your family, the higher your income can be and still qualify for benefits. For example, a family of four with a gross income of $3,500 per month may be eligible for SNAP benefits, while a single individual with the same income would not.
What Resources are Considered in SNAP Eligibility?
Resources, such as cash, savings, and assets, can also impact SNAP eligibility. The program considers the following resources:
- Cash: Cash on hand, such as money in a checking or savings account, is considered a resource.
- Savings: Savings accounts, including CDs and IRAs, are considered resources.
- Assets: Assets, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, are considered resources.
How Can You Apply for Food Stamps?
If you're interested in applying for food stamps, you can start by visiting your local SNAP office or applying online through your state's website. You'll need to provide documentation, such as:
- Identification: A valid government-issued ID, such as a driver's license or passport.
- Income Verification: Pay stubs, tax returns, or other documents to verify your income.
- Expense Verification: Documents to verify your expenses, such as rent or mortgage payments, and utility bills.
Conclusion
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) is a vital government program that helps low-income individuals and families purchase the food they need to maintain good health. When applying for food stamps, your income is a critical factor in determining eligibility. By understanding how the program checks income, you can better navigate the application process and access the benefits you need.
Gallery of Food Stamps and SNAP Eligibility
Food Stamps and SNAP Eligibility Image Gallery








We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the SNAP program and the factors that affect eligibility. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to comment below or reach out to your local SNAP office.
