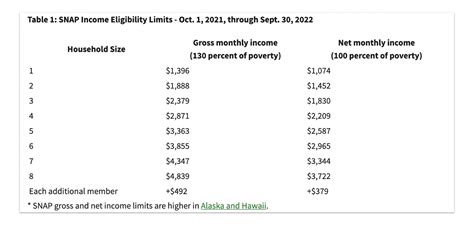Intro
Discover how rent payments impact food stamp benefits. Learn how the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) considers housing costs, including rent, utilities, and mortgage payments, when determining eligibility and benefit amounts. Understand the calculations and deductions involved to maximize your food stamp assistance.
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), also known as food stamps, is a vital assistance program for low-income individuals and families in the United States. One of the key factors in determining SNAP benefits is household expenses, including rent payments. However, the way rent payments are considered can be complex and varies from state to state. In this article, we will delve into the details of how rent payments are factored into SNAP benefit calculations.
Understanding SNAP Eligibility and Benefits

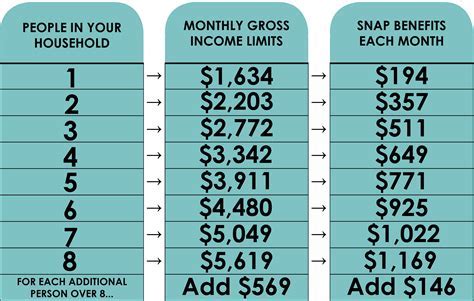
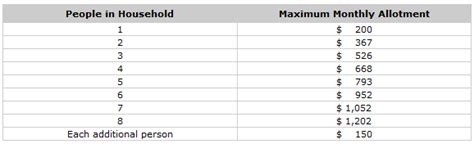
To qualify for SNAP, applicants must meet certain income and resource requirements. The program takes into account a household's gross income, deductions, and expenses to determine the amount of benefits they are eligible to receive. SNAP benefits are calculated based on a household's net income, which is the amount of income left after deducting allowable expenses.
How Rent Payments Are Considered in SNAP Benefit Calculations
Rent payments are considered a necessary expense for SNAP households. The program allows households to deduct a portion of their rent payments from their gross income when calculating their net income. However, the amount of rent that can be deducted varies depending on the state and the household's circumstances.
In general, SNAP households can deduct the following types of rent payments:
- Rent or mortgage payments for their primary residence
- Property taxes and insurance
- Utility bills, such as electricity, gas, and water
However, not all rent payments are created equal. SNAP households can only deduct rent payments that are considered "reasonable" and "necessary." For example, if a household is paying an unusually high rent, the state may not allow the full amount to be deducted.
Excess Shelter Deduction

The Excess Shelter Deduction is a key factor in determining SNAP benefits for households with high rent payments. This deduction allows households to deduct a portion of their excess shelter costs from their gross income. Excess shelter costs are defined as the amount of rent or mortgage payments that exceed 50% of a household's gross income.
For example, let's say a household has a gross income of $1,500 per month and pays $1,000 in rent. The excess shelter cost would be $500 ($1,000 - $500, which is 50% of $1,000). The household could deduct this amount from their gross income, reducing their net income and potentially increasing their SNAP benefits.
State-Specific Variations
While the Excess Shelter Deduction is a standard part of SNAP benefit calculations, states have some flexibility in how they implement this deduction. Some states may have different income limits or deductions, which can affect the amount of rent that can be deducted.
For example, some states may have a higher or lower income limit for the Excess Shelter Deduction. Other states may allow households to deduct additional expenses, such as utility bills or childcare costs.
Impact of Rent Payments on SNAP Benefits

The impact of rent payments on SNAP benefits can be significant. Households with high rent payments may be eligible for higher benefits due to the Excess Shelter Deduction. However, households with low rent payments may not be eligible for as many benefits.
To illustrate this, let's consider an example. Suppose we have two households, both with a gross income of $1,500 per month. Household A pays $1,000 in rent, while Household B pays $500 in rent. Due to the Excess Shelter Deduction, Household A may be eligible for higher SNAP benefits because their rent payment exceeds 50% of their gross income.
Other Factors That Affect SNAP Benefits
While rent payments are an important factor in determining SNAP benefits, they are not the only factor. Other expenses, such as utility bills, childcare costs, and medical expenses, can also affect benefit calculations.
Additionally, state-specific policies and programs can impact SNAP benefits. For example, some states may have programs that provide additional assistance to households with high rent payments or other expenses.
Conclusion

In conclusion, rent payments play a crucial role in determining SNAP benefits. The Excess Shelter Deduction allows households to deduct a portion of their excess shelter costs from their gross income, which can impact their benefit calculations. However, the amount of rent that can be deducted varies depending on the state and the household's circumstances.
If you are receiving SNAP benefits or are applying for the program, it is essential to understand how rent payments are factored into benefit calculations. By knowing how to navigate the system, you can ensure that you receive the maximum benefits you are eligible for.
Gallery of SNAP-Related Images
SNAP Image Gallery