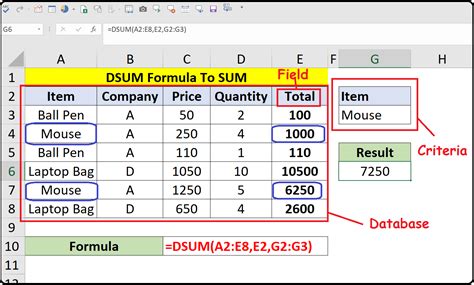
In the world of Excel, formulas are the backbone of data analysis and manipulation. Among the many powerful functions available, the DSUM function stands out for its ability to summarize data based on specific conditions. This article will delve into the capabilities of the DSUM function and provide you with five practical ways to use it in your Excel spreadsheets.
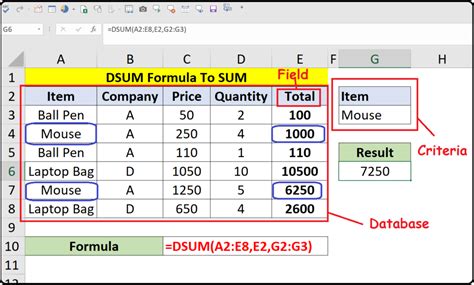
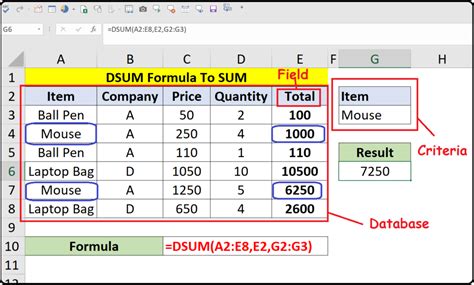
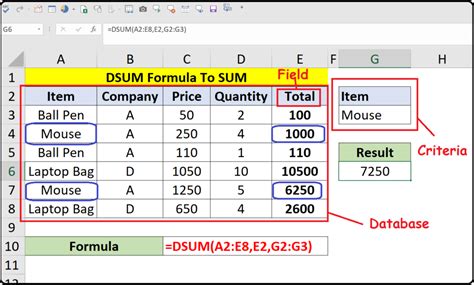
Understanding the Basics of DSUM
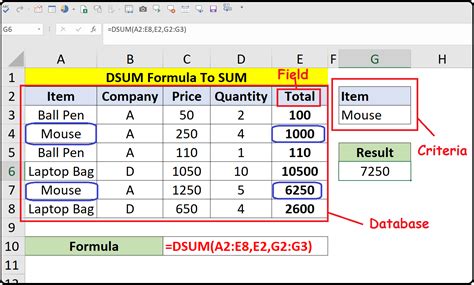
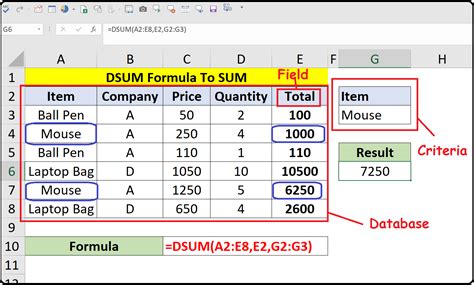
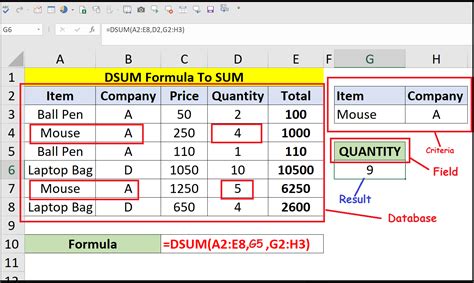
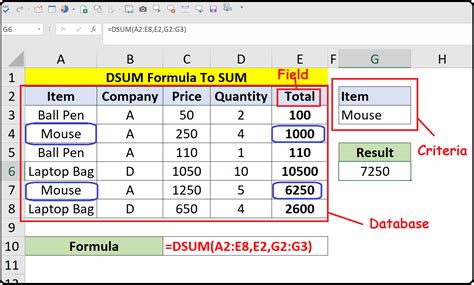
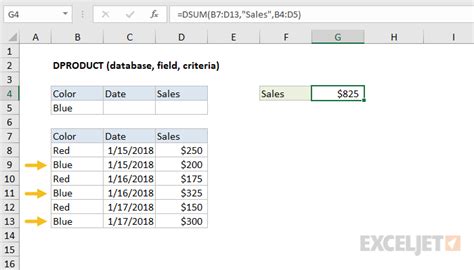
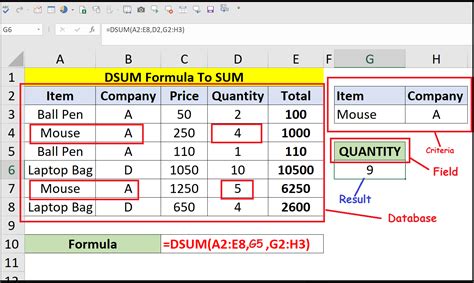
The DSUM function is part of Excel's database functions, which allow you to manipulate and analyze data in a database format. The syntax for the DSUM function is as follows:
DSUM(database, field, criteria)
databaserefers to the range of cells that contains the data you want to analyze.fieldspecifies the column you want to summarize.criteriais the range of cells that contains the conditions you want to apply to the data.
Now, let's explore five ways to use the DSUM function in Excel.
1. Summing Values Based on a Single Criteria
Suppose you have a database of sales data, and you want to find the total sales for a specific region.
| Salesperson | Region | Sales |
|---|---|---|
| John | North | 1000 |
| Jane | South | 500 |
| Joe | North | 800 |
| Sarah | South | 1200 |
To use the DSUM function, you would:
- Select the cell where you want to display the result.
- Enter the formula
=DSUM(A1:C4, "Sales", A5:B6), assuming the data is in cells A1:C4 and the criteria is in cells A5:B6. - Press Enter to get the result.
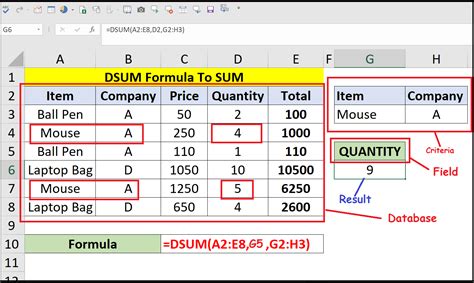
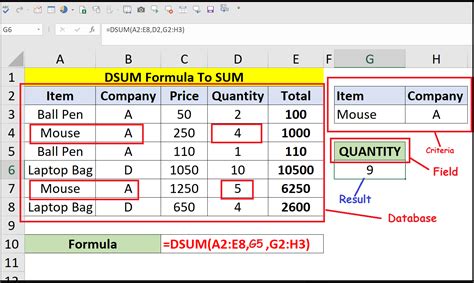
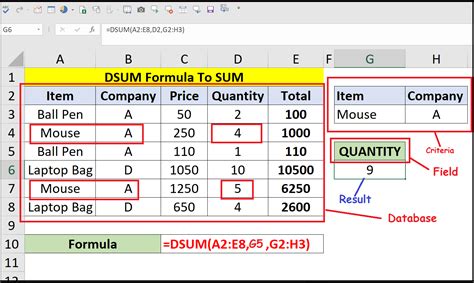
2. Summing Values Based on Multiple Criteria
What if you want to find the total sales for a specific region and salesperson?
| Salesperson | Region | Sales |
|---|---|---|
| John | North | 1000 |
| Jane | South | 500 |
| Joe | North | 800 |
| Sarah | South | 1200 |
To use the DSUM function with multiple criteria, you would:
- Select the cell where you want to display the result.
- Enter the formula
=DSUM(A1:C4, "Sales", A5:C6), assuming the data is in cells A1:C4 and the criteria is in cells A5:C6. - Press Enter to get the result.
3. Summing Values Based on a Date Range
Suppose you want to find the total sales for a specific date range.
| Salesperson | Date | Sales |
|---|---|---|
| John | 2022-01-01 | 1000 |
| Jane | 2022-01-05 | 500 |
| Joe | 2022-01-10 | 800 |
| Sarah | 2022-01-15 | 1200 |
To use the DSUM function with a date range, you would:
- Select the cell where you want to display the result.
- Enter the formula
=DSUM(A1:C4, "Sales", A5:B6), assuming the data is in cells A1:C4 and the criteria is in cells A5:B6. - Press Enter to get the result.
4. Summing Values Based on a Text Criteria
What if you want to find the total sales for a specific product?
| Product | Sales |
|---|---|
| Apple | 1000 |
| Banana | 500 |
| Orange | 800 |
| Grapes | 1200 |
To use the DSUM function with a text criteria, you would:
- Select the cell where you want to display the result.
- Enter the formula
=DSUM(A1:B4, "Sales", A5:B6), assuming the data is in cells A1:B4 and the criteria is in cells A5:B6. - Press Enter to get the result.
5. Summing Values Based on a Multiple Criteria with OR Condition
Suppose you want to find the total sales for a specific region or salesperson.
| Salesperson | Region | Sales |
|---|---|---|
| John | North | 1000 |
| Jane | South | 500 |
| Joe | North | 800 |
| Sarah | South | 1200 |
To use the DSUM function with a multiple criteria with OR condition, you would:
- Select the cell where you want to display the result.
- Enter the formula
=DSUM(A1:C4, "Sales", A5:C6), assuming the data is in cells A1:C4 and the criteria is in cells A5:C6. - Press Enter to get the result.
Gallery of DSUM Function Examples
DSUM Function Examples
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the DSUM function and its applications in Excel. By mastering this powerful function, you can take your data analysis skills to the next level and make more informed decisions. If you have any questions or need further clarification, feel free to ask in the comments below.
