Intro
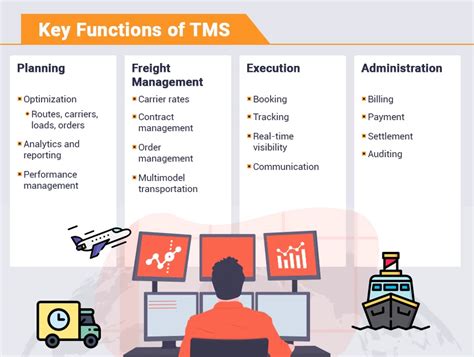
Discover the pivotal role of a Transportation Manager in logistics operations. Learn the 7 key duties, including route optimization, carrier management, and freight audit, to ensure efficient and cost-effective transportation of goods. Master the skills to streamline supply chain management, improve delivery times, and reduce transportation costs with this expert guide.
The role of a transportation manager is crucial in ensuring the smooth and efficient movement of goods, products, and people from one place to another. With the rise of globalization and e-commerce, the demand for effective transportation management has never been more critical. In this article, we will explore the 7 key duties of a transportation manager and how they contribute to the success of an organization.

Strategic Planning and Coordination
One of the primary duties of a transportation manager is to develop and implement strategic plans to ensure the efficient movement of goods and products. This involves coordinating with various stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers, to ensure that goods are delivered on time and in the right condition. A transportation manager must be able to analyze data and market trends to identify opportunities for improvement and optimize transportation routes and modes.
Supply Chain Optimization
A transportation manager plays a critical role in optimizing the supply chain by streamlining processes, reducing costs, and improving delivery times. This involves analyzing data on transportation modes, routes, and carriers to identify areas for improvement. By optimizing the supply chain, a transportation manager can help reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and increase competitiveness.
Carrier Management and Selection
Another key duty of a transportation manager is to select and manage carriers that can provide reliable and efficient transportation services. This involves evaluating carrier performance, negotiating contracts, and managing relationships with carriers. A transportation manager must be able to analyze data on carrier performance, including on-time delivery rates, claims rates, and customer satisfaction, to make informed decisions about carrier selection and management.
Carrier Selection Criteria
When selecting carriers, a transportation manager should consider the following criteria:
- On-time delivery rates
- Claims rates
- Customer satisfaction
- Cost
- Service quality
- Reputation

Risk Management and Compliance
A transportation manager must also ensure that all transportation activities are compliant with relevant laws and regulations, including those related to safety, security, and environmental protection. This involves developing and implementing risk management strategies to minimize the risk of accidents, cargo theft, and other disruptions to the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance
Some of the key regulations that a transportation manager must comply with include:
- Hours of Service (HOS) regulations
- Electronic Logging Device (ELD) regulations
- Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) regulations
- Customs regulations

Budgeting and Cost Control
A transportation manager is responsible for managing the transportation budget and controlling costs. This involves analyzing data on transportation costs, including fuel, labor, and equipment costs, to identify areas for cost reduction. A transportation manager must also be able to negotiate with carriers and suppliers to secure the best rates and terms.
Cost Control Strategies
Some of the key cost control strategies that a transportation manager can use include:
- Route optimization
- Load consolidation
- Mode optimization
- Carrier negotiation
- Fuel management

Performance Metrics and Monitoring
A transportation manager must also establish and track key performance metrics (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of transportation operations. This involves collecting and analyzing data on transportation performance, including on-time delivery rates, transit times, and cargo claims rates.
Key Performance Metrics
Some of the key performance metrics that a transportation manager should track include:
- On-time delivery rate
- Transit time
- Cargo claims rate
- Cost per mile
- Fuel efficiency
Communication and Collaboration
Finally, a transportation manager must be able to communicate effectively with various stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, and customers, to ensure that transportation operations are aligned with business objectives. This involves collaborating with other departments, such as logistics and supply chain management, to ensure that transportation operations are integrated with overall business strategy.
Communication Strategies
Some of the key communication strategies that a transportation manager can use include:
- Regular meetings with stakeholders
- Email updates
- Phone calls
- Performance reports
- Dashboards

Gallery of Transportation Management Images
Transportation Management Image Gallery






In conclusion, the role of a transportation manager is critical to the success of an organization. By performing these 7 key duties, a transportation manager can ensure that goods and products are delivered on time, in the right condition, and at the right cost. If you have any questions or comments about transportation management, please feel free to share them in the comments section below.
