Intro
Discover how ear pain affects the jaw, causing TMJ discomfort, jaw clicking, and facial tension, with 5 key ways ear issues impact jaw health and overall well-being.
Ear pain can be a debilitating and frustrating experience, affecting not only the ear itself but also surrounding areas, including the jaw. The connection between ear pain and jaw discomfort is more intricate than one might initially think, stemming from the complex anatomy of the head and neck region. Understanding how ear pain can radiate to or exacerbate jaw pain is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Here, we delve into the ways ear pain can impact the jaw, exploring the underlying mechanisms and potential remedies.
The human head and neck are a network of interconnected structures, with pain in one area often influencing another. Ear pain, whether due to infection, trauma, or other conditions, can lead to referred pain in the jaw. This phenomenon occurs because the nerves that transmit pain signals from the ear and jaw are closely linked, sometimes making it difficult to pinpoint the exact source of discomfort. For individuals experiencing ear pain that seems to be affecting their jaw, it's essential to consider the various pathways through which this pain can travel.
Ear pain can manifest in numerous ways, from sharp, stabbing sensations to dull, throbbing aches. When this pain radiates to the jaw, it can significantly impact daily activities such as eating, speaking, and even sleeping. The jaw, or temporomandibular joint (TMJ), is a complex structure that plays a critical role in these functions, and its discomfort can be a symptom of underlying issues that need medical attention. The connection between ear pain and jaw discomfort is multifaceted, involving anatomical, neurological, and sometimes psychological factors.
Understanding the Connection Between Ear Pain and Jaw Discomfort

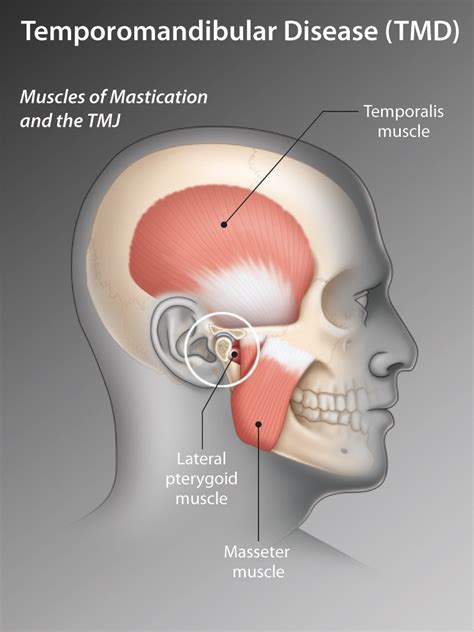
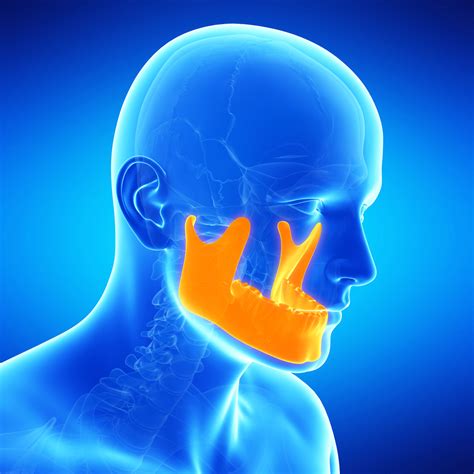
The ear and jaw are connected through a series of nerves and muscles. The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is located close to the ear, and the nerves that supply the TMJ also innervate parts of the ear. This proximity and shared innervation can lead to referred pain, where pain from one area is perceived in another. For instance, inflammation or infection in the ear can irritate the nerves that also serve the jaw, resulting in jaw pain or discomfort.
Shared Nerve Pathways
One of the primary reasons ear pain can affect the jaw is the shared nerve pathways. The trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for facial sensation, including pain, has branches that innervate both the ear and the jaw. When there is inflammation or irritation in the ear, it can stimulate these nerve branches, leading to the perception of pain in the jaw, even if the jaw itself is not directly affected.5 Ways Ear Pain Can Affect the Jaw

-
Referred Pain: As mentioned, the phenomenon of referred pain is a significant way ear pain can affect the jaw. The brain can misinterpret pain signals from the ear as originating from the jaw due to the complex innervation of the head and neck.
-
Muscle Tension: Pain in the ear can lead to muscle tension in the surrounding areas, including the jaw. This tension can cause discomfort, limited range of motion, and even exacerbate conditions like temporomandibular joint disorder (TMD).
-
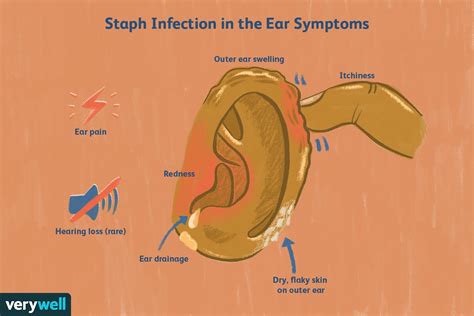
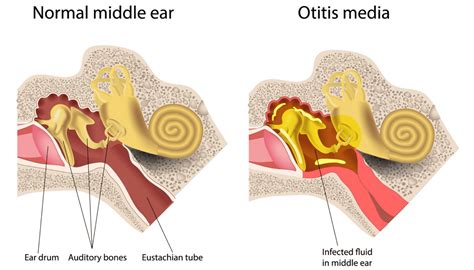
Nerve Stimulation: The stimulation of nerves that serve both the ear and the jaw can directly lead to jaw pain. This is particularly relevant in cases of ear infections or conditions that cause inflammation, such as otitis media or externa.
-
TMJ Disorders: Ear pain can sometimes be a symptom of underlying TMJ disorders. The proximity of the TMJ to the ear and the shared nerve pathways mean that issues with the jaw joint can radiate pain to the ear and vice versa.
-
Psychological Factors: In some cases, the perception of ear pain affecting the jaw can have psychological components. Stress and anxiety can exacerbate pain perception and lead to muscle tension, further complicating the relationship between ear and jaw pain.
Treatment and Management
Treating ear pain that affects the jaw requires a comprehensive approach, considering both the ear and the jaw. For infections, antibiotics may be prescribed, while anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce swelling and ease pain. In cases where TMJ disorders are involved, dental treatments, physical therapy, or even counseling for stress management may be necessary.Diagnosis and Treatment Options

Diagnosing the cause of ear pain that affects the jaw involves a thorough examination, including hearing tests, jaw movement assessments, and sometimes imaging studies like MRI or CT scans. Treatment options vary widely depending on the underlying cause but can include:
- Medications for pain and inflammation
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Dental treatments for TMJ disorders
- Physical therapy to improve jaw mobility and reduce muscle tension
- Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to address psychological factors
Prevention Strategies
Preventing ear pain from affecting the jaw involves maintaining good ear and jaw health. Regular dental check-ups can help identify and treat TMJ issues early. Practicing good hygiene, avoiding loud noises, and managing stress can also reduce the risk of developing conditions that lead to ear and jaw pain.Lifestyle Changes for Relief

Making certain lifestyle changes can provide relief from ear pain that affects the jaw. These include:
- Eating soft foods to reduce jaw strain
- Avoiding chewing gum or other habits that exacerbate jaw tension
- Practicing relaxation techniques to manage stress
- Getting regular exercise to improve overall health and reduce muscle tension
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the relationship between ear pain and jaw discomfort is complex and multifaceted. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, whether anatomical, neurological, or psychological, is key to effective management and treatment. By recognizing the signs of ear pain that affects the jaw and seeking appropriate medical attention, individuals can find relief from this debilitating condition. Future research into the interconnectedness of the head and neck region will continue to shed light on the best practices for diagnosis and treatment, offering hope for those suffering from these often interconnected pains.Final Thoughts on Ear Pain and Jaw Discomfort

As we continue to explore the intricacies of human anatomy and the complex interactions between different body parts, it becomes increasingly clear that a holistic approach to health is essential. Ear pain and jaw discomfort, while distinct, are often intertwined, highlighting the need for comprehensive care that addresses the whole individual, not just the symptoms.
Gallery of Ear and Jaw Conditions
Ear and Jaw Conditions Image Gallery




We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into the complex relationship between ear pain and jaw discomfort. Whether you're seeking to understand the causes, find relief from symptoms, or explore treatment options, it's essential to approach your health with a nuanced perspective that considers the interconnectedness of your body. By doing so, you'll be better equipped to navigate the challenges of ear and jaw pain, ultimately finding a path towards healing and wellness. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions in the comments below, and to spread awareness about the importance of holistic health by sharing this article with others.
