Intro
Discover the 5 most significant EU fines imposed on companies for major data breaches, violating the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Learn about the hefty penalties, non-compliance consequences, and the impact of data protection laws on businesses. Stay informed about EU data breach fines, GDPR enforcement, and cybersecurity regulations.
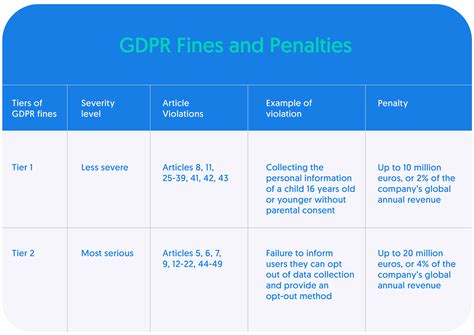
The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has been in effect since May 2018, aiming to protect the personal data of EU citizens and impose strict penalties on organizations that fail to comply. The GDPR has been instrumental in changing the way companies handle and protect sensitive information, and the fines imposed on non-compliant organizations have been substantial.
Why GDPR Fines Matter

The GDPR fines serve as a deterrent to companies that would otherwise neglect data protection. The regulation applies to any organization that processes the personal data of EU citizens, regardless of where the company is based. This means that businesses worldwide must take data protection seriously to avoid facing significant penalties.
5 Major Data Breach Penalties
In this section, we'll explore five major data breach penalties imposed by the EU under the GDPR. These cases demonstrate the severity of the fines and the importance of prioritizing data protection.
1. British Airways: €22 Million Fine
In 2020, British Airways was fined €22 million for a data breach that occurred in 2018. The breach affected over 400,000 customers, exposing their personal data, including credit card numbers and addresses. The UK's Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) imposed the fine, stating that British Airways had failed to implement adequate security measures to protect customer data.
Key Takeaway: Inadequate Security Measures
The British Airways case highlights the importance of implementing robust security measures to protect customer data. Companies must prioritize data protection and invest in adequate security measures to avoid facing significant fines.
2. Marriott International: €20.6 Million Fine
In 2020, Marriott International was fined €20.6 million for a data breach that occurred in 2018. The breach affected over 339 million customers, exposing their personal data, including passport numbers and credit card details. The ICO imposed the fine, stating that Marriott had failed to implement adequate security measures to protect customer data.
Key Takeaway: Due Diligence in Acquisitions
The Marriott International case highlights the importance of conducting thorough due diligence when acquiring other companies. Marriott acquired Starwood Hotels in 2016, but failed to identify and address the security vulnerabilities in Starwood's systems.
3. H&M: €35 Million Fine
In 2020, H&M was fined €35 million for a data breach that occurred in 2019. The breach affected over 425,000 employees, exposing their personal data, including salary information and social security numbers. The German data protection authority imposed the fine, stating that H&M had failed to implement adequate security measures to protect employee data.
Key Takeaway: Importance of Employee Data Protection
The H&M case highlights the importance of protecting employee data. Companies must prioritize the protection of employee data, including implementing adequate security measures and ensuring that employees are aware of data protection policies.
4. WhatsApp: €225 Million Fine
In 2021, WhatsApp was fined €225 million for a data breach that occurred in 2018. The breach affected over 1.3 billion users, exposing their personal data, including phone numbers and profile pictures. The Irish Data Protection Commission imposed the fine, stating that WhatsApp had failed to implement adequate security measures to protect user data.
Key Takeaway: Transparency in Data Protection
The WhatsApp case highlights the importance of transparency in data protection. Companies must be transparent about their data protection policies and procedures, ensuring that users are aware of how their data is being used and protected.
5. Amazon: €746 Million Fine
In 2021, Amazon was fined €746 million for a data breach that occurred in 2020. The breach affected over 1 billion users, exposing their personal data, including shopping history and browsing behavior. The Luxembourg National Commission for Data Protection imposed the fine, stating that Amazon had failed to implement adequate security measures to protect user data.
Key Takeaway: Importance of Data Minimization
The Amazon case highlights the importance of data minimization. Companies must only collect and process the minimum amount of personal data necessary to achieve their purposes, reducing the risk of data breaches and fines.
Lessons Learned from GDPR Fines
The GDPR fines imposed on these companies demonstrate the importance of prioritizing data protection. To avoid facing significant penalties, companies must:
- Implement robust security measures to protect customer and employee data
- Conduct thorough due diligence when acquiring other companies
- Protect employee data and ensure that employees are aware of data protection policies
- Be transparent about data protection policies and procedures
- Implement data minimization practices to reduce the risk of data breaches
Gallery of GDPR Fines
GDPR Fines Image Gallery









Conclusion: Prioritizing Data Protection
The GDPR fines imposed on these companies demonstrate the importance of prioritizing data protection. To avoid facing significant penalties, companies must implement robust security measures, conduct thorough due diligence, protect employee data, be transparent about data protection policies, and implement data minimization practices. By prioritizing data protection, companies can build trust with their customers and employees, and avoid the financial and reputational consequences of a data breach.
