Intro
Discover the 5 effects of soil erosion, including landslides, nutrient depletion, and sedimentation, impacting ecosystems, agriculture, and water quality, highlighting the importance of erosion control and conservation.
Soil erosion is a significant environmental issue that affects not only the quality of soil but also has far-reaching consequences on the ecosystem, biodiversity, and human societies. It is essential to understand the importance of soil erosion and its effects to mitigate its impact and preserve the health of our planet. Soil erosion occurs when the top layer of soil is removed or worn away, often due to human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, and poor agricultural practices. The effects of soil erosion are multifaceted and can have devastating consequences on the environment, economy, and human well-being.
Soil erosion can lead to a decline in soil fertility, reduced crop yields, and decreased agricultural productivity. This, in turn, can affect food security, particularly in regions where agriculture is the primary source of livelihood. Moreover, soil erosion can also lead to increased greenhouse gas emissions, as the exposed soil releases stored carbon into the atmosphere. The loss of topsoil can also alter the hydrological cycle, leading to changes in water quality and availability. It is crucial to address soil erosion to prevent these negative consequences and ensure a sustainable future.
The effects of soil erosion can be seen in various aspects of our lives, from the environment to the economy. It is vital to understand these effects to develop effective strategies for mitigating soil erosion and promoting sustainable land management practices. By adopting conservation tillage, cover cropping, and agroforestry, we can reduce soil erosion and promote soil health. Additionally, implementing policies and regulations that encourage sustainable land use practices can also help to mitigate the effects of soil erosion.
Soil Erosion and Its Impact on Biodiversity
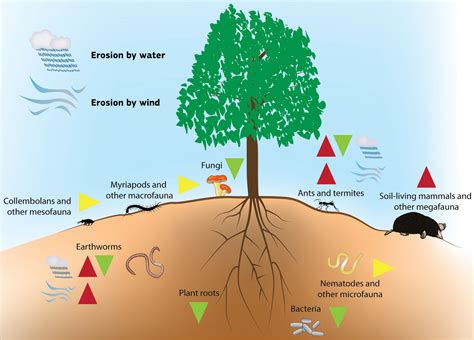
Soil erosion can also affect human health, as it can lead to the increased spread of diseases and pollutants. When soil is eroded, it can release pollutants and pathogens into waterways, posing a risk to human health. Moreover, soil erosion can also lead to the loss of soil organic matter, which is essential for filtering and purifying water. This can result in decreased water quality, making it unsuitable for human consumption. It is crucial to address soil erosion to protect human health and ensure access to clean water.
Effects of Soil Erosion on Water Quality

Soil erosion can also have significant economic consequences, particularly in regions where agriculture is the primary source of livelihood. When soil is eroded, it can lead to decreased crop yields and reduced agricultural productivity, resulting in economic losses. Moreover, soil erosion can also lead to increased costs for water treatment and infrastructure, as well as decreased property values. It is crucial to address soil erosion to mitigate its economic consequences and promote sustainable land management practices.
Soil Erosion and Its Impact on Food Security

Soil erosion can also have significant social consequences, particularly in regions where agriculture is the primary source of livelihood. When soil is eroded, it can lead to the loss of livelihoods and decreased economic opportunities, resulting in social instability. Soil erosion can also lead to the displacement of communities, as well as decreased access to basic services, including healthcare and education. It is crucial to address soil erosion to mitigate its social consequences and promote sustainable land management practices.
Strategies for Mitigating Soil Erosion
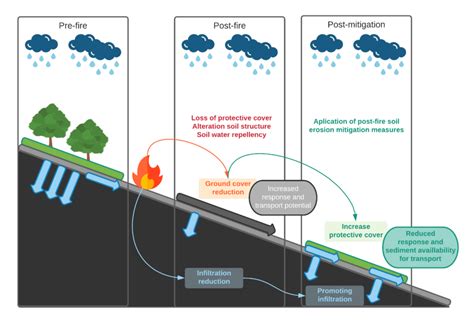
Soil erosion can also be mitigated through the use of terracing, contour farming, and buffer strips. Terracing involves creating flat plots of land on slopes to reduce soil erosion. Contour farming involves planting crops across slopes to reduce soil erosion. Buffer strips involve creating strips of vegetation along waterways to filter out sediment and pollutants. These strategies can help to reduce soil erosion and promote water quality.
Importance of Soil Conservation

Soil conservation can also have significant economic benefits, particularly in regions where agriculture is the primary source of livelihood. When soil is conserved, it can lead to increased crop yields and reduced agricultural productivity, resulting in economic gains. Moreover, soil conservation can also lead to increased property values, as well as decreased costs for water treatment and infrastructure. It is crucial to promote soil conservation to mitigate the economic consequences of soil erosion and promote sustainable land management practices.
Soil Erosion Prevention Techniques
There are several techniques for preventing soil erosion, including the use of geotextiles, riprap, and revegetation. Geotextiles involve using synthetic materials to stabilize the soil and prevent erosion. Riprap involves using rocks or other materials to armor the soil and prevent erosion. Revegetation involves planting vegetation to stabilize the soil and prevent erosion. These techniques can help to prevent soil erosion and promote soil health.Soil erosion prevention techniques can also include the use of soil amendments, such as compost or manure, to improve soil structure and fertility. Soil amendments can help to increase the water-holding capacity of the soil, reducing the risk of erosion. Moreover, soil amendments can also help to promote soil biota, which can help to stabilize the soil and prevent erosion.
Gallery of Soil Erosion
Soil Erosion Image Gallery









In conclusion, soil erosion is a significant environmental issue that affects not only the quality of soil but also has far-reaching consequences on the ecosystem, biodiversity, and human societies. It is essential to understand the importance of soil erosion and its effects to mitigate its impact and preserve the health of our planet. By adopting conservation tillage, cover cropping, and agroforestry, we can reduce soil erosion and promote soil health. Additionally, implementing policies and regulations that encourage sustainable land use practices can also help to mitigate the effects of soil erosion. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on soil erosion and its impact on the environment. Please comment below and share this article with others to raise awareness about the importance of soil conservation and sustainable land management practices.
