Discover the 8 facial bones, including maxilla, zygoma, and mandible, and learn about facial structure, skull anatomy, and cranial bones in this informative guide.
The human face is a complex and fascinating structure, comprising multiple bones that work together to provide a framework for our facial features. Among these, the 8 facial bones play a crucial role in forming the shape of our face, supporting our teeth, and facilitating various functions such as eating, speaking, and breathing. Understanding the structure and function of these bones is essential for appreciating the intricacies of the human face. In this article, we will delve into the world of facial bones, exploring their importance, functions, and characteristics.
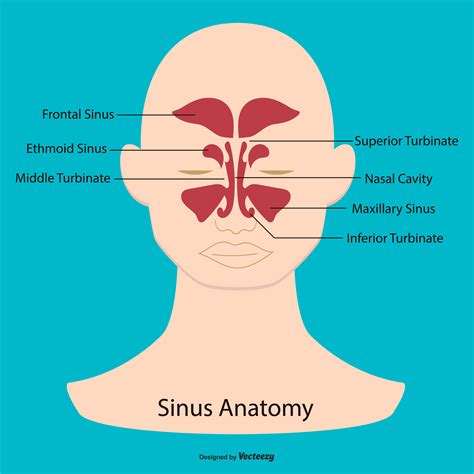
The 8 facial bones are a vital component of the human skull, which is made up of 22 bones in total. These bones are connected by sutures, which are fibrous joints that allow for minimal movement. The facial bones are responsible for forming the orbit (eye socket), nasal cavity, and mouth, as well as providing attachment points for muscles of facial expression. The 8 facial bones are: the frontal bone, zygomatic bones, nasal bones, lacrimal bones, palatine bones, inferior nasal conchae, maxillae, and mandible. Each of these bones has a unique shape and function, and together they form a complex and dynamic structure.
The study of facial bones is essential for various fields, including medicine, anthropology, and forensics. By analyzing the shape and structure of the facial bones, researchers can gain insights into human evolution, population dynamics, and individual characteristics. Additionally, understanding the facial bones is crucial for medical professionals, such as surgeons and dentists, who need to navigate the complex anatomy of the face to perform procedures and treatments. In this article, we will explore the 8 facial bones in detail, discussing their functions, characteristics, and importance in various contexts.
Introduction to Facial Bones
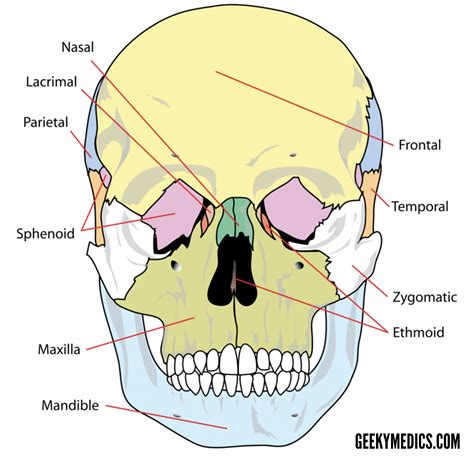
Functions of Facial Bones
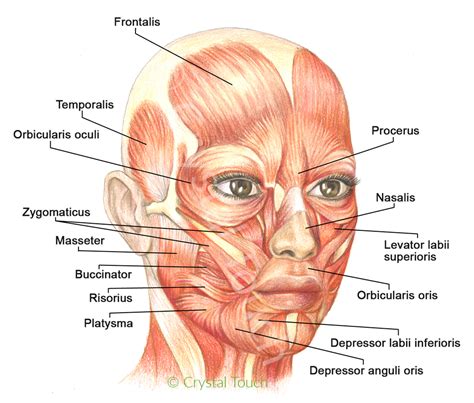
The facial bones have several important functions, including: * Forming the orbit (eye socket) and supporting the eyes * Creating the nasal cavity and supporting the nose * Providing attachment points for muscles of facial expression * Supporting the teeth and forming the jaw * Facilitating various functions such as eating, speaking, and breathing * Protecting the brain and other vital organsFrontal Bone
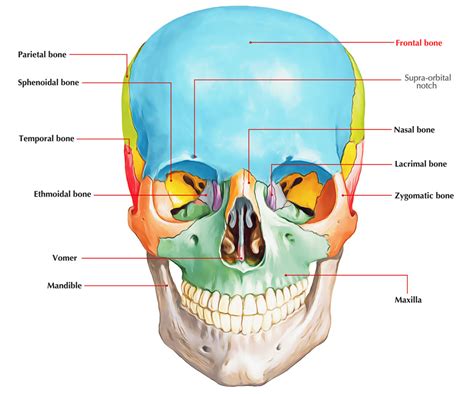
Characteristics of Frontal Bone
The frontal bone has several distinct characteristics, including: * A flat, fan-shaped structure * A smooth, convex surface * A rugged, irregular surface for muscle attachment * A small, triangular-shaped sinus (frontal sinus) that is filled with airZygomatic Bones
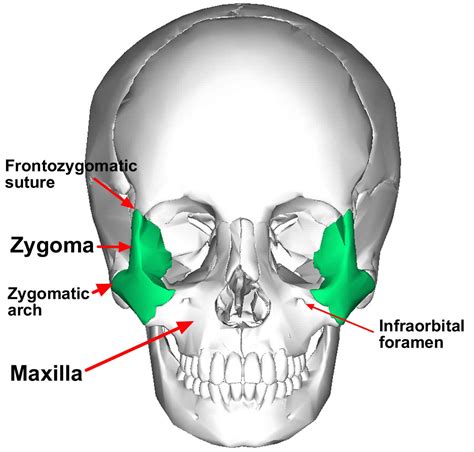
Characteristics of Zygomatic Bones
The zygomatic bones have several distinct characteristics, including: * A curved, quadrilateral shape * A smooth, convex surface * A rugged, irregular surface for muscle attachment * A small, triangular-shaped sinus (zygomatic sinus) that is filled with airNasal Bones
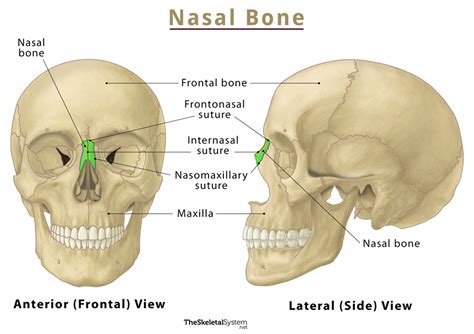
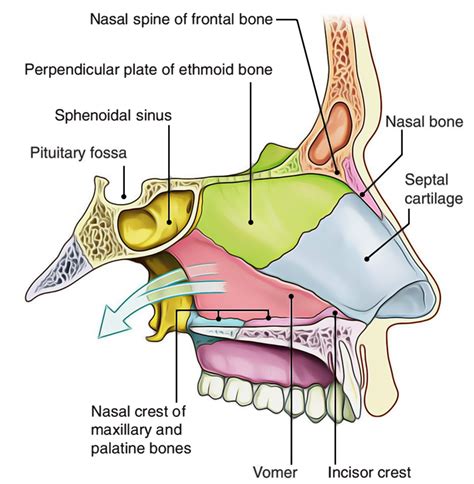
Characteristics of Nasal Bones
The nasal bones have several distinct characteristics, including: * A long, narrow shape * A smooth, convex surface * A rugged, irregular surface for muscle attachment * A small, triangular-shaped sinus (nasal sinus) that is filled with airLacrimal Bones
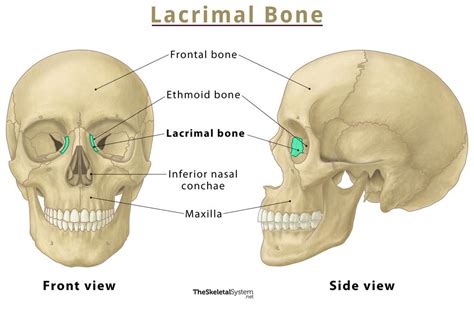
Characteristics of Lacrimal Bones
The lacrimal bones have several distinct characteristics, including: * A small, rectangular shape * A smooth, convex surface * A rugged, irregular surface for muscle attachment * A small, triangular-shaped sinus (lacrimal sinus) that is filled with airPalatine Bones
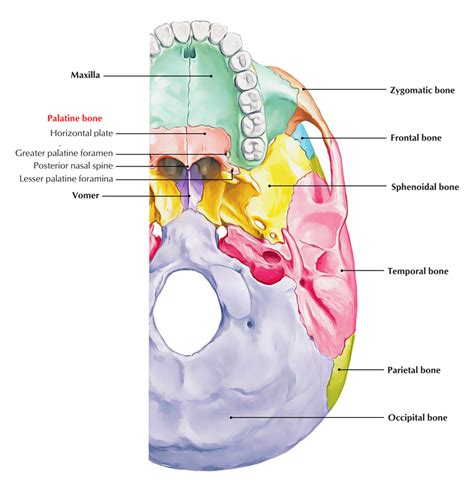
Characteristics of Palatine Bones
The palatine bones have several distinct characteristics, including: * A curved, quadrilateral shape * A smooth, convex surface * A rugged, irregular surface for muscle attachment * A small, triangular-shaped sinus (palatine sinus) that is filled with airInferior Nasal Conchae
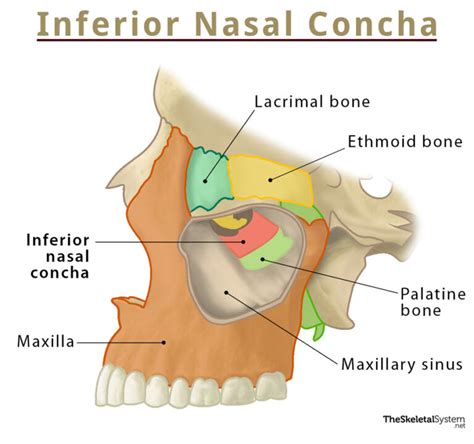
Characteristics of Inferior Nasal Conchae
The inferior nasal conchae have several distinct characteristics, including: * A long, narrow shape * A smooth, convex surface * A rugged, irregular surface for muscle attachment * A small, triangular-shaped sinus (inferior nasal sinus) that is filled with airMaxillae
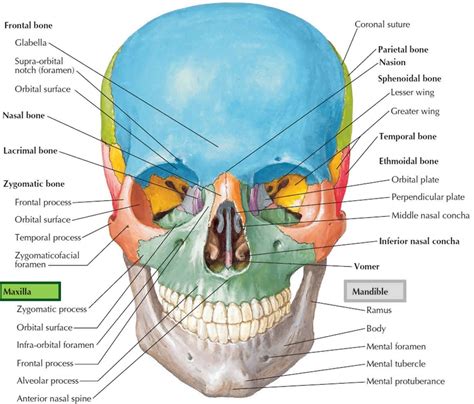
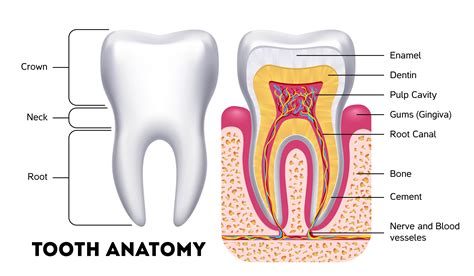
Characteristics of Maxillae
The maxillae have several distinct characteristics, including: * A curved, quadrilateral shape * A smooth, convex surface * A rugged, irregular surface for muscle attachment * A small, triangular-shaped sinus (maxillary sinus) that is filled with airMandible
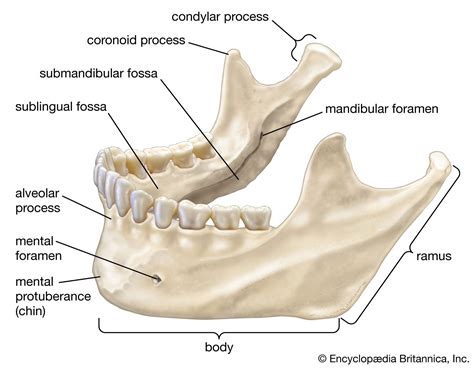
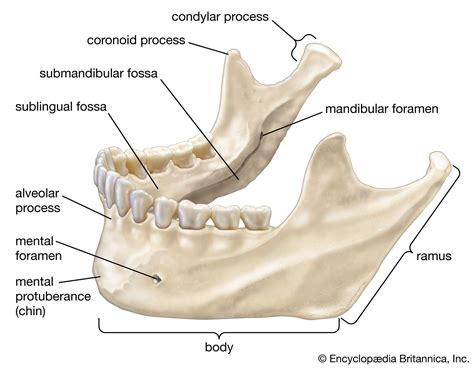
Characteristics of Mandible
The mandible has several distinct characteristics, including: * A curved, quadrilateral shape * A smooth, convex surface * A rugged, irregular surface for muscle attachment * A small, triangular-shaped sinus (mandibular sinus) that is filled with airFacial Bones Image Gallery
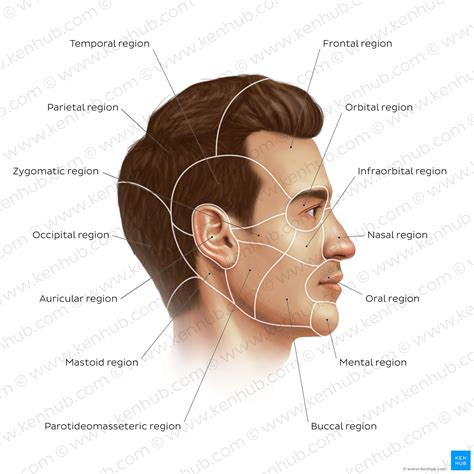
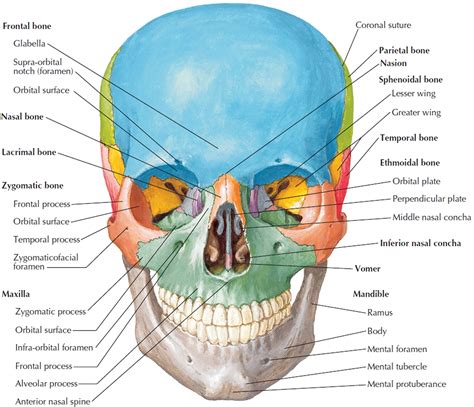
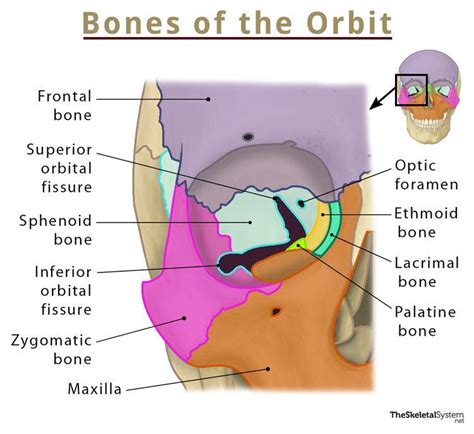
In conclusion, the 8 facial bones play a vital role in forming the structure of the face and facilitating various functions such as eating, speaking, and breathing. Understanding the characteristics and functions of these bones is essential for appreciating the intricacies of the human face and for various fields such as medicine, anthropology, and forensics. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the 8 facial bones and their importance in the human body. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to share them with us. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about the fascinating world of facial bones.
