Intro
Develop essential map skills with our interactive worksheet, designed to help learners explore and understand key elements on a map. Mastering map reading, navigation, and spatial awareness, this resource covers orientation, scale, legends, and more, perfect for geography students, travelers, and outdoor enthusiasts alike.
Learning to read and understand maps is an essential skill for anyone who loves to travel, explore new places, or simply navigate their surroundings. Maps provide a wealth of information about the world around us, from geographical features to man-made structures. In this article, we will delve into the world of maps and explore the various elements that make up a map, helping you to improve your map skills and become a more confident navigator.
Maps have been used for centuries to represent the world in a condensed and simplified way. From ancient civilizations to modern-day cartographers, maps have played a crucial role in helping people to understand their surroundings and plan their journeys. With the advent of technology, maps have become even more sophisticated, offering a wide range of features and tools to aid navigation.
Understanding Map Elements

To become proficient in reading maps, it's essential to understand the various elements that make up a map. These elements include:
- Legend: A key or legend is a crucial element on a map that explains the symbols, colors, and abbreviations used. It helps readers to understand the meaning behind the various markings on the map.
- Scale: The scale of a map indicates the relationship between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground. It's usually represented as a ratio, such as 1:10,000.
- Orientation: Maps typically have a north-south orientation, with north at the top. This helps readers to understand the direction of the map and navigate accordingly.
- Grid System: Many maps use a grid system to help readers locate specific points or features. The grid is usually made up of lines that intersect at right angles, forming squares or rectangles.
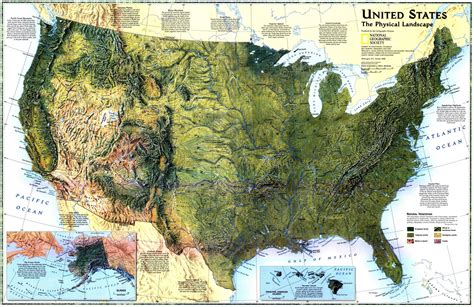
Geographical Features on a Map
Maps often represent various geographical features, including:
- Mountains and Hills: These are usually represented by contour lines or shading to indicate the height and shape of the terrain.
- Rivers and Lakes: These are typically represented by blue lines or shapes, with the width and shape of the line indicating the size and flow of the water.
- Forests and Woodlands: These are often represented by green shading or symbols, indicating the type and density of the vegetation.
- Coastlines and Boundaries: These are usually represented by a solid line, indicating the edge of a country, state, or other geographical feature.
Man-made Features on a Map
In addition to geographical features, maps often represent various man-made features, including:
- Roads and Highways: These are usually represented by solid lines, with the width and color of the line indicating the type and importance of the road.
- Buildings and Structures: These are often represented by symbols or shading, indicating the type and size of the building.
- Bridges and Tunnels: These are usually represented by a dashed line or a symbol, indicating the location and type of the bridge or tunnel.
Navigating with a Map
Now that we've explored the various elements on a map, let's talk about how to navigate using a map. Here are some tips:
- Orient the Map: Before starting to navigate, make sure to orient the map correctly, with north at the top.
- Use the Legend: Refer to the legend to understand the symbols and abbreviations used on the map.
- Measure Distances: Use the scale to measure distances between points on the map.
- Identify Landmarks: Look for recognizable landmarks, such as buildings or roads, to help navigate.
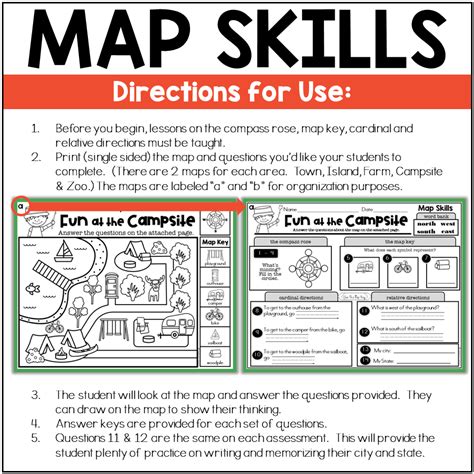
Map Skills Worksheet
To help you practice your map skills, we've included a worksheet with a series of exercises and questions. Try to complete the worksheet using the map elements and features we've discussed in this article.
- What is the scale of the map?
- What is the orientation of the map?
- Identify the following geographical features on the map:
- Mountains and hills
- Rivers and lakes
- Forests and woodlands
- Identify the following man-made features on the map:
- Roads and highways
- Buildings and structures
- Bridges and tunnels
- Measure the distance between two points on the map using the scale.
- Identify a recognizable landmark on the map and use it to navigate to a specific location.
Gallery of Map Elements
Map Elements Image Gallery
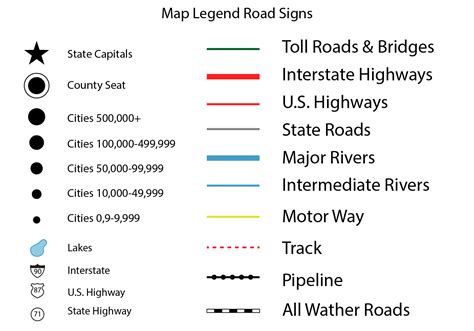
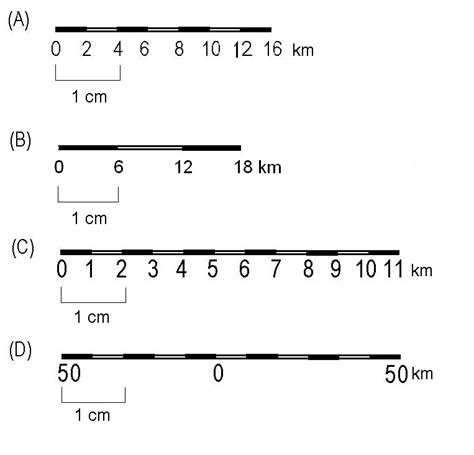




By understanding the various elements on a map, you can improve your navigation skills and become more confident in your ability to read and use maps. Remember to practice using the map skills worksheet and to explore different types of maps to become more familiar with the various features and symbols used.
