Intro
Discover the role of eumelanin and pheomelanin in melanin variations, influencing skin and hair color through pigment production, with effects on melanogenesis and photoprotection.
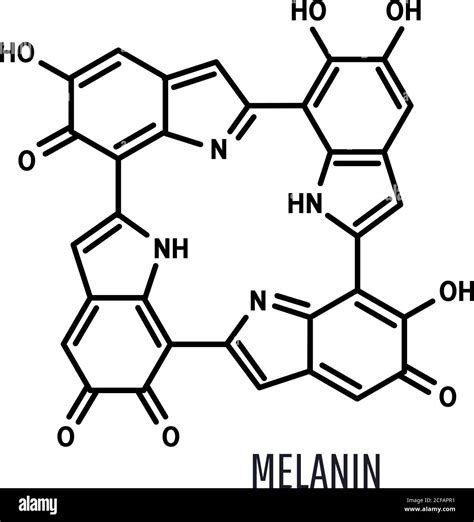
The human body is a complex and fascinating entity, with many intricate systems working together to create the unique individuals we are. One of the most interesting aspects of human biology is the production and distribution of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color. Melanin is not just a single substance, but rather a group of related compounds that come in different forms, each with its own distinct characteristics. In this article, we will delve into the world of melanin variations, specifically exploring the two main types: eumelanin and pheomelanin.
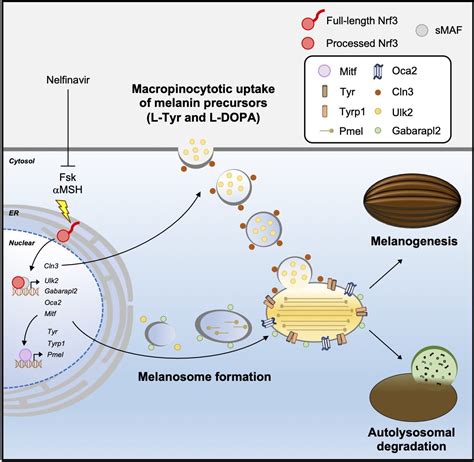
Melanin is produced by cells called melanocytes, which are found in the skin, hair follicles, and eyes. The production of melanin is a complex process that involves the interaction of multiple enzymes, hormones, and other factors. While melanin is often associated with skin color, it also plays a crucial role in protecting the body from damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The amount and type of melanin produced can vary greatly from person to person, resulting in a wide range of skin, hair, and eye colors.
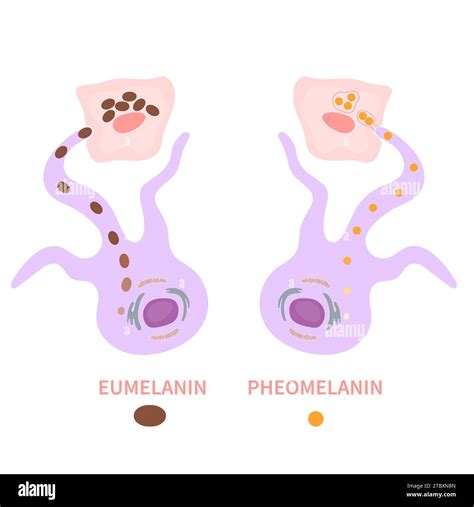
The diversity of human melanin is due in part to the existence of two main types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin is the most common type of melanin and is responsible for brown and black pigmentation. It is produced through a complex process involving the enzyme tyrosinase, which converts the amino acid tyrosine into eumelanin. Eumelanin is found in the skin, hair, and eyes, and is the primary pigment responsible for skin color.
Understanding Eumelanin

Eumelanin is a complex molecule that is made up of several subunits. It is produced in the melanosome, a specialized organelle found in melanocytes. The production of eumelanin is regulated by a variety of factors, including hormones, enzymes, and genetic mutations. Eumelanin is responsible for the brown and black colors found in skin, hair, and eyes, and is also involved in the production of freckles and moles.
Benefits of Eumelanin
Eumelanin has several benefits, including: * Protecting the skin from UV radiation * Reducing the risk of skin cancer * Improving skin health and appearance * Enhancing eye color and vision * Playing a role in the production of hair color and texturePheomelanin: The Reddish-Brown Pigment
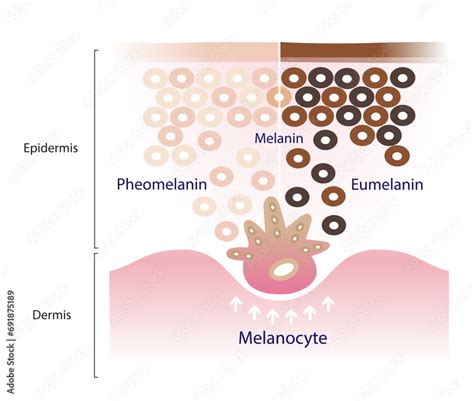
Pheomelanin is the second most common type of melanin and is responsible for reddish-brown pigmentation. It is produced through a similar process to eumelanin, but involves a different set of enzymes and intermediates. Pheomelanin is found in the skin, hair, and eyes, and is the primary pigment responsible for red and yellow colors.
Characteristics of Pheomelanin
Pheomelanin has several distinct characteristics, including: * A reddish-brown color * A higher sensitivity to UV radiation * A role in the production of freckles and moles * An association with an increased risk of skin cancer * A involvement in the production of hair color and textureInteractions Between Eumelanin and Pheomelanin

The interaction between eumelanin and pheomelanin is complex and not fully understood. However, it is known that the ratio of eumelanin to pheomelanin can affect skin, hair, and eye color. For example, individuals with a higher ratio of eumelanin to pheomelanin tend to have darker skin and hair, while those with a lower ratio tend to have lighter skin and hair.
Factors That Influence Melanin Production
Several factors can influence melanin production, including: * Genetics: Genetic mutations can affect the production of eumelanin and pheomelanin, resulting in changes to skin, hair, and eye color. * Hormones: Hormonal changes can stimulate or inhibit melanin production, resulting in changes to skin, hair, and eye color. * UV radiation: Exposure to UV radiation can stimulate melanin production, resulting in darker skin and an increased risk of skin cancer. * Nutrition: A diet rich in antioxidants and other nutrients can help protect the skin from damage caused by UV radiation and promote healthy melanin production.Melanin-Related Disorders

Several disorders are related to melanin production, including:
- Albinism: A genetic disorder characterized by a complete lack of melanin production.
- Vitiligo: A disorder characterized by the loss of melanin-producing cells, resulting in white patches on the skin.
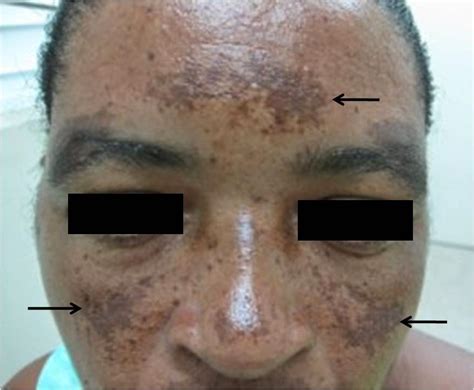
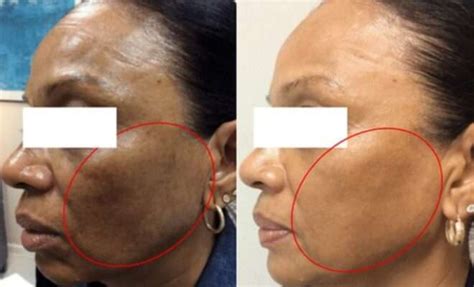
- Melasma: A disorder characterized by the overproduction of melanin, resulting in dark patches on the skin.
- Skin cancer: A type of cancer that can be caused by excessive exposure to UV radiation and abnormal melanin production.
Treatment Options for Melanin-Related Disorders
Treatment options for melanin-related disorders vary depending on the specific condition and its severity. Some common treatments include: * Topical creams and ointments to reduce inflammation and promote melanin production * Light therapy to stimulate melanin production * Surgery to remove affected skin or melanin-producing cells * Medications to reduce the risk of skin cancer and promote healthy melanin productionConclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, melanin is a complex and fascinating molecule that plays a crucial role in human biology. The two main types of melanin, eumelanin and pheomelanin, have distinct characteristics and functions, and their interaction can affect skin, hair, and eye color. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms of melanin production and the factors that influence it. By understanding more about melanin, we can develop new treatments for melanin-related disorders and promote healthy skin, hair, and eye color.
Melanin Image Gallery




We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of melanin variations, specifically eumelanin and pheomelanin. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about melanin and its role in human biology. By working together, we can promote a better understanding of melanin and its importance in maintaining healthy skin, hair, and eye color.
