Intro
Discover 5 examples of democracies, exploring democratic systems, democratic governments, and democratic countries, showcasing democratic values and principles in action, with a focus on democracy examples worldwide.
The concept of democracy has been a cornerstone of modern governance, aiming to provide citizens with a voice in how their country is run. Democracies come in various forms, each with its unique characteristics, strengths, and challenges. Understanding different democratic systems can offer insights into how diverse countries approach the ideals of freedom, equality, and representation. In this exploration, we will delve into five examples of democracies around the world, examining their structures, benefits, and the ways in which they engage their citizens.
Democracy, in its essence, is a system of government where power is vested in the people, either directly or through elected representatives. The core principles of democracy include free and fair elections, protection of individual rights and freedoms, and the rule of law. These principles are fundamental in ensuring that the government is accountable to its citizens and that the rights of all individuals are respected and protected.
The diversity in democratic systems is reflective of the unique histories, cultures, and values of different nations. For instance, some democracies are characterized by a strong presidential system, while others operate under a parliamentary framework. The choice of system often influences how policies are made, how leaders are held accountable, and how citizens participate in the political process.
Introduction to Democracies

As we explore the examples of democracies, it's crucial to understand that each country's approach to democracy is shaped by its specific context. Factors such as the country's size, economic system, and social structure play significant roles in determining the democratic model that is adopted. Furthermore, the effectiveness of a democracy is not solely measured by its structure but also by how well it serves the needs and aspirations of its citizens.
Characteristics of Democracies
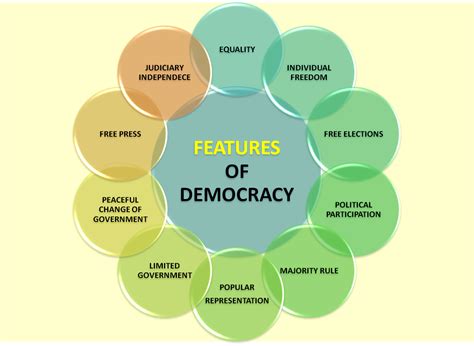
Democracies are characterized by several key elements, including competitive elections, political pluralism, and the protection of human rights. These elements are essential for ensuring that power is distributed evenly and that no single entity dominates the political landscape. Additionally, democracies often have independent judiciaries and free media, which serve as checks on power and provide citizens with accurate information to make informed decisions.
Types of Democracies
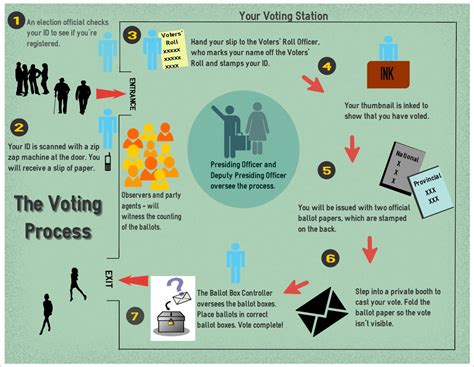
There are several types of democracies, each with its unique features. For example, direct democracy involves citizens making decisions directly, either through referendums or initiatives. Representative democracy, on the other hand, involves citizens electing representatives to make decisions on their behalf. Hybrid systems combine elements of both, offering a balanced approach to governance.Examples of Democracies
Let's consider five notable examples of democracies: the United States, Germany, India, Australia, and Sweden. Each of these countries has a distinct approach to democracy, reflecting their historical, cultural, and political contexts.
-
United States: The U.S. operates under a federal constitutional republic framework, with a strong emphasis on individual rights and freedoms. Its democratic system is characterized by a presidential system, where the president serves as both the head of state and the head of government.
-
Germany: Germany's democracy is built on a federal parliamentary republic model. This system emphasizes coalition building and consensus, often leading to more stable and enduring governments. Germany's approach to democracy also places a strong emphasis on social welfare and environmental protection.
-
India: As the world's largest democracy, India operates under a federal parliamentary democratic republic system. Its democracy is marked by a diverse and vibrant political landscape, with numerous political parties and a strong emphasis on state and local governance.
-
Australia: Australia's democracy is characterized by a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy. This unique system combines elements of monarchy and republicanism, with the monarch serving as the head of state and a prime minister as the head of government. Australia's democracy is also notable for its compulsory voting system, which ensures high levels of political participation.
-
Sweden: Sweden's democracy is often cited as an example of a successful social democracy. It operates under a parliamentary representative democratic constitutional monarchy, with a strong emphasis on social welfare, equality, and environmental sustainability. Sweden's democratic system is characterized by a high level of transparency and citizen participation.
Benefits of Democracies

The benefits of democracies are numerous and well-documented. Democracies tend to have higher levels of economic prosperity, better human rights records, and more stable political environments. They also foster innovation, creativity, and progress, as they encourage the free exchange of ideas and the protection of individual freedoms.
Challenges Facing Democracies
Despite their many benefits, democracies also face significant challenges. These include the threat of authoritarianism, the erosion of trust in institutions, and the impact of disinformation and polarization. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from citizens, leaders, and institutions to uphold the principles of democracy and ensure that democratic systems remain vibrant and effective.Engaging Citizens in Democracies

Engaging citizens is crucial for the health and vitality of democracies. This can be achieved through various means, including voter education programs, public debates, and participatory budgeting processes. Technology also plays a significant role, with online platforms and digital tools providing new avenues for citizens to access information, participate in discussions, and influence policy decisions.
Empowering Future Democracies
As the world continues to evolve, it's essential to empower future democracies by promoting democratic values, supporting democratic institutions, and fostering a culture of participation and engagement. This involves not only strengthening existing democracies but also assisting countries transitioning to democratic systems. International cooperation, education, and dialogue are key in this endeavor, as they help to build a global community that values democracy and human rights.Democracy Image Gallery








In conclusion, democracies around the world offer a glimpse into the diverse ways in which the principles of democracy can be applied. From the presidential system of the United States to the parliamentary democracy of Germany, each country's unique approach to governance reflects its history, culture, and values. As we move forward, it's essential to learn from these examples, to address the challenges facing democracies, and to empower future generations to participate in and strengthen democratic systems. We invite you to share your thoughts on the importance of democracy, how you think democracies can be improved, and what actions can be taken to promote democratic values globally. Your engagement and participation are crucial in shaping the future of democracies and ensuring that these systems continue to serve the needs and aspirations of citizens around the world.
