Intro
Master the art of Two-Factor Analysis with our expert guide. Learn how to excel in Anova Two Factor Analysis and uncover the significance of interaction effects, main effects, and error rates. Discover the benefits of 2-way Anova, including improved statistical power and precision, and how to apply it in research and real-world applications.
As researchers and data analysts, we often encounter situations where we need to analyze the effect of two or more independent variables on a continuous outcome variable. This is where the two-factor Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) comes into play. Two-factor ANOVA is a powerful statistical technique that helps us understand the relationship between two independent variables and a continuous outcome variable. In this article, we will explore six ways to excel in two-factor ANOVA analysis.
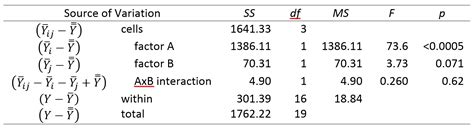
Understanding the Basics of Two-Factor ANOVA
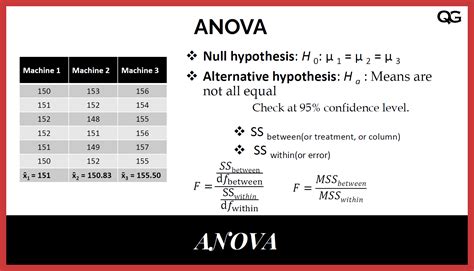
Before we dive into the six ways to excel in two-factor ANOVA, let's first understand the basics of this statistical technique. Two-factor ANOVA is used to analyze the effect of two independent variables ( factors) on a continuous outcome variable. The two factors can be either categorical or continuous, but the outcome variable must be continuous. The goal of two-factor ANOVA is to determine if there is a significant interaction between the two factors and if each factor has a significant effect on the outcome variable.
1. Clearly Define the Research Question and Hypotheses
The first step to exceling in two-factor ANOVA is to clearly define the research question and hypotheses. What is the research question that you want to answer? What are the hypotheses that you want to test? Make sure that your research question and hypotheses are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). A well-defined research question and hypotheses will guide the entire analysis process.

2. Check the Assumptions of Two-Factor ANOVA
The second step is to check the assumptions of two-factor ANOVA. These assumptions include normality, homogeneity of variance, and independence of observations. Make sure that your data meet these assumptions before proceeding with the analysis. If your data do not meet these assumptions, you may need to transform your data or use alternative statistical techniques.
3. Use the Correct Statistical Software
The third step is to use the correct statistical software to perform the two-factor ANOVA analysis. There are many statistical software packages that can perform two-factor ANOVA, including R, Python, SPSS, and SAS. Choose the software that you are most familiar with and that meets your analysis needs.
4. Interpret the Results Correctly
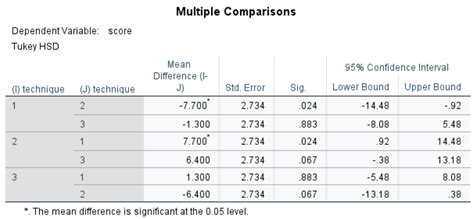
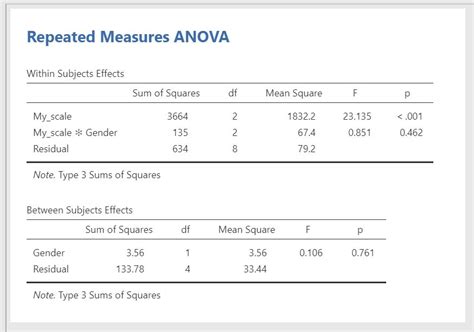
The fourth step is to interpret the results correctly. The output of two-factor ANOVA includes the F-statistic, p-value, and effect size. Make sure that you understand what each of these statistics means and how to interpret them correctly. The F-statistic indicates whether there is a significant interaction between the two factors and whether each factor has a significant effect on the outcome variable. The p-value indicates the probability of obtaining the observed results (or more extreme) assuming that the null hypothesis is true. The effect size indicates the magnitude of the effect of each factor on the outcome variable.
5. Visualize the Results
The fifth step is to visualize the results. Visualization is an essential step in data analysis, as it helps to communicate complex results in a simple and intuitive way. Use plots and charts to visualize the interaction between the two factors and the effect of each factor on the outcome variable.
6. Report the Results Correctly
The sixth and final step is to report the results correctly. When reporting the results, make sure to include the research question and hypotheses, the statistical software used, the assumptions checked, the results of the two-factor ANOVA analysis, and the interpretation of the results. Use tables and figures to present the results in a clear and concise way.
Gallery of Two-Factor ANOVA Images
Two-Factor ANOVA Image Gallery
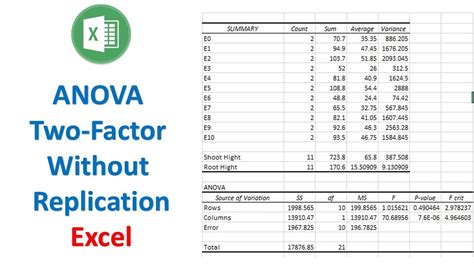
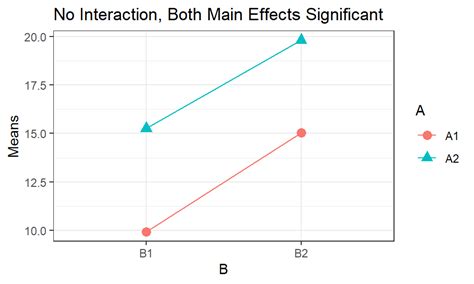
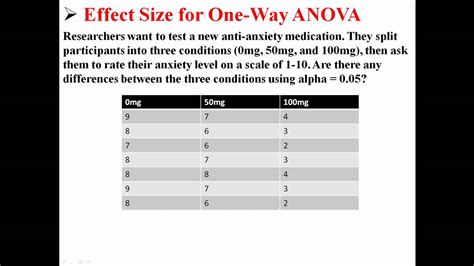

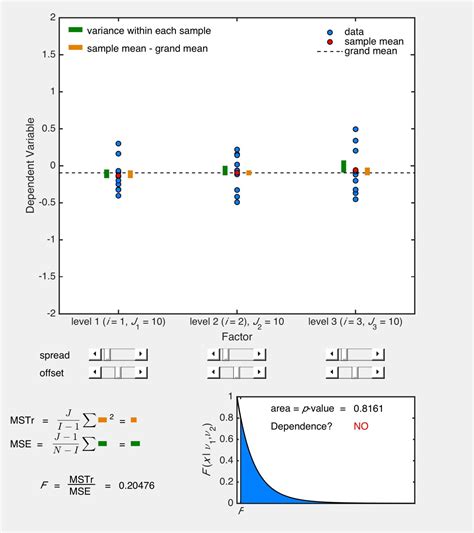


Conclusion
In conclusion, two-factor ANOVA is a powerful statistical technique that helps us understand the relationship between two independent variables and a continuous outcome variable. By following the six steps outlined in this article, you can excel in two-factor ANOVA analysis and make informed decisions based on your research findings. Remember to clearly define the research question and hypotheses, check the assumptions of two-factor ANOVA, use the correct statistical software, interpret the results correctly, visualize the results, and report the results correctly.
