Conditional formatting is a powerful tool in spreadsheet applications like Google Sheets or Microsoft Excel that allows you to highlight cells based on specific conditions. This feature is particularly useful when working with text data, as it enables you to visually identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in your dataset. In this article, we will explore five ways to excel with conditional formatting based on text, providing you with practical examples and step-by-step instructions to enhance your data analysis skills.
Method 1: Highlighting Cells Containing Specific Text
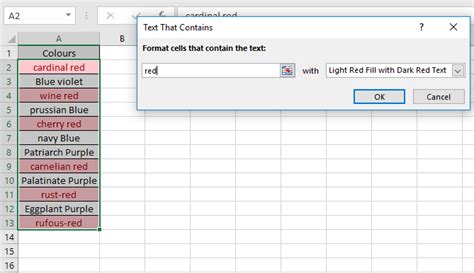
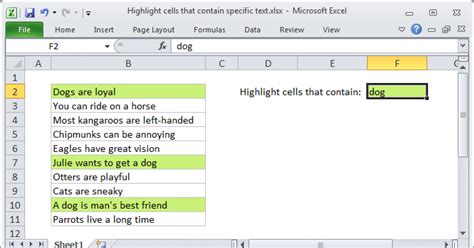
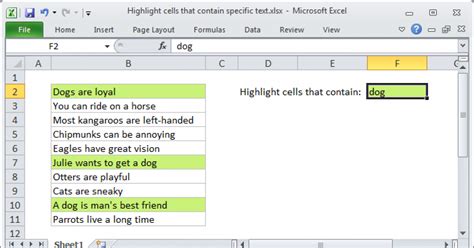
One of the most common uses of conditional formatting based on text is to highlight cells containing specific words or phrases. This feature is particularly useful when searching for errors or inconsistencies in your data.
To apply this formatting rule:
- Select the range of cells you want to format.
- Go to the "Home" tab in the ribbon.
- Click on "Conditional Formatting" in the "Styles" group.
- Select "New Rule" from the dropdown menu.
- Choose "Use a formula to determine which cells to format."
- Enter the formula:
=A1="specific text"(replace "specific text" with the text you want to search for). - Click "Format" and select the desired formatting options (e.g., fill color, font color, etc.).
- Click "OK" to apply the rule.
For example, if you want to highlight cells containing the word "error" in a column, you can use the formula =A1="error".
Example Use Case:
Suppose you have a dataset of customer feedback, and you want to highlight all the cells containing the word "complaint." By using the formula =A1="complaint", you can quickly identify the cells that require attention.
Method 2: Highlighting Cells Containing Text Starting with a Specific Character
Another useful application of conditional formatting based on text is to highlight cells containing text starting with a specific character. This feature is particularly useful when working with datasets containing prefixes or codes.
To apply this formatting rule:
- Select the range of cells you want to format.
- Go to the "Home" tab in the ribbon.
- Click on "Conditional Formatting" in the "Styles" group.
- Select "New Rule" from the dropdown menu.
- Choose "Use a formula to determine which cells to format."
- Enter the formula:
=LEFT(A1,1)="specific character"(replace "specific character" with the character you want to search for). - Click "Format" and select the desired formatting options (e.g., fill color, font color, etc.).
- Click "OK" to apply the rule.
For example, if you want to highlight cells containing text starting with the letter "A," you can use the formula =LEFT(A1,1)="A".
Example Use Case:
Suppose you have a dataset of employee IDs, and you want to highlight all the IDs starting with the letter "E." By using the formula =LEFT(A1,1)="E", you can quickly identify the employees who meet this criterion.
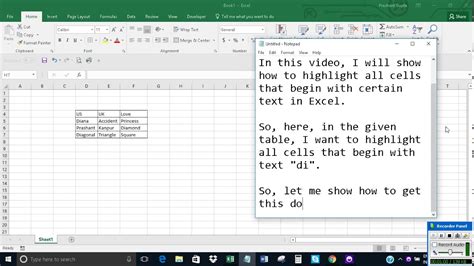
Method 3: Highlighting Cells Containing Text Ending with a Specific Character
You can also use conditional formatting to highlight cells containing text ending with a specific character. This feature is particularly useful when working with datasets containing suffixes or extensions.
To apply this formatting rule:
- Select the range of cells you want to format.
- Go to the "Home" tab in the ribbon.
- Click on "Conditional Formatting" in the "Styles" group.
- Select "New Rule" from the dropdown menu.
- Choose "Use a formula to determine which cells to format."
- Enter the formula:
=RIGHT(A1,1)="specific character"(replace "specific character" with the character you want to search for). - Click "Format" and select the desired formatting options (e.g., fill color, font color, etc.).
- Click "OK" to apply the rule.
For example, if you want to highlight cells containing text ending with the letter "T," you can use the formula =RIGHT(A1,1)="T".
Example Use Case:
Suppose you have a dataset of file names, and you want to highlight all the files ending with the extension ".docx." By using the formula =RIGHT(A1,4)=".docx", you can quickly identify the files that meet this criterion.
Method 4: Highlighting Cells Containing Text with a Specific Length
You can also use conditional formatting to highlight cells containing text with a specific length. This feature is particularly useful when working with datasets containing codes or passwords.
To apply this formatting rule:
- Select the range of cells you want to format.
- Go to the "Home" tab in the ribbon.
- Click on "Conditional Formatting" in the "Styles" group.
- Select "New Rule" from the dropdown menu.
- Choose "Use a formula to determine which cells to format."
- Enter the formula:
=LEN(A1)=specific length(replace "specific length" with the length you want to search for). - Click "Format" and select the desired formatting options (e.g., fill color, font color, etc.).
- Click "OK" to apply the rule.
For example, if you want to highlight cells containing text with a length of 10 characters, you can use the formula =LEN(A1)=10.
Example Use Case:
Suppose you have a dataset of passwords, and you want to highlight all the passwords with a length of 12 characters. By using the formula =LEN(A1)=12, you can quickly identify the passwords that meet this criterion.
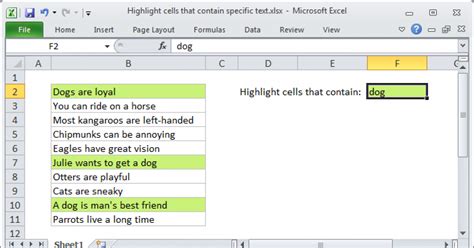
Method 5: Highlighting Cells Containing Text with a Specific Pattern
Finally, you can use conditional formatting to highlight cells containing text with a specific pattern. This feature is particularly useful when working with datasets containing patterns or codes.
To apply this formatting rule:
- Select the range of cells you want to format.
- Go to the "Home" tab in the ribbon.
- Click on "Conditional Formatting" in the "Styles" group.
- Select "New Rule" from the dropdown menu.
- Choose "Use a formula to determine which cells to format."
- Enter the formula:
=REGEXMATCH(A1,"specific pattern")(replace "specific pattern" with the pattern you want to search for). - Click "Format" and select the desired formatting options (e.g., fill color, font color, etc.).
- Click "OK" to apply the rule.
For example, if you want to highlight cells containing text with the pattern "AB-####", you can use the formula =REGEXMATCH(A1,"AB-\d{4}").
Example Use Case:
Suppose you have a dataset of customer IDs, and you want to highlight all the IDs with the pattern "AB-####." By using the formula =REGEXMATCH(A1,"AB-\d{4}"), you can quickly identify the customers who meet this criterion.
Conditional Formatting Image Gallery
In conclusion, conditional formatting based on text is a powerful feature in spreadsheet applications that can help you to visualize and analyze your data more effectively. By using the methods outlined in this article, you can create custom formatting rules to highlight cells containing specific text, characters, lengths, and patterns. Remember to experiment with different formulas and formatting options to get the most out of this feature. Share your own conditional formatting tips and tricks in the comments below!
