Intro
Boost your Excel productivity with VBA! Learn how to copy ranges with ease using Visual Basic for Applications. Master the art of automating tasks and streamline your workflow with our expert guide. Discover the power of VBA in Excel and take your spreadsheet skills to the next level.
When working with large datasets in Excel, copying and pasting ranges can be a tedious and time-consuming task. Fortunately, Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) can help automate this process, making it more efficient and reducing the risk of errors. In this article, we will explore how to copy ranges with ease in Excel using VBA.
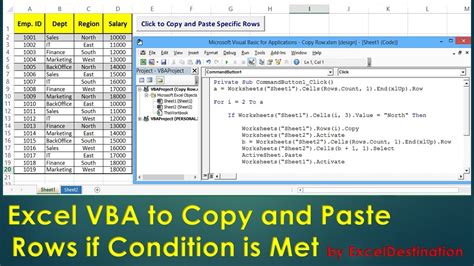
The Importance of Efficient Data Transfer
In today's fast-paced business environment, being able to quickly and accurately transfer data between worksheets, workbooks, or even applications is crucial. Manual copying and pasting can lead to mistakes, wasted time, and frustration. By leveraging VBA, you can streamline your workflow, reduce errors, and increase productivity.
Basic VBA Concepts
Before diving into the world of VBA, it's essential to understand some basic concepts:
- Variables: Store and manipulate data using variables, such as
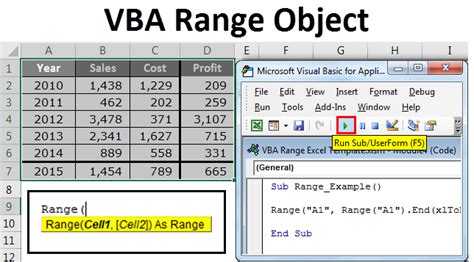
Range,Worksheet, andWorkbook. - Objects: Interact with Excel objects, like worksheets, ranges, and charts.
- Methods: Perform actions on objects, such as
CopyandPaste. - Properties: Access and modify object attributes, like
ValueandFormula.
Copying Ranges with VBA
To copy a range using VBA, you'll need to:
- Declare variables for the source and destination ranges.
- Use the
Rangeobject to specify the source range. - Employ the
Copymethod to copy the range. - Specify the destination range using the
Rangeobject. - Use the
Pastemethod to paste the copied range.
Here's a simple example:
Sub CopyRangeExample()
' Declare variables
Dim sourceRange As Range
Dim destinationRange As Range
' Set source range
Set sourceRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A1:B2")
' Copy source range
sourceRange.Copy
' Set destination range
Set destinationRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet2").Range("C3:D4")
' Paste copied range
destinationRange.Paste
End Sub
Tips and Variations
- Copy and Paste Values: To copy only values, use the
PasteSpecialmethod with thexlPasteValuesargument. - Copy and Paste Formulas: To copy formulas, use the
PasteSpecialmethod with thexlPasteFormulasargument. - Copy and Paste Formatting: To copy formatting, use the
PasteSpecialmethod with thexlPasteFormatsargument. - Dynamic Ranges: Use variables to dynamically define the source and destination ranges based on user input or data changes.
Advanced Techniques
- Looping through Ranges: Use
Forloops to iterate through multiple ranges and perform actions on each one. - Conditional Copying: Use
Ifstatements to copy ranges based on specific conditions, such as cell values or formatting. - Error Handling: Implement error handling mechanisms, like
On Error Resume Next, to handle unexpected errors during the copying process.
Best Practices
- Use Meaningful Variable Names: Choose descriptive variable names to improve code readability and maintainability.
- Keep Code Organized: Structure your code using modules, procedures, and comments to facilitate understanding and modification.
- Test Thoroughly: Verify your code's functionality and performance before deploying it in a production environment.
Conclusion
Copying ranges with ease in Excel using VBA can significantly improve your productivity and reduce errors. By understanding the basics of VBA, leveraging its power, and following best practices, you can automate tedious tasks and focus on higher-level activities. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced VBA user, this article has provided you with a solid foundation to take your data transfer skills to the next level.
Excel VBA Copy Range Image Gallery