Intro
Discover the ultimate showdown between Excel on Mac vs Windows. Learn how the two operating systems impact spreadsheet performance, compatibility, and user experience. Explore key differences in features, shortcuts, and integrations to decide which platform is best for your Excel needs, from data analysis to visualization.
As one of the most widely used spreadsheet software in the world, Microsoft Excel is a powerful tool for data analysis, visualization, and management. Whether you're a business professional, student, or simply a data enthusiast, Excel is an essential tool to have in your arsenal. But when it comes to choosing the right platform to run Excel on, the debate between Mac and Windows often arises. In this article, we'll delve into the details of Excel on Mac vs Windows, exploring the differences, similarities, and ultimately, which platform is better suited for your needs.

Similarities Between Excel on Mac and Windows
Before we dive into the differences, it's essential to note that Excel on Mac and Windows share many similarities. Both versions offer the same core features, including:
- Data analysis and visualization tools
- Formula and function support
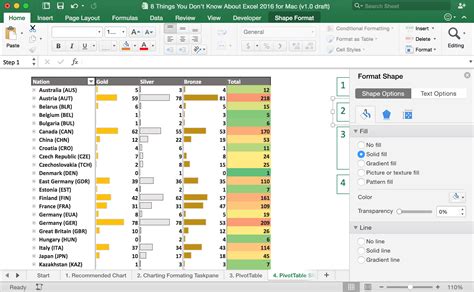
- PivotTables and charts
- Conditional formatting and filtering
- Collaboration and sharing features
In terms of functionality, both Mac and Windows versions of Excel are virtually identical. You can create, edit, and share spreadsheets with ease, regardless of the platform you choose.
Differences Between Excel on Mac and Windows
While the core functionality remains the same, there are some key differences between Excel on Mac and Windows:
- User Interface: The most noticeable difference is the user interface. Excel on Mac has a more streamlined and minimalist design, which may appeal to those who value aesthetics. On the other hand, Excel on Windows has a more traditional and familiar interface, which may be preferred by those who are accustomed to the Windows environment.
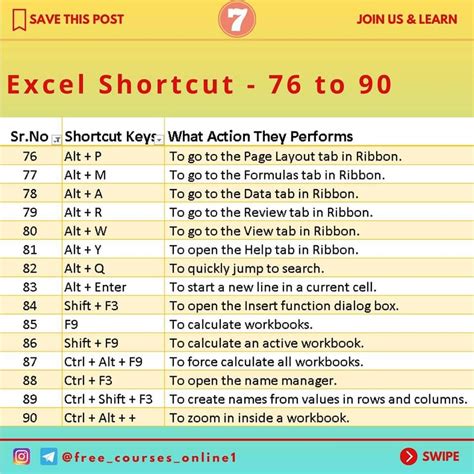
- Shortcut Keys: Another difference lies in the shortcut keys. Mac users will need to use the Command (⌘) key instead of the Control key, which can take some getting used to. For example, the shortcut to copy a cell is ⌘+C on Mac, whereas it's Ctrl+C on Windows.
- File System: The file system on Mac and Windows differs, which can affect how you manage and store your Excel files. Mac uses the APFS (Apple File System) file system, while Windows uses the NTFS (New Technology File System) file system.
- Integration with Other Microsoft Office Apps: Excel on Windows integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft Office apps, such as Word and PowerPoint. While Mac users can still use these apps, the integration may not be as smooth.
Performance and Compatibility
In terms of performance, both Mac and Windows versions of Excel can handle large datasets and complex calculations with ease. However, some users may notice slight differences in performance, depending on the specific hardware and software configuration.
When it comes to compatibility, Excel on Mac and Windows can both read and write files in the same format (.xlsx,.xls, etc.). However, some users may encounter issues when sharing files between platforms, particularly if they use specific features or add-ins.
Add-ins and Plugins
Speaking of add-ins and plugins, Excel on Windows has a more extensive library of third-party tools and extensions available. This can be a significant advantage for Windows users, particularly those in industries that rely heavily on specific software integrations.
Cost and Licensing
Finally, let's talk about cost and licensing. Excel on Mac and Windows can be purchased as part of the Microsoft Office suite or as a standalone application. However, the pricing and licensing models differ between the two platforms.
Mac users can purchase Excel as part of the Microsoft Office 365 subscription, which includes access to other Office apps, such as Word, PowerPoint, and Outlook. Windows users, on the other hand, can purchase Excel as part of the Microsoft Office suite or as a standalone application, with various pricing options available.
Which Platform is Better for You?
Ultimately, the choice between Excel on Mac and Windows depends on your individual needs and preferences. If you're already invested in the Mac ecosystem and value the streamlined design and user interface, Excel on Mac may be the better choice for you.
On the other hand, if you're already familiar with the Windows environment and prefer the traditional interface, Excel on Windows may be the way to go. Additionally, if you rely heavily on specific third-party add-ins or plugins, Windows may be the better option.
Tips and Tricks for Using Excel on Mac and Windows
Regardless of which platform you choose, here are some tips and tricks to help you get the most out of Excel:
- Use keyboard shortcuts: Familiarize yourself with the keyboard shortcuts for both Mac and Windows to increase productivity and efficiency.
- Customize your ribbon: Tailor your ribbon to fit your specific needs and workflow.
- Use data validation: Ensure data accuracy and consistency with data validation rules.
- Leverage pivot tables: Unlock the power of pivot tables to analyze and visualize complex data.
- Explore add-ins and plugins: Discover new tools and extensions to enhance your Excel experience.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the debate between Excel on Mac and Windows ultimately comes down to personal preference and specific needs. While both platforms offer the same core functionality, differences in user interface, shortcut keys, file system, and integration with other Microsoft Office apps may influence your decision.
By understanding the similarities and differences between Excel on Mac and Windows, you can make an informed decision and get the most out of your spreadsheet software.
Share Your Thoughts!
We'd love to hear from you! Share your experiences with Excel on Mac and Windows in the comments below. Which platform do you prefer, and why? Do you have any favorite tips or tricks to share?
Excel Image Gallery