Intro
Discover the power of Excel in calculating sample sizes with ease. Learn how to use an Excel sample size calculator to determine the ideal sample size for your research or statistical analysis. Master confidence levels, margin of error, and population sizes to make informed decisions. Say goodbye to manual calculations and hello to data-driven insights.
The importance of accurate sample size calculation cannot be overstated in various fields, including research, marketing, and finance. Incorrect sample sizes can lead to unreliable results, wasted resources, and poor decision-making. Fortunately, Excel offers a convenient and user-friendly solution for calculating sample sizes, making it an essential tool for professionals and students alike. In this article, we will explore the world of sample size calculation in Excel, providing a comprehensive guide on how to use this powerful feature.
The Benefits of Using Excel for Sample Size Calculation
Excel offers several advantages when it comes to calculating sample sizes. Firstly, it is widely available and easily accessible, making it a convenient option for those who are already familiar with the software. Secondly, Excel's built-in formulas and functions simplify the calculation process, reducing the risk of human error. Finally, Excel allows users to easily update and modify their calculations as needed, making it an ideal tool for iterative research and analysis.
Understanding the Basics of Sample Size Calculation
Before diving into the world of Excel, it's essential to understand the basics of sample size calculation. The most common method used is the confidence interval approach, which involves calculating the sample size required to achieve a desired level of precision. This approach takes into account several factors, including:
- The desired confidence level (e.g., 95%)
- The margin of error (e.g., 5%)
- The population size (e.g., 1000)
- The variability of the data (e.g., standard deviation)
Using Excel to Calculate Sample Size
Now that we have covered the basics, let's explore how to use Excel to calculate sample size. The process involves several steps:
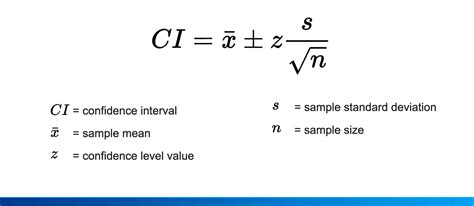
Step 1: Determine the Desired Confidence Level
The desired confidence level is the probability that the sample mean will fall within a certain range of the true population mean. Common confidence levels include 95% and 99%.
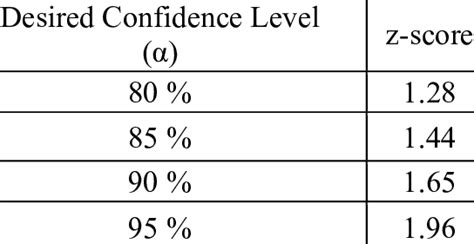
Step 2: Determine the Margin of Error
The margin of error is the maximum amount of variation allowed between the sample mean and the true population mean. A smaller margin of error requires a larger sample size.
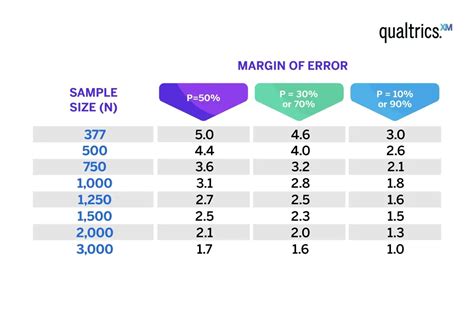
Step 3: Determine the Population Size
The population size is the total number of items in the population. This value is used to calculate the sample size.
Step 4: Determine the Variability of the Data
The variability of the data is measured using the standard deviation. This value is used to calculate the sample size.
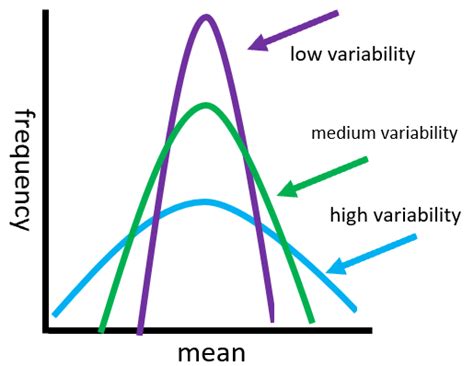
Step 5: Calculate the Sample Size
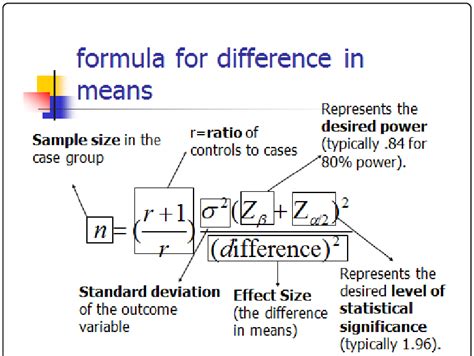
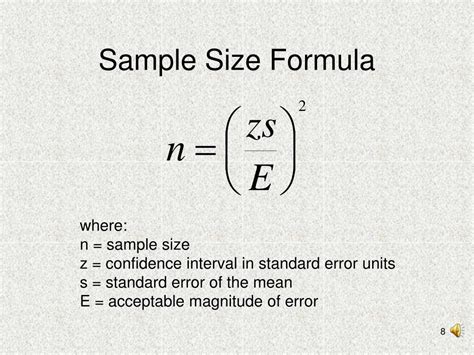
Using the values determined in the previous steps, we can calculate the sample size using the following formula:
n = (Z^2 * σ^2) / E^2
Where:
- n is the sample size
- Z is the Z-score corresponding to the desired confidence level
- σ is the standard deviation of the data
- E is the margin of error
This formula can be implemented in Excel using the following steps:
- Enter the desired confidence level, margin of error, population size, and variability of the data into separate cells.
- Use the
NORMSINVfunction to calculate the Z-score corresponding to the desired confidence level. - Use the
POWERfunction to calculate the squared Z-score. - Use the
POWERfunction to calculate the squared standard deviation. - Use the
POWERfunction to calculate the squared margin of error. - Use the
=POWER(Z,2)*POWER(σ,2)/POWER(E,2)formula to calculate the sample size.
Excel Sample Size Calculator Template
To make the process even easier, we can create an Excel template that automates the calculation process. The template can be set up as follows:
| Input | Formula |
|---|---|
| Desired Confidence Level | =NORMSINV(Desired Confidence Level) |
| Margin of Error | =POWER(Margin of Error,2) |
| Population Size | =Population Size |
| Variability of Data | =POWER(Standard Deviation,2) |
| Sample Size | =POWER(Z,2)*POWER(σ,2)/POWER(E,2) |
Using this template, we can easily calculate the sample size by entering the desired confidence level, margin of error, population size, and variability of the data.
Common Applications of Sample Size Calculation
Sample size calculation has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Market research: Determining the optimal sample size for surveys and focus groups.
- Medical research: Calculating the required sample size for clinical trials.
- Finance: Determining the sample size for financial analysis and modeling.
Gallery of Sample Size Calculation Images
Sample Size Calculation Image Gallery







Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, Excel provides a powerful and user-friendly tool for calculating sample sizes. By understanding the basics of sample size calculation and using the NORMSINV and POWER functions, we can easily automate the calculation process. Whether you're a researcher, marketer, or financial analyst, accurate sample size calculation is essential for making informed decisions. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can create your own Excel sample size calculator template and start calculating sample sizes with confidence.
We hope this article has been informative and helpful. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
