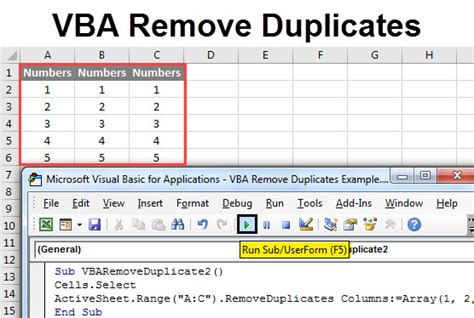
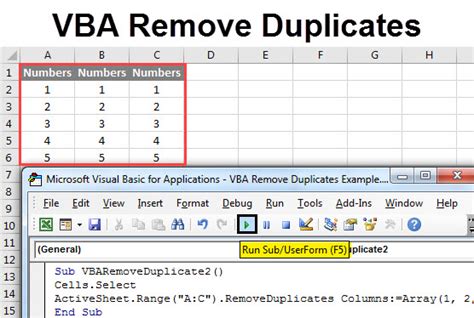
Intro
Effortlessly remove duplicates in Excel using VBA with our step-by-step guide. Master the art of data cleansing and learn how to eliminate duplicate rows, values, and records using Excel VBA macros, formulas, and techniques. Improve data accuracy, reduce errors, and boost productivity with our expert VBA solutions for duplicate removal.
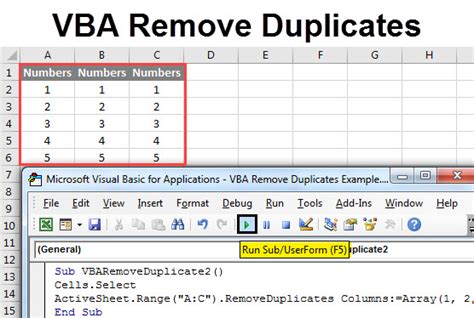
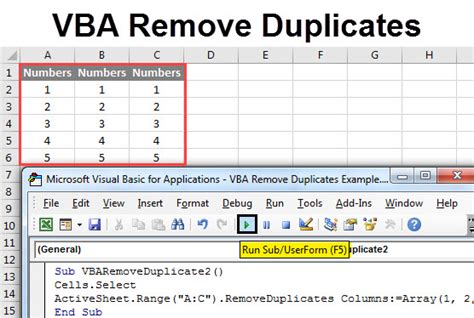
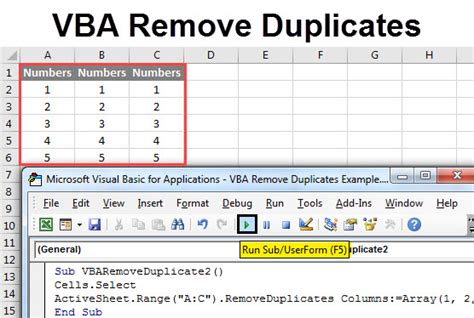
Removing duplicates in Excel can be a tedious task, especially when dealing with large datasets. However, with the help of VBA (Visual Basic for Applications), you can automate this process and save time. In this article, we will explore how to remove duplicates in Excel using VBA easily.
The Importance of Removing Duplicates
Duplicates in a dataset can lead to inaccurate analysis, incorrect conclusions, and poor decision-making. Removing duplicates is essential to ensure data integrity, consistency, and reliability. Moreover, duplicates can slow down your Excel workbook, making it difficult to work with.
Why Use VBA to Remove Duplicates?
While Excel provides a built-in feature to remove duplicates, it has its limitations. The built-in feature only removes duplicates based on a single column or a range of columns. However, with VBA, you can create a custom solution that removes duplicates based on multiple conditions, specific columns, or even entire rows.
Benefits of Using VBA to Remove Duplicates
- Flexibility: VBA allows you to create a custom solution tailored to your specific needs.
- Efficiency: VBA can automate the process of removing duplicates, saving you time and effort.
- Accuracy: VBA can help you avoid errors that may occur when using the built-in feature.
How to Remove Duplicates in Excel Using VBA
Step 1: Open the Visual Basic Editor
To start, open the Visual Basic Editor by pressing Alt + F11 or navigating to Developer > Visual Basic in the ribbon.
Step 2: Create a New Module
In the Visual Basic Editor, click Insert > Module to create a new module.
Step 3: Write the VBA Code
In the new module, paste the following code:
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
' Declare variables
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim rng As Range
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim i As Long
' Set worksheet and range
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
Set rng = ws.Range("A1").CurrentRegion
' Find last row with data
lastRow = rng.Rows.Count
' Loop through rows and remove duplicates
For i = lastRow To 2 Step -1
If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountIf(rng.Columns(1), rng.Cells(i, 1).Value) > 1 Then
rng.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next i
End Sub
Step 4: Adjust the Code to Your Needs
Modify the code to suit your specific requirements:
- Change
Sheet1to the name of your worksheet. - Adjust the range
A1to the starting cell of your data range. - If you want to remove duplicates based on multiple columns, modify the
CountIffunction accordingly.
Step 5: Run the VBA Code
Press F5 to run the code, or click Run > Run Sub/UserForm in the Visual Basic Editor.
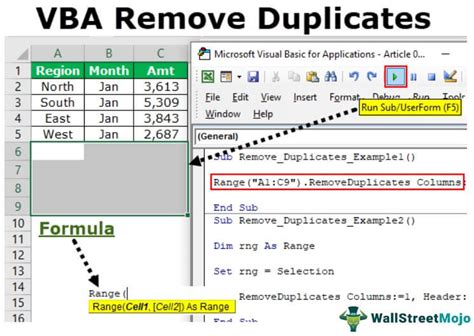
Example Use Case: Removing Duplicates in a Sales Dataset
Suppose you have a sales dataset with the following columns: Order ID, Customer Name, Product, and Date. You want to remove duplicates based on the Order ID column.
To do this, modify the VBA code as follows:
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
' Declare variables
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim rng As Range
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim i As Long
' Set worksheet and range
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sales")
Set rng = ws.Range("A1").CurrentRegion
' Find last row with data
lastRow = rng.Rows.Count
' Loop through rows and remove duplicates
For i = lastRow To 2 Step -1
If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountIf(rng.Columns(1), rng.Cells(i, 1).Value) > 1 Then
rng.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next i
End Sub
Tips and Variations
- To remove duplicates based on multiple columns, modify the
CountIffunction to include multiple ranges, separated by commas. - To remove duplicates from an entire row, use the
EntireRowproperty:rng.Rows(i).EntireRow.Delete. - To remove duplicates from a specific range, modify the
rngvariable to include the desired range.
Best Practices for Using VBA to Remove Duplicates
- Test the code: Before running the code on your actual dataset, test it on a sample dataset to ensure it works as expected.
- Backup your data: Always backup your data before running the code to avoid losing important information.
- Optimize the code: If you have a large dataset, optimize the code to improve performance by using techniques such as looping through rows in reverse order.
Conclusion
Removing duplicates in Excel using VBA is a powerful way to automate data cleaning tasks. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can create a custom solution that suits your specific needs. Remember to test the code, backup your data, and optimize the code for large datasets. With VBA, you can efficiently and accurately remove duplicates, ensuring data integrity and consistency.
Gallery of Remove Duplicates in Excel using VBA
Remove Duplicates in Excel using VBA Image Gallery