Intro
Learn how to set date format to dd/mm/yyyy in Excel VBA with ease. Discover the simple steps to change date formats in Excel using VBA macros, including the use of Format function, Date data type, and cell formatting. Master Excel VBA date formatting and simplify your workflow with our expert tips.
Setting the date format in Excel VBA can be a bit tricky, but don't worry, I'm here to guide you through it.
Setting the date format in Excel VBA is essential to ensure that your dates are displayed correctly and consistently throughout your workbook. Whether you're working with dates in a specific column or using them in formulas, getting the format right is crucial.
Understanding Date Formats in Excel VBA
In Excel VBA, dates are stored as serial numbers, which represent the number of days since January 1, 1900. However, when you display a date in a cell, Excel uses a specific format to show the date in a human-readable format.
Excel VBA provides several ways to set the date format, and we'll explore them in this article.
Method 1: Using the `NumberFormat` Property
One way to set the date format in Excel VBA is by using the NumberFormat property of a range or a cell. Here's an example:
Sub SetDateFormat()
Range("A1").NumberFormat = "dd/mm/yyyy"
End Sub
In this example, we're setting the date format of cell A1 to dd/mm/yyyy. You can change the format to any valid date format, such as mm/dd/yyyy or yyyy-mm-dd.
Method 2: Using the `Format` Function
Another way to set the date format is by using the Format function. Here's an example:
Sub SetDateFormat()
Range("A1").Value = Format(Range("A1").Value, "dd/mm/yyyy")
End Sub
In this example, we're using the Format function to set the date format of the value in cell A1 to dd/mm/yyyy.
Method 3: Using the `TextToColumns` Method
If you have a column of dates in a text format and you want to convert them to a date format, you can use the TextToColumns method. Here's an example:
Sub SetDateFormat()
Range("A1:A10").TextToColumns Destination:=Range("A1"), DataType:=xlDelimitedText, _
TextQualifier:=xlDoubleQuote, ConsecutiveDelimiter:=False, Tab:=False, _
Semicolon:=False, Comma:=False, Space:=False, Other:=False, FieldInfo _
:=Array(Array(1, 4)), TrailingMinusNumbers:=True
Range("A1:A10").NumberFormat = "dd/mm/yyyy"
End Sub
In this example, we're using the TextToColumns method to convert the text dates in column A to a date format, and then setting the number format to dd/mm/yyyy.
Best Practices for Working with Dates in Excel VBA
When working with dates in Excel VBA, here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Always use a consistent date format throughout your workbook.
- Use the
Datedata type to store dates in variables. - Avoid using text dates, as they can lead to errors and inconsistencies.
- Use the
Formatfunction to display dates in a human-readable format. - Use the
NumberFormatproperty to set the date format of a range or cell.
By following these best practices and using the methods outlined in this article, you'll be able to work with dates in Excel VBA with confidence.
Gallery of Excel VBA Date Formats
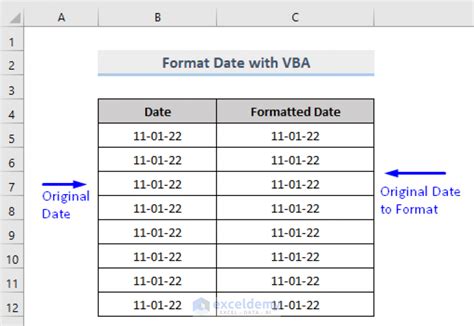
I hope this article has helped you understand how to set the date format in Excel VBA. If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to ask in the comments below.
