Intro
Uncover the secrets of the worlds first operational stealth fighter jet, the F-117 Nighthawk. Discover its impressive top speed, cutting-edge design, and advanced technology that revolutionized air combat. Learn about its radar-absorbent materials, serrated edges, and faceted surface design that made it nearly invisible to enemy radar systems.
The F-117 Nighthawk, a single-seat, twin-engine stealth ground attack aircraft developed by Lockheed Skunk Works, has been a subject of interest for many aviation enthusiasts and military personnel alike. One of the most sought-after pieces of information about this aircraft is its top speed, which has been shrouded in secrecy for many years.
The F-117 Nighthawk was the world's first operational stealth aircraft, designed to evade detection by radar and other detection systems. Its unique design and radar-absorbing materials made it nearly invisible to enemy defenses, allowing it to penetrate deep into hostile territory undetected. The aircraft's speed, maneuverability, and advanced avionics made it an ideal platform for precision strikes against high-value targets.

The F-117 Nighthawk's top speed has been a topic of speculation for many years, with various sources citing different figures. However, according to official sources, the F-117 Nighthawk's top speed is classified, but it is believed to be around Mach 0.92 (700 mph or 1,127 km/h) at sea level.
Design and Development
The F-117 Nighthawk was designed and developed by Lockheed Skunk Works, a division of Lockheed Corporation, in the 1970s and 1980s. The aircraft was designed to meet the United States Air Force's requirement for a stealthy ground attack aircraft that could penetrate deep into hostile territory undetected.
The F-117 Nighthawk's design was influenced by the Have Blue prototype, a small-scale stealth aircraft developed by Lockheed Skunk Works in the 1970s. The Have Blue prototype demonstrated the feasibility of stealth technology, and its design was used as the basis for the F-117 Nighthawk.
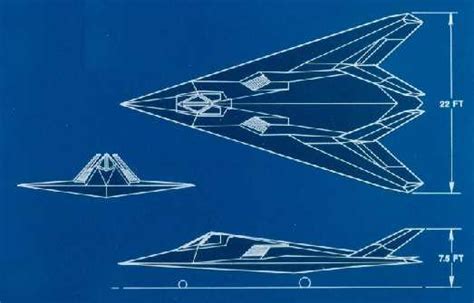
The F-117 Nighthawk's airframe is made of a combination of metal and composite materials, with a radar-absorbing material (RAM) coating to reduce its radar cross-section. The aircraft's unique design features a faceted shape, with flat surfaces and sharp edges, which helps to scatter radar waves and reduce its visibility on radar.
Operational History
The F-117 Nighthawk entered service with the United States Air Force in 1983 and saw action in several conflicts, including the Gulf War, the Kosovo War, and the Iraq War. The aircraft was operated by the 49th Fighter Wing at Holloman Air Force Base, New Mexico, and the 37th Fighter Wing at Tonopah Test Range, Nevada.
The F-117 Nighthawk was used for precision strikes against high-value targets, such as command and control centers, radar sites, and airfields. The aircraft's stealth capabilities allowed it to penetrate deep into hostile territory undetected, making it an ideal platform for precision strikes.
Notable Missions
The F-117 Nighthawk was involved in several notable missions during its operational history. One of the most notable missions was during the Gulf War, when F-117 Nighthawks attacked Iraqi command and control centers, radar sites, and airfields.
On January 17, 1991, F-117 Nighthawks launched a surprise attack on Iraqi air defenses, destroying several radar sites and airfields. The attack marked the beginning of Operation Desert Storm, a coalition operation to liberate Kuwait from Iraqi occupation.

Retirement
The F-117 Nighthawk was retired from service in 2008, after 25 years of operational service. The aircraft was replaced by the F-22 Raptor and the F-35 Lightning II, both of which offer advanced stealth capabilities and improved performance.
The F-117 Nighthawk's retirement marked the end of an era in stealth aviation, but its legacy continues to influence the development of future stealth aircraft.

Gallery of F-117 Nighthawk Images
F-117 Nighthawk Image Gallery










We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the F-117 Nighthawk's top speed and its operational history. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below.
