Intro
Discover the 5 Fahrenheit grades, exploring temperature conversions, freezing points, and boiling points with related metrics like Celsius and Kelvin scales.
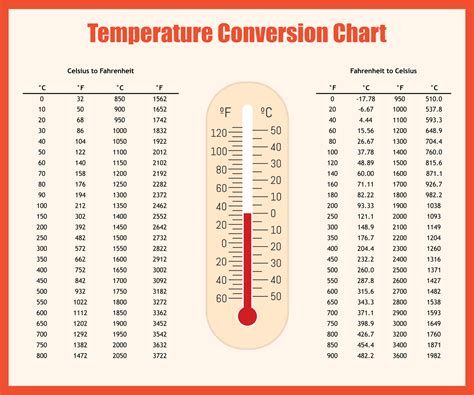
The concept of temperature and its measurement is crucial in various fields, including science, engineering, and everyday life. One of the most widely used temperature scales is the Fahrenheit scale, which was introduced by Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century. The Fahrenheit scale is still widely used in the United States, although most other countries have adopted the Celsius scale. Understanding the different grades of temperature on the Fahrenheit scale is essential for various applications, including weather forecasting, cooking, and scientific research. In this article, we will explore the 5 Fahrenheit grades, their significance, and practical applications.
The Fahrenheit scale is divided into several grades, each representing a specific range of temperatures. The 5 Fahrenheit grades are:
- Extremely cold temperatures, ranging from -22°F to 14°F
- Cold temperatures, ranging from 15°F to 32°F
- Mild temperatures, ranging from 33°F to 50°F
- Warm temperatures, ranging from 51°F to 64°F
- Hot temperatures, ranging from 65°F to 86°F Each of these grades has its unique characteristics and implications for various aspects of life, from climate and weather to human health and comfort.
Introduction to Fahrenheit Grades
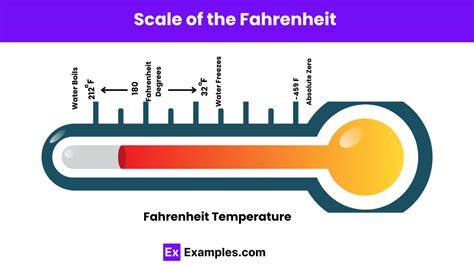
Extremely Cold Temperatures

Effects of Extremely Cold Temperatures
The effects of extremely cold temperatures are far-reaching and can have significant impacts on various aspects of life. Some of the key effects include: * Human health risks, such as hypothermia and frostbite * Reduced performance of materials and equipment * Increased risk of accidents and injuries * Disruption of transportation and communication systems * Impact on agriculture and food productionCold Temperatures

Effects of Cold Temperatures
The effects of cold temperatures are significant and can have far-reaching impacts on various aspects of life. Some of the key effects include: * Human health risks, such as respiratory illnesses and hypothermia * Reduced performance of materials and equipment * Increased risk of accidents and injuries * Disruption of transportation and communication systems * Impact on agriculture and food productionMild Temperatures

Effects of Mild Temperatures
The effects of mild temperatures are significant and can have far-reaching impacts on various aspects of life. Some of the key effects include: * Improved human health and well-being * Increased outdoor activities and tourism * Enhanced performance of materials and equipment * Reduced risk of accidents and injuries * Positive impact on agriculture and food productionWarm Temperatures

Effects of Warm Temperatures
The effects of warm temperatures are significant and can have far-reaching impacts on various aspects of life. Some of the key effects include: * Human health risks, such as heat-related illnesses and dehydration * Reduced performance of materials and equipment * Increased risk of accidents and injuries * Disruption of transportation and communication systems * Impact on agriculture and food productionHot Temperatures
Effects of Hot Temperatures
The effects of hot temperatures are significant and can have far-reaching impacts on various aspects of life. Some of the key effects include: * Human health risks, such as heat-related illnesses and dehydration * Reduced performance of materials and equipment * Increased risk of accidents and injuries * Disruption of transportation and communication systems * Impact on agriculture and food productionFahrenheit Temperature Scale Image Gallery
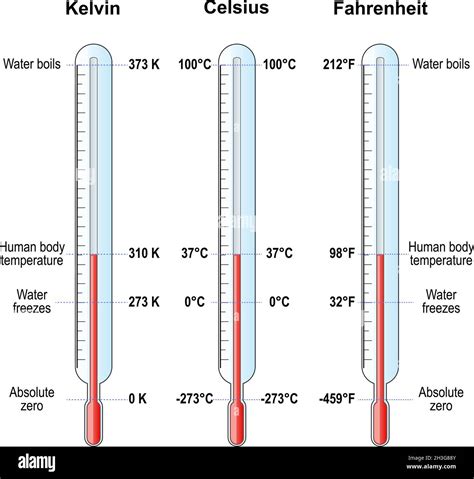







In conclusion, the 5 Fahrenheit grades are essential for understanding temperature and its measurement. Each grade has its unique characteristics and implications for various aspects of life, from climate and weather to human health and comfort. By understanding the different Fahrenheit grades, we can make informed decisions about temperature-related issues and take necessary precautions to mitigate the effects of extreme temperatures. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with temperature and its measurement, and to explore the various applications of the Fahrenheit scale in everyday life. Please comment below, share this article with others, and join the conversation on social media using relevant hashtags.
