Intro
Master the art of finding the last row in VBA with ease. Learn simple and efficient methods to identify the last row with data in Excel using VBA. Discover how to avoid common pitfalls and optimize your code with expert tips and tricks, making data processing a breeze with VBA last row solutions.
Finding the last row in a worksheet is a common task in VBA programming, and it's essential to do it correctly to avoid errors and ensure that your code works as intended. In this article, we'll explore the different methods to find the last row in VBA and provide you with the most efficient and reliable techniques.
Why Finding the Last Row is Important
When working with data in Excel, it's often necessary to determine the last row that contains data. This can be useful in various scenarios, such as:
- Looping through a range of cells to perform calculations or formatting
- Copying or moving data to another worksheet or workbook
- Creating charts or pivot tables
- Validating data entry or formatting
Common Mistakes When Finding the Last Row
Before we dive into the solutions, let's quickly discuss some common mistakes that people make when trying to find the last row in VBA:
- Using the
Range("A1").End(xlDown).Rowmethod, which can be unreliable if there are blank cells in the column - Using the
Range("A1").CurrentRegion.Rows.Countmethod, which can include blank rows - Using the
Cells.Find("*", SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Rowmethod, which can be slow and may not work if the worksheet is very large
Method 1: Using the Find Method
One of the most reliable methods to find the last row is to use the Find method, which searches for a specific value or formatting in a range of cells. Here's an example:
Sub FindLastRow()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
Dim lastRow As Long
lastRow = ws.Cells.Find("*", SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
MsgBox "The last row is " & lastRow
End Sub
This method searches for any value ("*") in the worksheet, starting from the bottom row and moving up. The SearchOrder parameter is set to xlByRows to search by rows, and the SearchDirection parameter is set to xlPrevious to search from the bottom up.
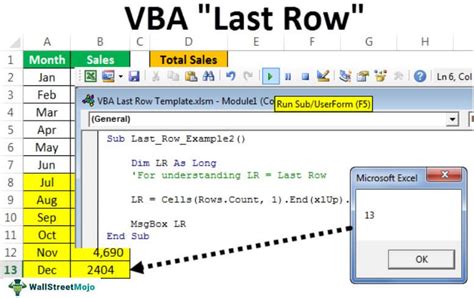
Method 2: Using the UsedRange Property
Another method to find the last row is to use the UsedRange property, which returns the range of cells that contain data. Here's an example:
Sub UsedRangeLastRow()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
Dim lastRow As Long
lastRow = ws.UsedRange.Rows.Count + ws.UsedRange.Row - 1
MsgBox "The last row is " & lastRow
End Sub
This method returns the range of cells that contain data, and then calculates the last row by adding the number of rows in the range to the starting row of the range, minus 1.

Method 3: Using the Range Object
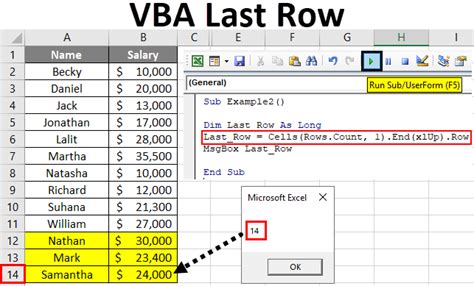
A third method to find the last row is to use the Range object, which allows you to specify a range of cells and then find the last row. Here's an example:
Sub RangeLastRow()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
Dim lastRow As Long
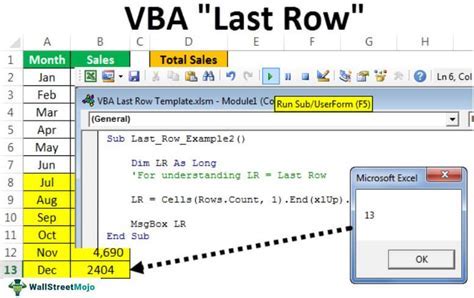
lastRow = ws.Range("A" & ws.Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
MsgBox "The last row is " & lastRow
End Sub
This method specifies a range of cells starting from the bottom row of the worksheet and then finds the last row by moving up until it finds a cell with data.
Conclusion
Finding the last row in VBA can be a challenging task, but by using one of the methods outlined in this article, you can ensure that your code works correctly and efficiently. Remember to avoid common mistakes and use the most reliable method for your specific use case.
Gallery of Last Row VBA
Last Row VBA Image Gallery




We hope this article has been helpful in explaining how to find the last row in VBA. If you have any questions or need further assistance, please don't hesitate to ask.
