Intro
Discover the impact of fluoride in food on oral health, exploring its benefits, risks, and sources, including fluoridated water, toothpaste, and fortified foods, to make informed dietary choices.
Fluoride is a naturally occurring compound that can be found in various food sources, including water, soil, and certain types of rocks. It is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining strong teeth and bones, as well as preventing tooth decay and other oral health problems. However, excessive consumption of fluoride can have negative health effects, making it essential to understand the importance of fluoride in food and how to maintain a healthy balance.
The presence of fluoride in food is not a new phenomenon, as it has been a part of the human diet for centuries. In fact, many communities around the world have been consuming fluoride-rich foods, such as fish and tea, for generations. However, with the advent of modern agriculture and food processing, the levels of fluoride in food have increased significantly, leading to concerns about the potential health risks associated with excessive fluoride consumption. As a result, it is essential to be aware of the sources of fluoride in food and to take steps to maintain a healthy balance.
Fluoride is an essential nutrient that is necessary for maintaining strong teeth and bones. It helps to prevent tooth decay by making teeth more resistant to acid attacks from plaque bacteria and sugars in the mouth. Fluoride also helps to reverse early stages of tooth decay, making it an essential component of oral health. In addition to its oral health benefits, fluoride also plays a role in maintaining strong bones, as it helps to regulate the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus, two essential minerals for bone health. With the numerous benefits of fluoride, it is essential to understand the sources of fluoride in food and how to maintain a healthy balance.
Benefits of Fluoride in Food

Food Sources of Fluoride
Fluoride can be found in a variety of food sources, including: * Water: Fluoridated water is a significant source of fluoride, particularly in communities where the water supply is fluoridated. * Tea: Tea, particularly black tea, is a rich source of fluoride. * Fish: Fish, such as salmon and sardines, are good sources of fluoride. * Coffee: Coffee, particularly instant coffee, can contain high levels of fluoride. * Grains: Grains, such as rice and wheat, can contain fluoride, particularly if they are grown in areas with high levels of fluoride in the soil. * Processed foods: Many processed foods, such as cereals and energy bars, can contain fluoride.Risks Associated with Excessive Fluoride Consumption
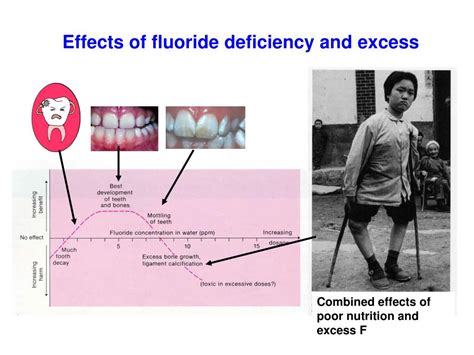
Regulating Fluoride Intake
To maintain a healthy balance of fluoride, it is essential to regulate fluoride intake. Some ways to regulate fluoride intake include: * Using non-fluoridated toothpaste * Avoiding processed foods that contain fluoride * Drinking non-fluoridated water * Limiting consumption of tea and coffee * Eating a balanced diet that includes a variety of foodsFluoride in Infant Formula

Fluoride in Pregnancy
Fluoride in pregnancy is also a topic of concern. Excessive fluoride consumption during pregnancy can lead to health problems in the fetus, including dental fluorosis and skeletal fluorosis. To minimize the risks associated with fluoride in pregnancy, pregnant women can take the following steps: * Drink non-fluoridated water * Limit consumption of tea and coffee * Avoid processed foods that contain fluoride * Consult with a healthcare provider about the best way to minimize fluoride intake during pregnancyFluoride and Oral Health

Fluoride and Bone Health
Fluoride also plays a role in maintaining bone health. It helps to regulate the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus, two essential minerals for bone health. Fluoride also helps to increase bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Some of the ways that fluoride promotes bone health include: * Regulating the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus * Increasing bone density * Reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures * Supporting overall bone healthConclusion and Recommendations

Fluoride Image Gallery

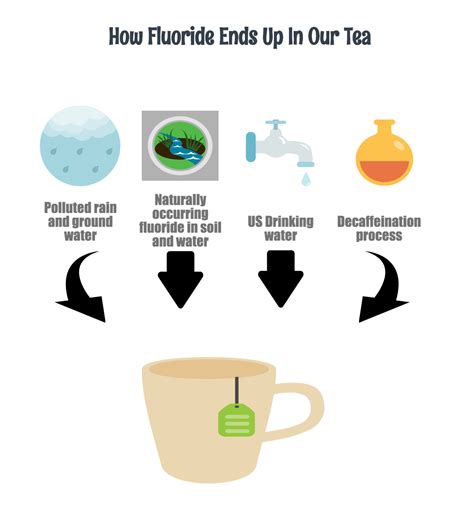




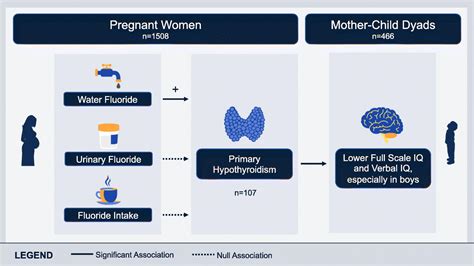
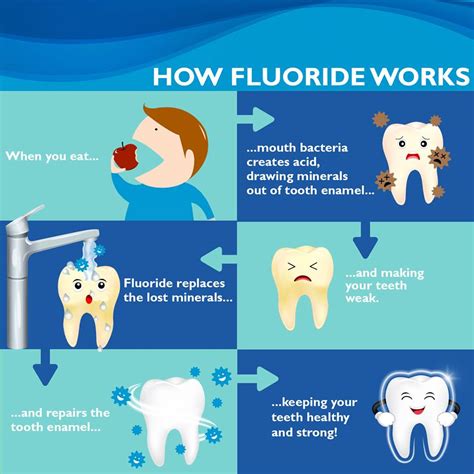


We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the importance of fluoride in food. By regulating fluoride intake and maintaining a balanced diet, you can minimize the risks associated with excessive fluoride consumption and promote overall health and well-being. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of fluoride in food.
