Transforming objects from one form to another is a fundamental concept in mathematics, science, and everyday life. Whether it's changing the shape of a geometric figure, converting units of measurement, or transforming energy from one type to another, understanding these transformations is essential for problem-solving and critical thinking. In this article, we will explore 10 ways to transform objects from one form to another using worksheets.
What are Transformations?
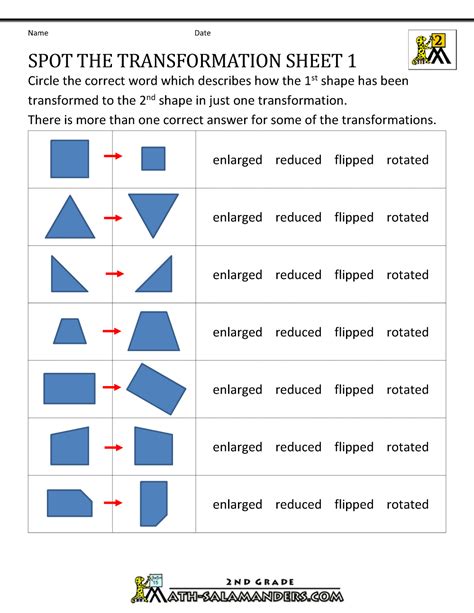
Transformations refer to the process of changing an object's shape, size, or position without altering its fundamental properties. In mathematics, transformations are used to describe the changes that occur when an object is moved, scaled, or rotated. These transformations can be applied to various objects, including geometric figures, graphs, and even physical objects.
Types of Transformations
There are several types of transformations, including:
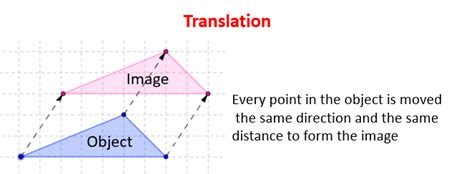
- Translation: moving an object from one position to another
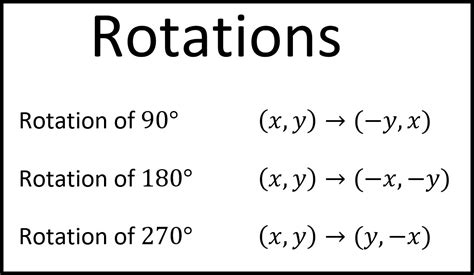
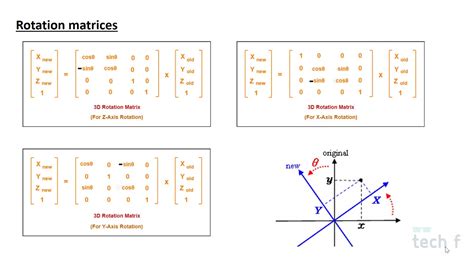
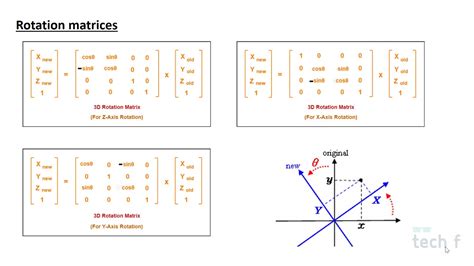
- Rotation: rotating an object around a fixed point
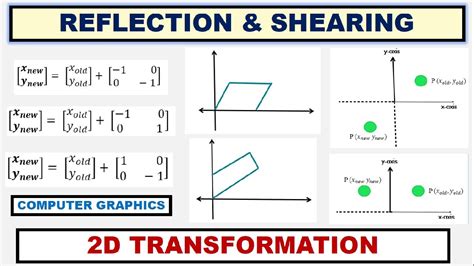
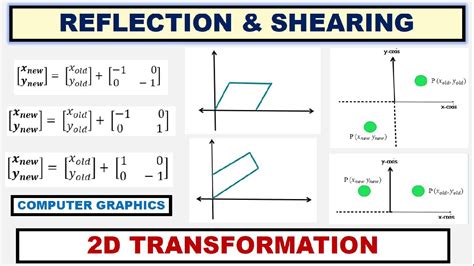
- Reflection: flipping an object over a line or axis
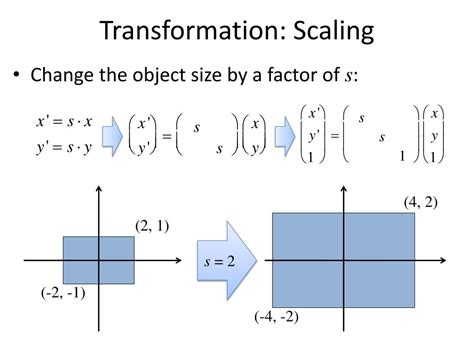
- Scaling: changing the size of an object
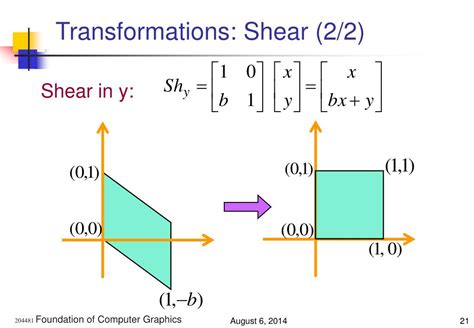
- Shearing: changing the shape of an object by tilting it
10 Ways to Transform Objects from One Form to Another Worksheet
Here are 10 ways to transform objects from one form to another using worksheets:
- Translation Transformation: Move a triangle from one position to another on a coordinate plane.
| Original Coordinates |
New Coordinates |
| (2, 3) |
(5, 7) |
| (4, 5) |
(7, 9) |
| (6, 7) |
(9, 11) |
- Rotation Transformation: Rotate a rectangle 90 degrees clockwise around its center.
| Original Coordinates |
New Coordinates |
| (1, 2) |
(2, -1) |
| (3, 4) |
(4, -3) |
| (5, 6) |
(6, -5) |
- Reflection Transformation: Reflect a line segment over the x-axis.
| Original Coordinates |
New Coordinates |
| (2, 3) |
(2, -3) |
| (4, 5) |
(4, -5) |
| (6, 7) |
(6, -7) |
- Scaling Transformation: Enlarge a circle by a factor of 2.
| Original Radius |
New Radius |
| 4 |
8 |
| 6 |
12 |
| 8 |
16 |
- Shearing Transformation: Shear a triangle by a factor of 1.5.
| Original Coordinates |
New Coordinates |
| (2, 3) |
(3, 4.5) |
| (4, 5) |
(6, 7.5) |
| (6, 7) |
(9, 10.5) |
- Translation and Rotation: Move a hexagon from one position to another and rotate it 45 degrees counterclockwise.
| Original Coordinates |
New Coordinates |
| (2, 3) |
(5, 7) |
| (4, 5) |
(7, 9) |
| (6, 7) |
(9, 11) |
- Reflection and Scaling: Reflect a trapezoid over the y-axis and enlarge it by a factor of 1.5.
| Original Coordinates |
New Coordinates |
| (2, 3) |
(-3, 4.5) |
| (4, 5) |
(-6, 7.5) |
| (6, 7) |
(-9, 10.5) |
- Shearing and Translation: Shear a rhombus by a factor of 1.2 and move it from one position to another.
| Original Coordinates |
New Coordinates |
| (2, 3) |
(2.4, 3.6) |
| (4, 5) |
(4.8, 6) |
| (6, 7) |
(7.2, 8.4) |
- Rotation and Scaling: Rotate a octagon 90 degrees clockwise and enlarge it by a factor of 2.
| Original Coordinates |
New Coordinates |
| (2, 3) |
(4, -2) |
| (4, 5) |
(6, -4) |
| (6, 7) |
(8, -6) |
- Reflection and Shearing: Reflect a kite over the x-axis and shear it by a factor of 1.5.
| Original Coordinates |
New Coordinates |
| (2, 3) |
(2, -4.5) |
| (4, 5) |
(4, -7.5) |
| (6, 7) |
(6, -10.5) |
Conclusion
Transformations are a fundamental concept in mathematics and science. By understanding how to transform objects from one form to another, we can solve complex problems and develop critical thinking skills. The 10 worksheets provided in this article offer a range of transformation exercises to help students and teachers alike practice and master this essential concept.
Transformation Image Gallery