Intro
Discover the essential facts about Gabapentin ATi medication, a popular prescription drug used to treat nerve pain, seizures, and anxiety. Learn about its uses, dosage, side effects, and interactions, as well as its benefits and risks. Understand how Gabapentin works and what to expect when taking this medication for neuropathic pain, epilepsy, and other conditions.
Gabapentin is a medication that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its versatility and effectiveness in treating various medical conditions. As a medication, gabapentin is widely used to alleviate symptoms associated with epilepsy, nerve pain, and anxiety disorders, among others. However, despite its popularity, there are still many misconceptions and misunderstandings surrounding gabapentin. In this article, we will delve into five essential facts about gabapentin ATi medication, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of this medication.
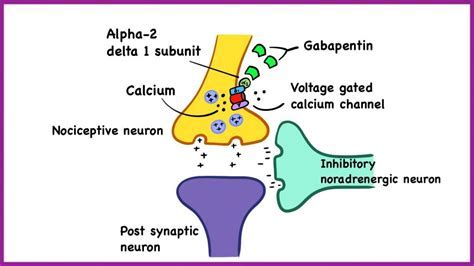
Gabapentin is a medication that was initially developed to treat epilepsy, but its therapeutic applications have expanded significantly over the years. Today, gabapentin is used to treat a range of medical conditions, including nerve pain, anxiety disorders, and even insomnia. However, what makes gabapentin so effective, and what are the essential facts that patients should know about this medication?
What is Gabapentin?
Gabapentin is a type of anticonvulsant medication, which means it is primarily used to treat seizures and epilepsy. However, its mechanism of action is unique, and it works differently compared to other anticonvulsant medications. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, which means it mimics the action of the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) in the brain. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps regulate the activity of neurons, and gabapentin works by increasing the levels of GABA in the brain.
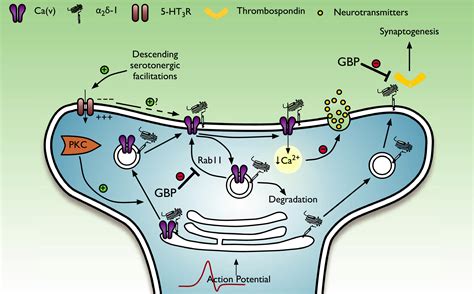
How Does Gabapentin Work?
Gabapentin works by binding to voltage-gated calcium channels in the brain, which reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. This leads to a decrease in the activity of neurons, resulting in a calming effect on the nervous system. Gabapentin also has a unique ability to increase the levels of GABA in the brain, which further contributes to its therapeutic effects.
What are the Therapeutic Applications of Gabapentin?
Gabapentin has a wide range of therapeutic applications, making it a versatile medication in the medical field. Some of the most common uses of gabapentin include:
- Epilepsy: Gabapentin is primarily used to treat partial seizures, which are seizures that affect only a part of the brain. It is often used in combination with other medications to control seizures.
- Nerve Pain: Gabapentin is effective in treating nerve pain, also known as neuropathic pain, which is often associated with conditions such as diabetes, shingles, and multiple sclerosis.
- Anxiety Disorders: Gabapentin has been shown to be effective in treating anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder and social anxiety disorder.
- Insomnia: Gabapentin has been used to treat insomnia, particularly in patients who have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.

What are the Side Effects of Gabapentin?
Like all medications, gabapentin can cause side effects, some of which are mild and temporary, while others can be more serious. Common side effects of gabapentin include:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fatigue
More serious side effects of gabapentin can include:
- Increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors
- Allergic reactions
- Increased risk of seizures (in patients with a history of seizures)
How to Take Gabapentin?
Gabapentin is available in various formulations, including capsules, tablets, and oral solutions. The dosage and frequency of gabapentin depend on the individual's medical condition and response to treatment. Patients should always follow the dosage instructions provided by their doctor and take gabapentin exactly as prescribed.

What are the Interactions of Gabapentin with Other Medications?
Gabapentin can interact with other medications, which can affect its efficacy and safety. Patients should inform their doctor about all medications they are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and supplements. Some medications that can interact with gabapentin include:
- Antacids
- Opioids
- Sedatives
- Antidepressants
Gabapentin Image Gallery







We hope this article has provided readers with a comprehensive understanding of gabapentin ATi medication. As with any medication, it's essential to follow the dosage instructions provided by your doctor and to be aware of the potential side effects and interactions with other medications. If you have any questions or concerns about gabapentin, please don't hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Share your thoughts and experiences with gabapentin in the comments section below!
