Intro
Discover the evolution of air power with our in-depth look at the 5 generations of jet fighters. From the early turbojets of Gen 1 to the advanced stealth capabilities of Gen 5, explore the key features, technologies, and innovations that define each generation, including Mach speeds, avionics, and combat tactics.
The evolution of jet fighters has been a remarkable journey, marked by significant advancements in technology, design, and capabilities. From the early days of jet propulsion to the modern era of stealth and advanced avionics, jet fighters have played a crucial role in shaping the course of military aviation. In this article, we will explore the five generations of jet fighters, highlighting their key features, improvements, and notable examples.
First Generation: The Dawn of Jet Fighters

The first generation of jet fighters emerged in the late 1940s and early 1950s, with the introduction of the first operational jet fighter, the Messerschmitt Me 262. These early jet fighters were characterized by their basic design, simple avionics, and limited capabilities. They were primarily used for air-to-air combat and were often outperformed by propeller-driven aircraft in certain aspects.
Notable examples of first-generation jet fighters include:
- Messerschmitt Me 262 (Germany)
- Gloster Meteor (UK)
- Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star (USA)
Key Features:
- Basic design with straight wings and limited maneuverability
- Simple avionics with minimal radar and navigation systems
- Limited range and endurance
- Primarily used for air-to-air combat
Second Generation: The Advent of Swept Wings

The second generation of jet fighters, which emerged in the mid-1950s, saw significant improvements in design and capabilities. The introduction of swept wings, which improved high-speed performance and maneuverability, was a key feature of this generation. These aircraft also featured more advanced avionics, including radar and navigation systems.
Notable examples of second-generation jet fighters include:
- North American F-100 Super Sabre (USA)
- Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-17 (USSR)
- Dassault Mystère IV (France)
Key Features:
- Swept wings for improved high-speed performance and maneuverability
- More advanced avionics, including radar and navigation systems
- Improved range and endurance
- Primarily used for air-to-air combat and limited air-to-ground capabilities
Third Generation: The Era of Variable Geometry

The third generation of jet fighters, which emerged in the late 1960s and early 1970s, saw the introduction of variable geometry wings, which allowed for improved maneuverability and versatility. These aircraft also featured advanced avionics, including terrain-following radar and missile-guidance systems.
Notable examples of third-generation jet fighters include:
- McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II (USA)
- General Dynamics F-111 Aardvark (USA)
- Panavia Tornado (Europe)
Key Features:
- Variable geometry wings for improved maneuverability and versatility
- Advanced avionics, including terrain-following radar and missile-guidance systems
- Improved range and endurance
- Primarily used for air-to-air combat and air-to-ground capabilities
Fourth Generation: The Advent of Multi-Role Fighters

The fourth generation of jet fighters, which emerged in the 1970s and 1980s, saw the introduction of multi-role fighters, which could perform a variety of tasks, including air-to-air combat, air-to-ground strikes, and reconnaissance. These aircraft featured advanced avionics, including pulse-Doppler radar and electronic countermeasures.
Notable examples of fourth-generation jet fighters include:
- McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle (USA)
- General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon (USA)
- Dassault Mirage 2000 (France)
Key Features:
- Multi-role capabilities, including air-to-air combat, air-to-ground strikes, and reconnaissance
- Advanced avionics, including pulse-Doppler radar and electronic countermeasures
- Improved range and endurance
- Primarily used for a variety of tasks, including air-to-air combat, air-to-ground strikes, and reconnaissance
Fifth Generation: The Era of Stealth and Advanced Avionics
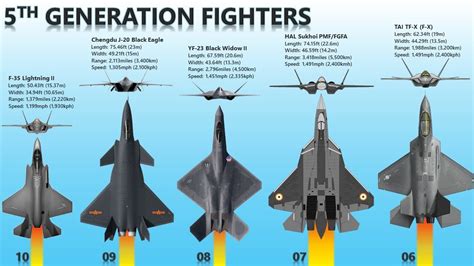
The fifth generation of jet fighters, which emerged in the 1990s and 2000s, saw the introduction of stealth technology, which allowed aircraft to evade detection by radar and other sensors. These aircraft also featured advanced avionics, including advanced radar systems, electronic countermeasures, and network-centric warfare capabilities.
Notable examples of fifth-generation jet fighters include:
- Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor (USA)
- Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II (USA)
- Sukhoi Su-57 (Russia)
Key Features:
- Stealth technology for reduced radar cross-section and improved survivability
- Advanced avionics, including advanced radar systems, electronic countermeasures, and network-centric warfare capabilities
- Improved range and endurance
- Primarily used for air-to-air combat, air-to-ground strikes, and reconnaissance
Jet Fighters Image Gallery










In conclusion, the evolution of jet fighters has been a remarkable journey, marked by significant advancements in technology, design, and capabilities. From the early days of jet propulsion to the modern era of stealth and advanced avionics, jet fighters have played a crucial role in shaping the course of military aviation. We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the five generations of jet fighters and their key features, improvements, and notable examples.
We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on the evolution of jet fighters and their impact on military aviation. Which generation of jet fighters do you think has been the most significant? What advancements do you think will shape the future of jet fighters? Let us know in the comments section below.
