Intro
Explore Germanys debt-to-GDP ratio, a growing concern in the European economy. Learn how high government debt, economic slowdown, and COVID-19 impact the countrys fiscal health. Discover the implications of debt sustainability, fiscal policy, and economic growth on Germanys financial future. Stay informed on this pressing issue affecting the EU and global markets.
Germany's economy has long been considered a bastion of stability in the European Union. However, in recent years, concerns have been growing about the country's rising debt levels. As the largest economy in the Eurozone, Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio has significant implications for the entire region. In this article, we will delve into the details of Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio, exploring its current state, historical context, and the potential consequences of rising debt levels.
What is the Debt-to-GDP Ratio?

The debt-to-GDP ratio is a widely used indicator to assess a country's fiscal health. It measures the total amount of debt a country owes relative to its gross domestic product (GDP). A higher ratio indicates a larger debt burden relative to the country's economic output. Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio has been steadily increasing over the past decade, sparking concerns among economists, policymakers, and investors.
Germany's Debt-to-GDP Ratio: A Historical Context
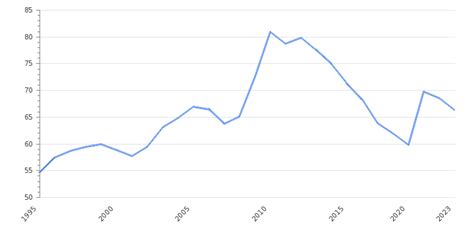
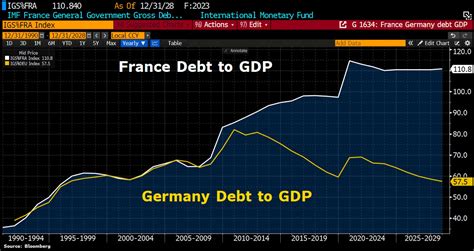
To understand Germany's current debt-to-GDP ratio, it's essential to examine its historical context. In the aftermath of the 2008 global financial crisis, Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio rose significantly as the government implemented fiscal stimulus packages to stabilize the economy. However, unlike some of its European counterparts, Germany has traditionally maintained a relatively low debt-to-GDP ratio.
In 2010, Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio stood at around 80%. However, by 2020, this ratio had increased to approximately 59.8%. While still below the Eurozone average, this trend is concerning. Germany's rising debt levels are largely driven by increased government spending on social welfare programs, infrastructure projects, and, more recently, COVID-19-related stimulus packages.
Drivers of Germany's Rising Debt
Several factors contribute to Germany's growing debt-to-GDP ratio:
- Increased government spending: Germany has been investing heavily in social welfare programs, such as pensions, healthcare, and education. These programs have contributed to increased government expenditure.
- Infrastructure development: Germany has been investing in infrastructure projects, such as transportation networks, renewable energy, and digital infrastructure.
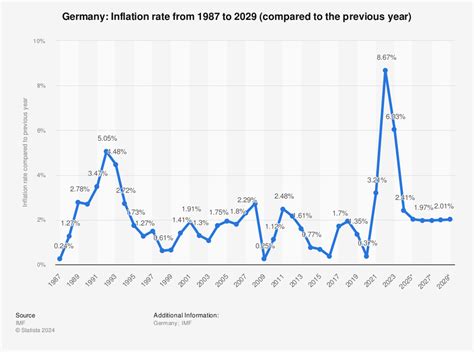
- COVID-19 stimulus packages: Germany has implemented significant fiscal stimulus packages to mitigate the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Consequences of Rising Debt Levels
Rising debt levels can have significant consequences for Germany's economy and the broader Eurozone:
- Reduced fiscal flexibility: High debt levels limit the government's ability to respond to future economic shocks or crises.
- Increased borrowing costs: Higher debt levels can lead to increased borrowing costs, as investors demand higher returns to compensate for the perceived risk.
- Risk of debt crisis: Excessive debt levels can increase the risk of a debt crisis, which could have severe consequences for the German economy and the Eurozone as a whole.
Potential Solutions
To address the growing concern of rising debt levels, the German government can consider the following potential solutions:
- Fiscal consolidation: Implementing measures to reduce government expenditure and increase revenue, such as tax reforms or spending cuts.
- Investing in growth-enhancing policies: Investing in policies that promote economic growth, such as education, research, and development, to increase the country's revenue base.
- Promoting private sector investment: Encouraging private sector investment in infrastructure and other growth-enhancing projects to reduce the burden on public finances.
Gallery of Germany's Debt-to-GDP Ratio
Germany's Debt-to-GDP Ratio Image Gallery
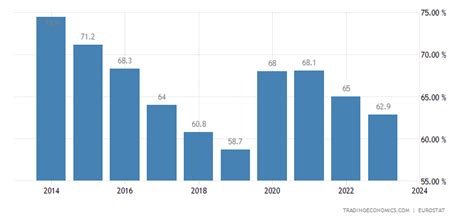
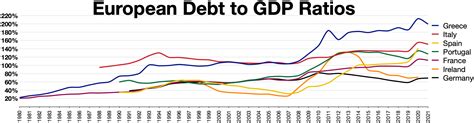
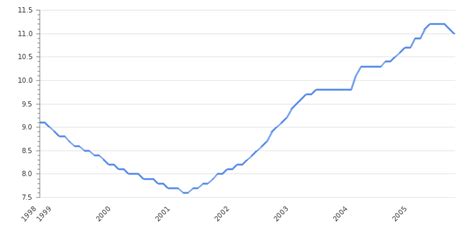
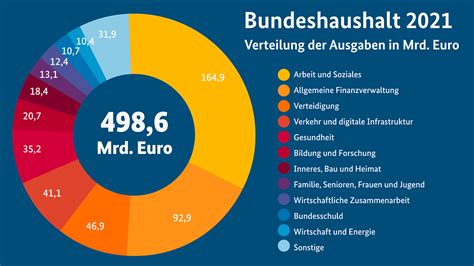
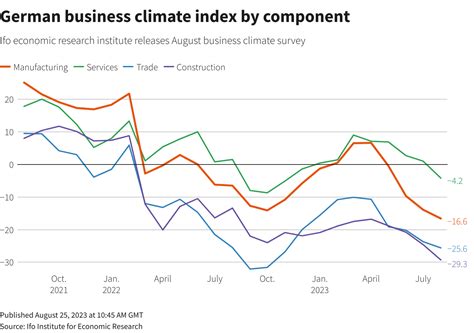
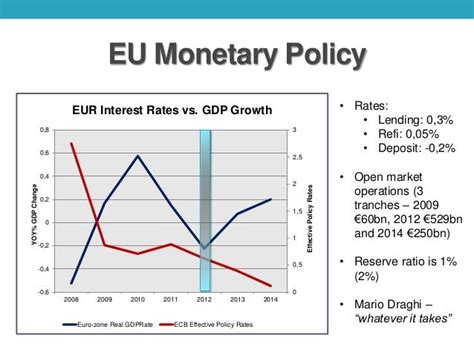
Germany's rising debt-to-GDP ratio is a growing concern that requires attention from policymakers and economists. While the country's debt levels are still manageable, the trend is concerning and could have significant consequences for the German economy and the broader Eurozone. By understanding the drivers of rising debt levels and exploring potential solutions, Germany can work towards ensuring a more sustainable fiscal future.
