Intro
Unlock the full potential of GI Bill education benefits for higher education. Learn how to leverage the GI Bill to cover college tuition, vocational training, and more. Discover eligibility requirements, application processes, and tips for maximizing benefits, empowering veterans to achieve their academic goals and shape their future.
Unlocking Higher Ed: Gi Bill Education Benefits Explained
Higher education can be a costly and daunting endeavor, but for military veterans and their families, the GI Bill education benefits can be a game-changer. The GI Bill is a federal program designed to provide education assistance to individuals who have served in the military, as well as their spouses and dependents. In this article, we will delve into the world of GI Bill education benefits, exploring the history, eligibility, benefits, and application process.
History of the GI Bill

The GI Bill, also known as the Servicemen's Readjustment Act, was first introduced in 1944 to provide financial assistance to veterans returning from World War II. The bill was designed to help veterans readjust to civilian life by providing education and training benefits. Over the years, the GI Bill has undergone several revisions and expansions, with the most significant update being the Post-9/11 GI Bill, which was signed into law in 2008.
Eligibility Requirements
To be eligible for GI Bill education benefits, individuals must meet specific requirements:
- Have served at least 90 days of active duty since September 10, 2001
- Be a veteran, active duty service member, or Selected Reserve member
- Have a high school diploma or equivalent
- Not be in default on a federal student loan or owe a refund on a federal grant
Spouses and dependents of veterans may also be eligible for education benefits through the Dependency and Indemnity Compensation (DIC) program or the Survivors' and Dependents' Educational Assistance (DEA) program.
Types of GI Bill Education Benefits
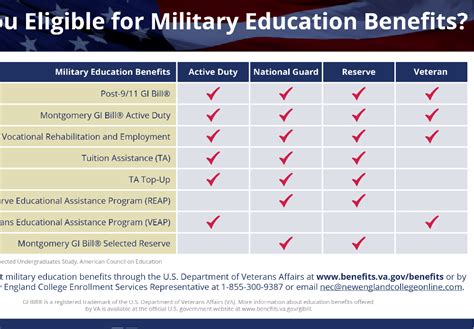
There are several types of GI Bill education benefits available, including:
- Post-9/11 GI Bill (Chapter 33): Provides up to 36 months of education benefits, including tuition and fees, housing stipend, and book stipend
- Montgomery GI Bill Active Duty (MGIB-AD) (Chapter 30): Provides up to 36 months of education benefits, including tuition and fees, housing stipend, and book stipend
- Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) (Chapter 1606): Provides up to 36 months of education benefits, including tuition and fees, housing stipend, and book stipend
- Dependent Education Assistance (DEA) Program (Chapter 35): Provides up to 45 months of education benefits for spouses and dependents of veterans
- Vocational Rehabilitation and Employment (VR&E) Program (Chapter 31): Provides education and training benefits for veterans with service-connected disabilities
How to Apply for GI Bill Education Benefits
To apply for GI Bill education benefits, individuals must:
- Check eligibility: Verify eligibility through the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) website or by calling the VA at 1-888-442-4551
- Gather required documents: Collect required documents, including DD Form 214, Certificate of Release or Discharge from Active Duty, and VA Form 22-1990, Application for Education Benefits
- Apply online or by mail: Submit the application online through the VA website or by mail to the VA regional office
- Certify enrollment: Provide proof of enrollment to the VA and certify each semester to receive benefits
GI Bill Education Benefits vs. Other Financial Aid Options

The GI Bill education benefits are a valuable resource for military veterans and their families. However, it's essential to compare the benefits with other financial aid options, such as:
- Federal Pell Grant: A need-based grant for undergraduate students
- Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grant (FSEOG): A need-based grant for undergraduate students
- Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans: Low-interest loans for undergraduate and graduate students
- Scholarships and grants: Merit-based and need-based awards from private organizations and institutions
Maximizing GI Bill Education Benefits
To maximize GI Bill education benefits, individuals should:
- Choose an eligible program: Select a program that is approved by the VA
- Take advantage of tuition-free benefits: Use the Post-9/11 GI Bill to cover tuition and fees at public institutions
- Apply for other financial aid: Combine GI Bill benefits with other financial aid options to cover living expenses and other costs
- Seek guidance: Consult with a VA education benefits counselor or a school's veterans' affairs office for guidance on maximizing benefits
Conclusion
The GI Bill education benefits are a valuable resource for military veterans and their families. By understanding the history, eligibility, benefits, and application process, individuals can unlock higher education and achieve their academic goals. Remember to compare the benefits with other financial aid options and maximize the benefits by choosing an eligible program, taking advantage of tuition-free benefits, applying for other financial aid, and seeking guidance.
GI Bill Education Benefits Image Gallery










We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the GI Bill education benefits. If you have any questions or would like to share your experiences, please leave a comment below.
