Intro
Learn about Hernia vs Pulled Groin Muscle, symptoms, treatment, and recovery. Understand groin strain, inguinal hernia, and abdominal pain differences.
The human body is a complex and intricate system, and sometimes, it can be difficult to diagnose and differentiate between various injuries or conditions. One such instance is when individuals experience pain in the groin area, which can be caused by either a hernia or a pulled groin muscle. Understanding the differences between these two conditions is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and recovery. In this article, we will delve into the world of hernias and pulled groin muscles, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
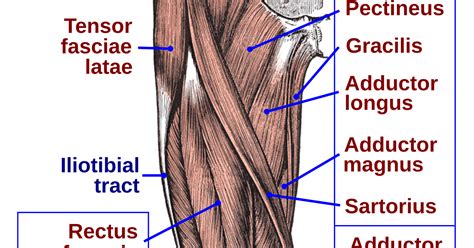
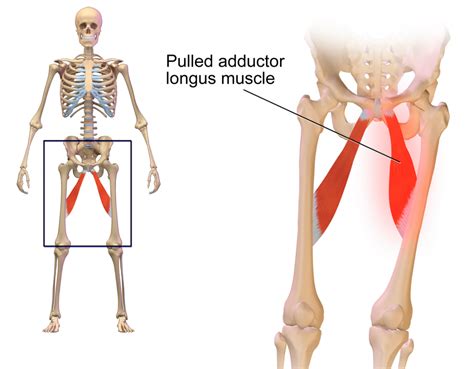
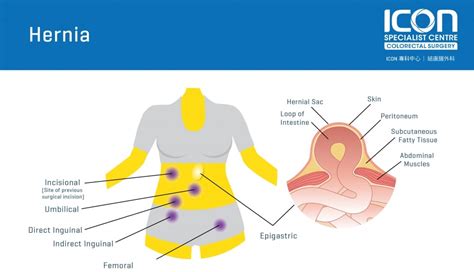
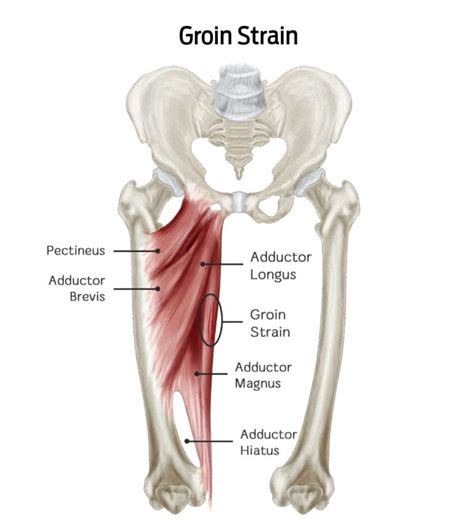
The groin area is a sensitive region, and any pain or discomfort can be quite debilitating. A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue bulges through a weakened area in the muscle or connective tissue that normally holds it in place. On the other hand, a pulled groin muscle, also known as a groin strain, is a common injury that occurs when the muscles in the groin area are stretched or torn. Both conditions can cause significant pain and discomfort, making it essential to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Hernias
Symptoms of Hernias
The symptoms of hernias can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include a bulge or lump in the affected area, pain or discomfort, especially when coughing, lifting, or straining, and a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the abdomen. In some cases, hernias can cause nausea, vomiting, and constipation. If left untreated, hernias can lead to serious complications, such as incarceration, where the hernia becomes trapped, and strangulation, where the blood supply to the hernia is cut off.Understanding Pulled Groin Muscles
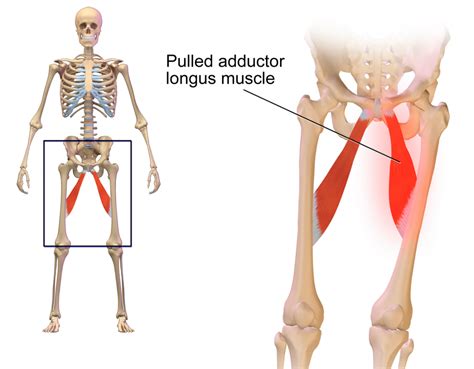
Symptoms of Pulled Groin Muscles
The symptoms of pulled groin muscles can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Common symptoms include pain or tenderness in the groin area, swelling or bruising, limited mobility or stiffness, and weakness or instability in the affected leg. In some cases, pulled groin muscles can cause numbness or tingling in the groin area or down the leg. If left untreated, pulled groin muscles can lead to chronic pain, limited mobility, and increased risk of further injury.Diagnosis and Treatment
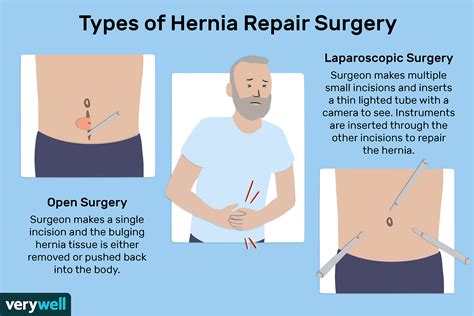
Treatment Options for Hernias
Treatment options for hernias depend on the type and severity of the condition. Watchful waiting, also known as expectant management, is a treatment approach that involves monitoring the hernia for any changes or complications. Lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, avoiding heavy lifting, and quitting smoking, can also help alleviate symptoms. Surgery is often necessary to repair the hernia, especially if it is large or causing significant symptoms. There are two main types of surgery: open repair and laparoscopic repair. Open repair involves making a single incision in the abdomen to repair the hernia, while laparoscopic repair involves making several small incisions to insert a laparoscope and repair the hernia.Treatment Options for Pulled Groin Muscles
Treatment options for pulled groin muscles depend on the severity of the injury. The RICE principle, which includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation, is often used to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Physical therapy can also help improve mobility and strength in the affected leg. Pain management, such as over-the-counter pain medications or prescription medications, can help alleviate pain and discomfort. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair any torn or damaged muscles.Prevention Strategies

Exercise and Stretching
Exercise and stretching can help improve flexibility and strength in the muscles, reducing the risk of injury. Examples of exercises that can help prevent pulled groin muscles include squats, lunges, and leg press. Stretching exercises, such as hamstring and hip flexor stretches, can also help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.Proper Lifting Techniques
Proper lifting techniques can help reduce the risk of straining the back and groin muscles. When lifting, it is essential to bend at the knees and lift with the legs, rather than the back. This can help reduce the strain on the muscles and prevent injury. Additionally, using proper lifting equipment, such as a back support or lifting belt, can help reduce the risk of injury.Hernia and Pulled Groin Muscle Image Gallery





Final Thoughts

