Explore the US Navy hierarchys 9 ranks, from Seaman Recruit to Fleet Admiral. Understand the chain of command, responsibilities, and requirements for each rank. Learn about the different pay grades, promotions, and career paths within the Navys enlisted and officer ranks. Discover how to advance through the ranks and achieve success in the US Navy.
The United States Navy is one of the most respected and formidable naval forces in the world, with a rich history of protecting American interests and promoting global security. At the heart of the Navy's effectiveness is its hierarchical structure, which enables clear communication, efficient decision-making, and a strong sense of accountability. In this article, we will delve into the 9 ranks in the US Navy hierarchy, exploring the roles, responsibilities, and requirements for each position.
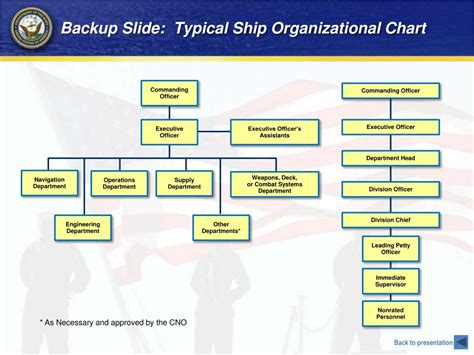
Understanding the Navy's rank structure is essential for anyone considering a career in the military or seeking to appreciate the complexities of naval operations. From the most junior enlisted personnel to the highest-ranking officers, each rank plays a vital role in the Navy's mission to protect and serve.
Enlisted Ranks
The enlisted ranks in the US Navy are divided into three categories: junior enlisted, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and senior enlisted.
Seaman Recruit (E-1)
The most junior rank in the Navy is Seaman Recruit (E-1). New recruits typically enter the Navy at this rank and are in the process of completing basic training. Seaman Recruits are responsible for learning the fundamental skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in the Navy.
Seaman Apprentice (E-2)
After completing basic training, sailors advance to Seaman Apprentice (E-2). At this rank, they continue to develop their skills and gain practical experience in their chosen rating (job specialty). Seaman Apprentices are expected to demonstrate a strong work ethic and a willingness to learn.
Seaman (E-3)
Seaman (E-3) is the third enlisted rank in the Navy. Sailors at this rank have gained significant experience and are expected to take on more responsibility. They may serve as team leaders or mentors to junior sailors.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks
NCOs in the Navy are responsible for leading and mentoring junior sailors. They have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills, technical expertise, and a strong commitment to the Navy's core values.
Petty Officer Third Class (E-4)
Petty Officer Third Class (E-4) is the first NCO rank in the Navy. Sailors at this rank have achieved a high level of technical proficiency and are responsible for leading small teams. They are also expected to mentor junior sailors and provide guidance on Navy procedures and protocols.
Petty Officer Second Class (E-5)
Petty Officer Second Class (E-5) is a senior NCO rank in the Navy. Sailors at this rank have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills and are responsible for leading larger teams. They may also serve as departmental leaders or division officers.
Petty Officer First Class (E-6)
Petty Officer First Class (E-6) is the highest NCO rank in the Navy. Sailors at this rank have achieved a high level of technical expertise and are responsible for leading complex teams. They may also serve as senior departmental leaders or executive officers.
Warrant Officer Rank
Warrant Officers in the Navy are technical experts who have demonstrated exceptional proficiency in their chosen field. They serve as advisors to senior officers and are responsible for leading specialized teams.
Chief Warrant Officer (W-2)
Chief Warrant Officer (W-2) is the most junior Warrant Officer rank in the Navy. Sailors at this rank have achieved a high level of technical expertise and are responsible for leading specialized teams.
Officer Ranks
Officer ranks in the Navy are divided into two categories: company-grade officers and field-grade officers.
Ensign (O-1)
Ensign (O-1) is the most junior officer rank in the Navy. Officers at this rank are responsible for leading small teams and developing their leadership skills.
Lieutenant Junior Grade (O-2)
Lieutenant Junior Grade (O-2) is a company-grade officer rank in the Navy. Officers at this rank have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills and are responsible for leading larger teams.
Lieutenant (O-3)
Lieutenant (O-3) is a senior company-grade officer rank in the Navy. Officers at this rank have achieved a high level of leadership expertise and are responsible for leading complex teams.
Lieutenant Commander (O-4)
Lieutenant Commander (O-4) is a field-grade officer rank in the Navy. Officers at this rank have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills and are responsible for leading senior teams.
Commander (O-5)
Commander (O-5) is a senior field-grade officer rank in the Navy. Officers at this rank have achieved a high level of leadership expertise and are responsible for leading large teams.
Captain (O-6)
Captain (O-6) is the highest field-grade officer rank in the Navy. Officers at this rank have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills and are responsible for leading entire departments or divisions.
US Navy Ranks Image Gallery









In conclusion, the US Navy's hierarchical structure is designed to promote clear communication, efficient decision-making, and a strong sense of accountability. From the most junior enlisted personnel to the highest-ranking officers, each rank plays a vital role in the Navy's mission to protect and serve. Whether you're considering a career in the Navy or simply seeking to appreciate the complexities of naval operations, understanding the 9 ranks in the US Navy hierarchy is essential.
