Intro
Discover the ancient art of warfare with our in-depth guide on how catapults work. Learn about the mechanics and history of these siege engines, from torsion and tension to the different types of catapults used in medieval warfare. Uncover the science behind these powerful machines and how they revolutionized battle tactics.
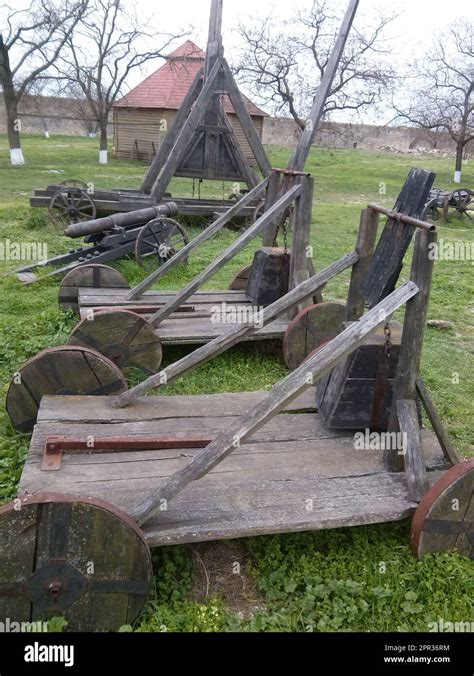
Throughout history, the use of catapults as siege engines has been a significant factor in the outcome of many battles. The earliest recorded use of catapults dates back to ancient Greece in the 4th century BC. However, it was the ancient Romans who perfected the design and used catapults extensively in their military campaigns. In this article, we will delve into the history and mechanics of catapults, exploring how they work and their significance in ancient warfare.
What is a Catapult?
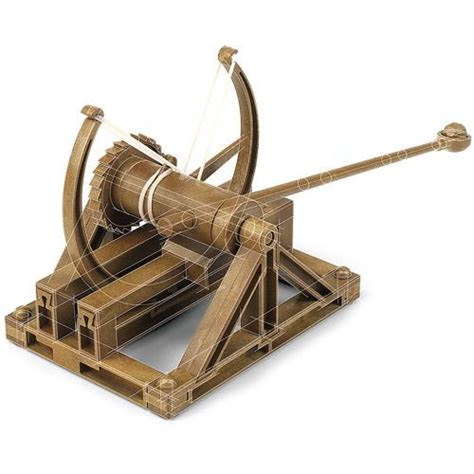

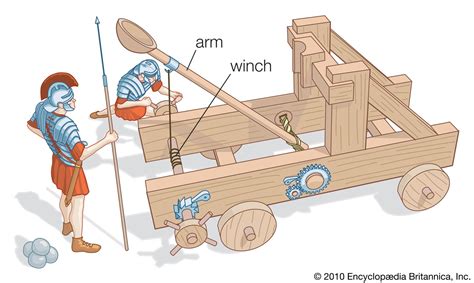
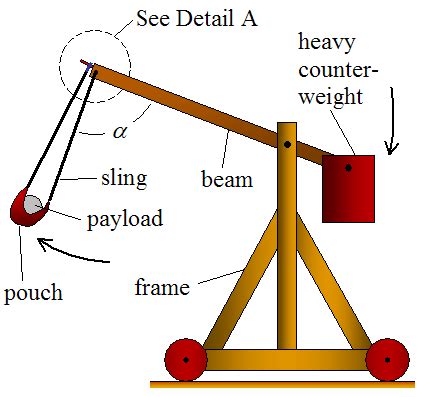
A catapult is a type of siege engine that uses stored energy to propel projectiles over long distances. The basic design of a catapult consists of a wooden frame, a torsion spring, and a throwing arm. The torsion spring is typically made from twisted animal sinew or human hair, which is then attached to the throwing arm. The throwing arm is designed to rotate around a pivot point, generating a significant amount of force as it releases the stored energy.
Types of Catapults
There were several types of catapults used in ancient warfare, each with its unique design and capabilities. Some of the most common types of catapults include:
- Ballistae: These were small, handheld catapults that were used to fire arrows and other small projectiles.
- Onagri: These were larger, more powerful catapults that were used to fire stones and other heavy projectiles.
- Scorpios: These were lightweight, mobile catapults that were used to fire arrows and other small projectiles.
How Catapults Work
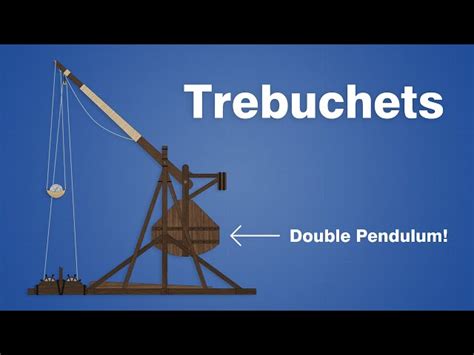
The working mechanism of a catapult is relatively simple. Here's a step-by-step explanation of how it works:
- Loading: The throwing arm is pulled back and loaded with a projectile, such as a stone or arrow.
- Torsion: The torsion spring is twisted, storing energy as it is wound.
- Release: The throwing arm is released, allowing the stored energy to be released as the arm rotates around the pivot point.
- Projection: The projectile is propelled through the air, traveling over long distances.
The Science Behind Catapults
The science behind catapults is based on the principles of physics and mathematics. The key concept is the use of stored energy, which is released as the throwing arm rotates around the pivot point. This release of energy generates a significant amount of force, propelling the projectile through the air.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Catapults

Catapults had several advantages that made them a valuable asset in ancient warfare. Some of the key advantages include:
- Range: Catapults could fire projectiles over long distances, allowing armies to attack enemy fortifications from a safe distance.
- Accuracy: Catapults were surprisingly accurate, with skilled operators able to hit targets with precision.
- Power: Catapults could fire heavy projectiles, such as stones and boulders, which could cause significant damage to enemy fortifications.
However, catapults also had several disadvantages, including:
- Complexity: Catapults were complex machines that required skilled operators to use effectively.
- Size: Catapults were often large and cumbersome, making them difficult to transport and deploy.
- Vulnerability: Catapults were vulnerable to counterattack, as enemy armies could target the machines and disable them.
Notable Uses of Catapults in History

Catapults have been used in many notable battles throughout history. Some of the most significant uses of catapults include:
- The Roman Siege of Alesia: In 52 BC, the Roman general Julius Caesar used catapults to breach the walls of the Gaulish city of Alesia.
- The Crusades: Catapults were used extensively during the Crusades, with both Christian and Muslim armies employing the machines to attack enemy fortifications.
- The Hundred Years' War: Catapults were used during the Hundred Years' War between England and France, with both sides employing the machines to attack enemy fortifications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, catapults were an important part of ancient warfare, providing armies with a means of attacking enemy fortifications from a safe distance. While catapults had several advantages, including range, accuracy, and power, they also had several disadvantages, including complexity, size, and vulnerability. Despite these limitations, catapults played a significant role in many notable battles throughout history.
Gallery of Catapult Images
Catapult Image Gallery