Intro
Discover how Native Americans were impacted by frontier expansion, displacement, and cultural erosion, affecting tribal sovereignty, land rights, and indigenous communities amidst westward settlement and colonization.
The history of the United States is marked by significant events that have shaped the country into what it is today. One such event is the frontier expansion, which had a profound impact on the indigenous population, particularly Native Americans. The westward expansion of the United States, which began in the early 19th century, led to the displacement, marginalization, and suffering of Native American tribes. As the American frontier expanded, Native Americans were forced to adapt to a new reality, one that was often marked by violence, loss, and trauma.
The frontier expansion was driven by the idea of Manifest Destiny, which held that the United States was destined to expand its territory across North America. This ideology was rooted in the belief that the United States had a divine right to expand its territory and spread its influence across the continent. As a result, the U.S. government and settlers began to push westward, encroaching on Native American lands and disrupting the delicate balance of power in the region. Native American tribes, who had lived in the region for centuries, were suddenly faced with the threat of displacement, violence, and cultural erasure.
The impact of frontier expansion on Native Americans was devastating. Many tribes were forcibly removed from their lands, relocated to reservations, and subjected to violence, disease, and poverty. The Trail of Tears, which took place in the 1830s, is a notorious example of the brutality and suffering inflicted upon Native Americans during this period. The trail, which spanned over 1,000 miles, was a forced relocation of the Cherokee Nation from their ancestral lands in Georgia to Indian Territory (present-day Oklahoma). Thousands of Cherokee people died during the journey, which was marked by exposure, disease, and starvation.
Native American Tribes and Frontier Expansion

The experience of Native American tribes during the frontier expansion was varied and complex. Some tribes, such as the Sioux and the Cheyenne, resisted the expansion of the United States, fighting battles against the U.S. military and settlers. Other tribes, such as the Cherokee and the Creek, attempted to adapt to the changing circumstances, adopting European-American customs and practices in an effort to survive. However, even these attempts at adaptation were often met with hostility and violence, as Native Americans were seen as inferior and uncivilized by many European-Americans.
Key Events in Native American History
Some key events in Native American history include: * The Indian Removal Act of 1830, which authorized the forced relocation of Native American tribes from their ancestral lands to Indian Territory. * The Wounded Knee Massacre, which took place in 1890 and marked the end of the Ghost Dance War. * The Dawes Act, which was passed in 1887 and divided Native American land into individual allotments that could be sold to non-Native Americans. * The Indian Reorganization Act, which was passed in 1934 and reversed the assimilation policies of the Dawes Act.Impact of Frontier Expansion on Native American Culture
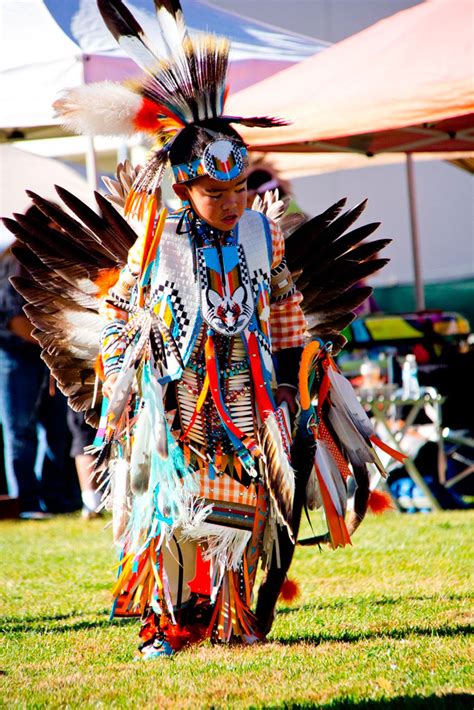

The impact of frontier expansion on Native American culture was profound. Many Native American tribes were forced to abandon their traditional ways of life, adopting European-American customs and practices in an effort to survive. The loss of land, culture, and identity was devastating, leading to a decline in population, a loss of traditional knowledge, and a disruption of social and cultural norms. The forced assimilation of Native Americans into European-American culture was a deliberate policy of the U.S. government, which sought to erase Native American culture and replace it with European-American values and customs.
Effects of Assimilation Policies
The effects of assimilation policies on Native American culture were far-reaching and devastating. Some of the effects include: * The loss of traditional languages and cultural practices. * The decline of traditional arts and crafts. * The disruption of social and cultural norms. * The loss of land and identity. * The decline of population and the loss of traditional knowledge.Native American Reservations and Frontier Expansion
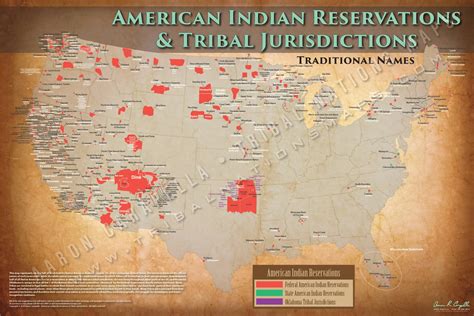
The creation of Native American reservations was a direct result of the frontier expansion. As the United States expanded its territory, Native American tribes were forcibly removed from their ancestral lands and relocated to reservations. These reservations were often poorly managed, with inadequate resources, poor living conditions, and limited access to education and healthcare. The conditions on reservations were often harsh, with high rates of poverty, unemployment, and disease.
Challenges Facing Native American Reservations
Some of the challenges facing Native American reservations include: * Limited access to education and healthcare. * High rates of poverty and unemployment. * Poor living conditions and inadequate resources. * Limited access to clean water and sanitation. * High rates of disease and mortality.Native American Rights and Frontier Expansion

The frontier expansion had a profound impact on Native American rights. As the United States expanded its territory, Native American tribes were subjected to violence, displacement, and marginalization. The U.S. government failed to recognize Native American rights, treating them as inferior and uncivilized. The Indian Citizenship Act of 1924, which granted citizenship to all Native Americans, was a significant step towards recognizing Native American rights. However, even today, Native American rights remain a contentious issue, with many Native American tribes fighting for recognition, self-determination, and justice.
Key Legislation Affecting Native American Rights
Some key legislation affecting Native American rights includes: * The Indian Removal Act of 1830. * The Dawes Act of 1887. * The Indian Reorganization Act of 1934. * The Indian Civil Rights Act of 1968. * The Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act of 1990.Native American Image Gallery





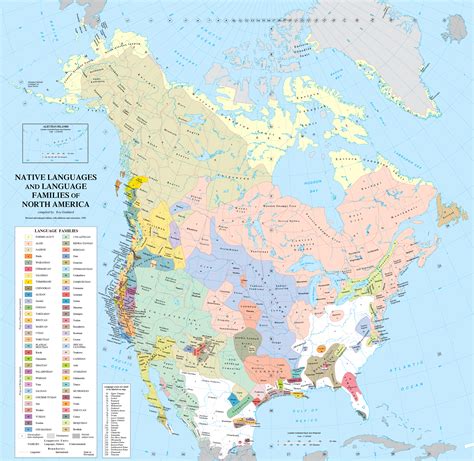

Final Thoughts on Native Americans and Frontier Expansion

In conclusion, the frontier expansion had a profound impact on Native Americans, leading to displacement, marginalization, and suffering. The loss of land, culture, and identity was devastating, and the effects of assimilation policies and the creation of Native American reservations continue to be felt today. It is essential to recognize the historical injustices inflicted upon Native Americans and to work towards a more equitable and just future. By acknowledging the past and working towards reconciliation, we can begin to heal the wounds of history and build a brighter future for all.
We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this article, and to learn more about the history and culture of Native Americans. By engaging in respectful and open dialogue, we can work towards a deeper understanding of the complex issues surrounding Native American rights and the legacy of frontier expansion. Please take a moment to share this article with others, and to explore the many resources available on this important topic. Together, we can build a more just and equitable future for all.
