Intro
The United States government spends a staggering $70 billion each year on food stamps, a program designed to help low-income individuals and families purchase food. This significant expenditure has sparked debate and discussion among policymakers, economists, and the general public. In this article, we will delve into the world of food stamps, exploring the program's history, benefits, and challenges, as well as its impact on the economy and society.
The History of Food Stamps

The food stamp program, now known as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), was first introduced in 1939 as part of President Franklin D. Roosevelt's New Deal. The program was designed to help farmers by providing them with a market for their surplus crops, while also assisting low-income families in purchasing food. Over the years, the program has undergone several changes, including the introduction of the food stamp card in 2002, which replaced paper coupons.
How Food Stamps Work
Food stamps are distributed to eligible individuals and families through a complex process involving federal, state, and local governments. The program is funded by the federal government, but administered by state agencies. To qualify for food stamps, applicants must meet certain income and resource requirements, which vary by state.
Once approved, recipients receive an Electronic Benefits Transfer (EBT) card, which can be used to purchase food at participating retailers. The card is loaded with a specific amount of funds each month, based on the recipient's eligibility and benefits level.
The Benefits of Food Stamps

The food stamp program provides numerous benefits to recipients, including:
- Access to nutritious food, essential for maintaining good health and well-being
- Assistance in purchasing food, which helps to alleviate poverty and food insecurity
- Support for local economies, as food stamp funds are spent at local retailers
- Job creation and economic growth, as the program helps to stimulate food production and sales
The Impact of Food Stamps on the Economy
The food stamp program has a significant impact on the economy, both positively and negatively. On the one hand, the program helps to stimulate food production and sales, which can create jobs and boost economic growth. On the other hand, the program's high costs can be a burden on taxpayers, particularly during times of economic downturn.
According to a study by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, every dollar spent on food stamps generates approximately $1.70 in economic activity. This means that the program can have a positive multiplier effect on the economy, helping to create jobs and stimulate growth.
Challenges Facing the Food Stamp Program

Despite its benefits, the food stamp program faces several challenges, including:
- High costs: The program's $70 billion annual price tag is a significant burden on taxpayers
- Efficiency: The program's complex administration and distribution process can be inefficient and wasteful
- Fraud: The program is vulnerable to fraud and abuse, which can result in wasted funds and undermine public trust
- Effectiveness: The program's effectiveness in reducing poverty and food insecurity is a subject of ongoing debate
Reform Efforts
In recent years, there have been efforts to reform the food stamp program, with a focus on improving efficiency, reducing waste, and promoting effectiveness. Some of these efforts include:
- Implementing new technologies, such as mobile apps and online platforms, to streamline the application and distribution process
- Introducing work requirements and job training programs to help recipients gain employment and become self-sufficient
- Enhancing program monitoring and evaluation to reduce waste and improve effectiveness
Food Stamps and Poverty Image Gallery
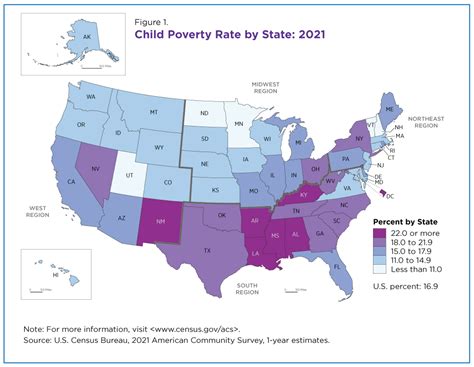




As we conclude this article, we invite you to share your thoughts on the food stamp program and its impact on poverty and food insecurity. What do you think are the most pressing challenges facing the program, and how can we work together to address them? Share your comments and ideas below, and let's continue the conversation.
